Aquarium water has a complex composition. The well-being of the fish in the aquarium, their health and life expectancy depend on whether the indicators of nitrates and phosphates, acidity and hardness of water and other parameters are within normal limits. This part of aquarium hobby seems especially difficult to beginners: some are deeply immersed in the theory, others pretend that the composition of the water does not concern them. Still others buy tests for ph, kh, ammonia and nitrites and, as needed, learn how to reduce or increase this or that indicator. As always, it is better to choose a middle ground: find out what water parameters affect and how to reduce the level of substances dangerous to the life of fish.
Aquarium water standards
Cloudy water in an aquarium is a clear sign that something is wrong and the fish are not feeling well there. But perfectly clear water is not always good either. Distilled water is considered absolutely pure, but it is unsuitable for fish. The norm is to maintain a balance of each of the following indicators:
- General hardness;
- Carbonate hardness;
- Nitrites (NO2);
- Nitrates (NO3);
- Acidity (pH);
- Phosphates, iron, chlorine and others.
The difficulty is that different fish need different conditions. Therefore, the task of the aquarist is to bring the life of fish at home as close as possible to natural conditions.
Acidity
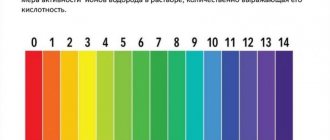
The pH level in water is measured on a scale from 0 to 10 units. A pH level of 5.5 is considered neutral; below this level, water is acidic; above this level, water is alkaline. The content of nutrients in water depends on acidity. Ideal conditions for most fish are when the pH level in the aquarium is from 6.8 to 7.2 pH.
In an alkaline environment above 7.3 pH, due to a lack of vital elements, the coordination of movements in fish is impaired, mucus forms on the body, the eyes become cloudy, and the gills cease to perform their function. If the pH is not lowered, the fish die from the inability to breathe normally. Plants suffer from a violation of chemical harmony. They get sick and die due to the inaccessibility of vital elements: iron, molybdenum, manganese, carbon dioxide: in alkaline water they take on indigestible forms.
Too low a pH level also affects the condition of the fish: they become unable to breathe due to the high level of carbon dioxide, they can swim upside down and eventually die. Acidic water is dangerous for plants due to irreversible changes in leaves, stems and roots.
In biological equilibrium, the pH level may change slightly, and the inhabitants of the aquarium have time to adapt to new conditions. A sudden change (for example, when replacing a large amount of water) is detrimental.
How to find out the pH level:
- Using special test strips that react to acidity with color.
- Drip test: water from the aquarium is mixed with the reagent in a separate container, observing the proportions, and the color change is observed.
- Electronic test - produces the most accurate result, since color fluctuations on test strips and indicators are not always clear to the average person.
How to lower pH
- Increase the amount of carbon dioxide in water using a special installation. The more hydrogen ions in aquarium water, the lower the acidity value.
- How to lower the pH in an aquarium is easy and relatively safe for fish - place driftwood in the aquarium.
- Add peat mixed with distilled water to the water in a proportion of 5 grams of peat per 1 liter of distillate. This method requires constant testing of the water, and the mixture is added gradually so that the decrease in acidity is not sudden.
- Raise the water temperature (a natural way to increase CO2 concentration).
- Introduce live plants into the aquarium if there are none.
How to increase pH
- Increase the oxygen supply using a compressor.
- Place minerals that increase acidity (coral, limestone) on the bottom.
- If there are living plants, provide them with good lighting, increasing photosynthesis - the conversion of carbon dioxide into oxygen.
- Add calcium carbonate (baking soda) to the water at the rate of 5 grams per 100 liters.
- Add water boiled for an hour (you need to add cooled water and only the lower third from the container where the water was boiled).
To change the acidity, you can also use special correctors that are sold at the pet store. This must be done in accordance with the instructions, observing the dosage!
Hardness of water
There are two types of hardness:
- Carbonate (temporary);
- Non-carbonate (permanent).
The ratio of these indicators is called total hardness (gH).
Carbonate hardness of water is the level of bicarbonate and hydrocarbonate anions. At high levels of acidity (in alkaline water), these elements precipitate. This process can be observed if you boil water with a high kH level: calcium carbonate scale forms at the bottom of the cookware. In an aquarium, its level increases at a pH above 8.3.
Aquarium fish have different rigidity requirements. Some people need soft water, others need a high level of gH:
- 0-8 – water is considered soft;
- 8-14 – average;
- 14-30 – high level.
In unsuitable water, fish die due to too high or too low levels of calcium and magnesium.
How to determine water hardness:
- Special test strips;
- Using drop tests;
- Using distilled water and laundry soap 60% or 72%. This is a whole chemical experiment. 1 gram of finely grated soap is dissolved in a small amount of warm distilled water. The soap solution is supplemented with water to a level of 6 cm (for 60% soap) or 7 cm (for 72% soap). Then in a separate jar you need to mix half a liter of water from the aquarium and a soap solution, pouring it in little by little until white foam appears. The remaining amount of solution in water is measured with a ruler. One centimeter of soap solution is equal to 2 degrees of hardness. If there was 7 cm in the glass and 4 are left, then the water hardness is 6 gH.
How to increase water hardness
- Add more hard water (little by little, repeating the measurement regularly).
- Boil ordinary water for an hour, add the bottom third of the dishes, as when changing the acidity level.
- Place items with a high calcium content in the aquarium: shells, corals, limestone.
- Add baking soda.
- Add calcium chloride (10%) and magnesium sulfate in a volume of 1 ml each.
- Add a mixture of magnesia and water in a ratio of 1 ml per 1 liter.
How to reduce water hardness
- Add distilled water.
- Boil the water and add the top 2/3 of the cooled boiled water to the aquarium.
- Large aquariums use remote filters with different filter components. How to soften the water in this case: add peat to the filter, and then activated carbon, which neutralizes the yellowness of the water.
- Reducing the carbonate hardness of water is more difficult than increasing it. You can put driftwood on the bottom for permanent softening.
pH controller
In aquariums with rich vegetation and powerful lighting, which require a CO2 supply, experienced aquarists actively use a drop checker. This device maintains the pH level by varying the supply of carbon dioxide. It is also called a long-term test. It is a small vessel with water and indicator liquid. Carbon dioxide penetrates the indicator liquid and changes its color, by which the pH level is determined. It should be taken into account that real values appear only 1.5 hours after the test starts.
A drop checker on aquarium water informs about a sharp drop or increase to critical pH levels. But there is a developed so-called standard solution in which the KH level is 4.0. Such a device monitors not only the exact pH level, but also the CO2 concentration, regardless of carbonate hardness.
Nitrates and nitrites
These parameters depend on the number of fish in the tank. The life of fish is impossible without the nitrogen cycle. It consists of three steps:
- Excretion of life waste by fish that contains ammonia. Leftover uneaten food also affects the concentration of this compound.
- The bacteria that make up the biosphere balance of the aquarium convert ammonia into nitrites (ammonium salts).
- Other bacteria, also an integral part of the biotope in glass walls, convert nitrites into nitrates (salts of nitric acid).
Both groups of bacteria are called by the same word - nitrifications. It is these that experienced aquarists strive to introduce into a new tank in order to prepare the water for the colonization of fish. This is done using water from an old aquarium, an old filter sponge or uncleaned decor.
Ammonia is a harmful compound that is harmful to fish and can cause poisoning. It is retained by the soil. Nitrites are also not harmless compounds that poison the water if their level is exceeded. Nitrates are considered the least harmful components of the nitrogen cycle, but if their levels are high, the question arises: how to lower nitrates in the aquarium. First, let’s figure out what level of each compound is acceptable.
- The normal nitrate level is 20-30 mg/l. If biological balance is maintained and other water parameters are observed, it remains so without additional actions on the part of the aquarist. True, there are fish for which this level is high; such representatives of the underwater world are considered sensitive and difficult to keep.
- Nitrite levels are acceptable within the range of 0.1 to 0.2 mg/l.
- Ammonia must immediately become a participant in the nitrogen cycle.
If the level of NO2 or NO3 in the water is higher than comfortable, the fish become lethargic, refuse food, do not reproduce, lose color, and do not grow. In the end, their immunity decreases: the fish die from any infection.
How to find out the level of nitrates and nitrites:
- Test strips with color indicator;
- Drip tests;
- Digital tests.
High levels of nitrogen compounds can be found not only in aquarium water, but also in tap water. Therefore, tests should be carried out regularly, including the water that is planned to be used for replacement.
In some cases it is necessary to increase the concentration of nitrogenous compounds. They are essential for the good growth of aquarium plants.
How to increase nitrate and nitrite levels
- Applying fertilizer or top dressing. Fertilizers contain potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen.
- Experienced aquarists make fertilizer for the aquarium with their own hands: potassium (potassium nitrate) is mixed with urea and ammonium nitrate in certain proportions.
- Herbalists need live fish - they create the basis for the nitrogen cycle.
How to reduce nitrates
- Water purification with a reverse osmosis filter.
- Using a special filler for the external filter.
- Adding special preparations to water to reduce the concentration of nitrogen compounds.
- Get aquarium plants. Unpretentious ones are suitable if there is no desire to care for capricious ones and create conditions for them to grow.
A good way to remove nitrates is to simply regularly (once a week or two) replace a quarter of the aquarium’s volume. Before changing the fresh water, it would be a good idea to add conditioner or special devices for water purification.
The importance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the aquarium and the change in their quantity.
Water is a good solvent for many compounds, including the gases in the air: oxygen and carbon dioxide.
1.1. Oxygen O2 and its significance
The oxygen content in water depends on many factors: the depth of the tank, water temperature, the presence of plants and animals. Water that is in motion is usually better oxygenated than water that is standing. The dependence of temperature on the degree of oxygenation is inversely proportional - with increasing temperature, the saturation of water with oxygen decreases. The water in the aquarium is saturated with oxygen primarily from the air. If it remains motionless, only its upper layers are saturated with oxygen. An additional oxygen producer is the healthy plants we grow. Recipients of oxygen are fish and other aquarium animals, microorganisms living in water (mainly in the substrate, in the filter) and at night (in the dark), as well as in plants. Hence the need for additional ventilation at night (setting the water in motion). In a well-oxygenated aquarium, oxygen decomposes organic pollutants and oxidizes organic compounds (proteins, carbohydrates or fats) into simple compounds that are easily digestible by fish and plants. Anaerobic decomposition processes (lack of oxygen in the aquarium) lead to the formation of toxic substances harmful to the aquarium inhabitants (for example, hydrogen sulfide, organic acids, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons), which cause, among other things, an unpleasant odor.
To increase the amount of oxygen in the aquarium, you need to install an additional filter or aerator, replace it with a new one, or introduce more plants into the aquarium.
1.2. Carbon dioxide CO 2 and its significance
During the day, carbon dioxide is released by fish and other aquatic animals, occurs during the decomposition of organic compounds, and at night is also released by plants. An excess of this gas in the water is promoted by an aquarium with few plants, insufficient ventilation and excessive fertilization of the substrate. An excessive number of plants in relation to fish in an aquarium is also not recommended - during the day this leads to a deficiency of carbon dioxide and oxygen at night. This is also the cause of biological decalcification of water (plants extract carbon dioxide from calcium bicarbonates and calcium carbonates). Only an aquarium maintains a biological balance (number of fish in relation to plants, optimal temperature, pH, water hardness, amount of light, systematic cleaning and replacement of water, appropriate filters and aerators, loose substrate) is able to function effectively for the benefit of our fish and plants. It should also be mentioned that excess carbon dioxide can cause a decrease in pH. If we exaggerate the amount of this gas when supplied to the aquarium (above 50 mg/litre) then the pH may drop to a level where the fish may begin to die. I will give here some examples of the dependence of the pH value on the amount of carbon dioxide dissolved in water:
| Carbonate hardness kH | Amount of carbon dioxide in water | ||
| more than 50 mg/liter | about 30 mg/liter | less than 15 mg/liter | |
| 2 | pH 6.1 | pH 6.4 | pH 6.7 |
| 5 | pH 6.4 | pH 6.7 | pH 7.1 |
| 10 | pH 6.7 | pH 7.1 | pH 7.4 |
| 20 | pH 6.9 | pH 7.4 | pH 7.7 |
The most recommended dose of carbon dioxide is 20-30 mg/l and must be maintained to ensure plant growth. It is also important that the amount of light is within 0.5 W so that plants can use CO 2 in the process of photosynthesis
Phosphates
Phosphorus compounds are important for underwater plants, as well as for maintaining biological balance. The higher the PO4 level, the higher the risk that the water will “bloom,” that is, the walls and decor in the aquarium will become covered with a coating of algae. The fish experience oxygen starvation, as well as the risk of poisoning from the waste products of cyanobacteria.
It is recommended for the herbalist to maintain nitrates and phosphates in a certain ratio in the aquarium. There are tables that determine this parameter depending on the type of plants in the water. This indicator can be increased easily: with special fertilizers.
How to reduce phosphates in a community aquarium
- Reduce population: the more fish, the higher the phosphorus level.
- Create conditions for good plant growth (fertilizers).
- PO4 concentrations can be reduced with water conditioners or phosphate neutralizers.
What it is?
Acid-base state or pH is the ratio of acids and bases contained in water.
The parameter includes 2 types of main particles:
- carbonates are stable elements that increase rigidity and alkalize the environment;
- carbonic acid is an unstable indicator, prone to constant changes, increases the level of acidity.
The parameter has a scale of 14 units. If it is equal to 7, it means that the environment is neutral. The lower limits are called acidic, the upper limits are called alkaline.
Metabolic products of fish and plants lead to an increase in acidity. Therefore, pH gradually shifts downward.
Iron
Another indicator that is important, primarily for plants, is the level of iron. Why is iron in an aquarium? It helps the active growth and development of plants, participates in their life support along with phosphorus. You can buy iron-containing fertilizers or make your own iron for the aquarium. It is important that the element reaches the plant and does not settle on the ground; for this, chelates (binders) are added.
Test strips and drop tests are used to assess iron levels in water. Aquariums without live plants practically do not suffer from an overdose or deficiency of iron compounds, only if the tap water does not contain elevated levels. If this is the case, you need to use neutralizers.
Ways to reduce overall hardness
Boiling. This method only reduces carbonate hardness. Because of this, the overall indicator varies slightly from a couple of percent to 40-50, it all depends on the initial parameters.
Freezing. Suitable for residents of Russia with its cold winter. To do this, water is poured into a container, for example a 5 liter bottle, and placed in the cold (balcony, loggia). First of all, water freezes near the walls. When the ice in the bottle takes up 2/3 of the total volume, the unfrozen water is poured out and the ice is melted. All salts are concentrated in the liquid, and almost no dissolved salts remain in the ice. This method allows you to reduce hardness from 1 to 30 dGH. As you understand, freezing water for a 200-liter aquarium is an absurd idea.
Using osmosis . The best option for performance. After osmosis, the water is purified from all impurities and even 99.9% of bacteria. This water is diluted with regular tap water and poured into the aquarium.
Ion exchange columns are special resins that react with magnesium and calcium salts. After using them, the water becomes soft. in practice it is used extremely rarely, unlike the above options.
About water testing
Modern pet stores selling aquarium products have available control tools in their arsenal. The choice is up to the owner:
- Test strips for each parameter.
- Comprehensive test strips that determine several parameters at once.
- Drip tests - they are cheaper than strips, but they are more hassle.
- Electronic meters.
If the fish are especially expensive and valuable, you can install a controller for the aquarium: it not only measures the parameters at the correct intervals, but can also automatically adjust the indicators.