A little about water hardness
The supply of water, hot and cold, to the consumer requires the company responsible for this process to comply with certain standards. They are regulated by GOSTs, Sanitary Rules and Norms (SanPiN) and other regulatory documents, according to which compliance with the requirements is determined.
Chemical reagents are used in processing to reduce the level of epidemiological safety.
Let's note some features:
- Drinking water of moderate hardness is considered relatively normal in water supply systems, and it is also the most common option in spring water and artesian wells.
- Soft is rain (although in today’s unfavorable ecology it can very likely contain harmful impurities). This definition includes a liquid that has been subjected to prolonged boiling, not very desirable for use in food needs, and distilled, completely freed from them.
- Hard water refers to any water (from the sea, ocean or flowing from mineral strata) with a high content of impurities. They can exceed a third of the total volume of the liquid under study, and only 2/3 are the usual hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
By using a hard liquid when working with household appliances, you can quickly come to the need for repairs. Ordinary soap does not dissolve well when washed by hand or when washed in it.
About the standard of hardness
The problem of meeting the required water hardness level at the tap is not only a matter of the source from which it is obtained. The general hardness of water can be permanent or temporary.
And if the second one, calcium and magnesium carbonate, can be neutralized by boiling, then the permanently present one can affect the health of the consumer, the serviceability of the washing machine or kettle. There is practically no way to eliminate it.
Natural water can change its properties as a result of seasonal migration of flows from rain and melting snow. In winter, when such phenomena are not observed in nature, the level of indicators usually becomes more severe.
Optimal softness according to standards is water from surface streams or that flowing in places where dolomite or limestone rocks occur.
Use a mirror
This method will allow you to guess how hard the water is flowing from the tap. But it will not give a specific meaning.
What you will need
- Mirror.
- Pipette.
- Distilled or boiled water.
What to do
Using a pipette, apply a drop of tap and distilled water to a horizontal mirror surface. Wait for the liquid to evaporate. And then analyze the two spots with sediment remaining on the glass.
The more saturated the sediment from tap water is, the more it differs from the almost imperceptible trace of distilled water, the higher the hardness.
Units for measuring drinking water hardness
Until recently, the hardness of drinking water was measured in the Russian Federation in moles per cubic meter (mol/m3). This unit was used in the Soviet Union and Russia from 1952 until 2014, when the international standard was reintroduced.
Until the middle of the last century, the USSR used the degree, corresponding to the modern German (dH), as a unit of measurement of hardness. It and the French degree (fo) are used as a unit of measurement in European countries. The United States of America has its own American degree, ppm.
Since 2014, Russia has introduced a degree of hardness (°Zh). Its meaning in the understanding of a common person will not be particularly difficult, because a mole per cubic meter and ½ millimole per liter (the value of 1 °F) are related concepts.
We are simply talking about reducing the scale of the raw materials being studied. Nowadays, the standard designation 1 mEq/L, which is equal to ½ millimole per liter, is more often used. But for calcium and magnesium ions it has a different numerical value:
- Ca 2+ ions – 20.04 mg;
- Mg 2+ ions – 12.16 mg.
These indicators are not at all the norm for drinking water hardness. These are generally accepted units of measurement, identical to each other in the context when we are talking about one °J, ½ millimole per liter (mmol/L) or 1 mEq/L.
For calcium and magnesium, all these designations are expressed in different numbers. The standards in the Russian Federation, defined in SanPiN, may be variable if it is necessary to indicate the normal hardness of drinking water (we are talking only about magnesium), bottled water (calcium and magnesium).
Accepted standards of rigidity
In the Russian Federation there are some discrepancies between the norms and international standards. The diversity of natural and climatic conditions, the variability of those used for the extraction of drinking water and liquids for domestic use does not allow us to establish unconditionally uniform standards that are mandatory for any region.
However, drinking water hardness standards generally correspond to WHO recommendations. In an unfavorable environmental situation, they are brought into compliance with the sanitary and hygienic standards of the country in various ways. There are quite a lot of options for this.
Today, the consumer can independently control the presence of hardness standards in the water supplied from the tap and install various devices to bring it into compliance with sanitation and hygiene standards.
The standards given below relate to temporary rigidity, the elimination of which is possible in the simplest ways. At home, the most famous - steam - is carried out by boiling water in a kettle.
Table of indicators of calcium and magnesium standards according to the requirements of SanPiN of the Russian Federation and WHO standards.
| Regulatory document | Product | Magnesium | Calcium | °F |
| SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01; GN 2.1.5.1315-03 | Drinking water | up to 50 mg/l | not regulated | 7 |
| SanPiN 2.1.4.1116-02 | Bottled water | 5–65 mg/l | 25–130 mg/l | 1,5–7 |
| WHO recommendations | Drinking water | 10–30 mg/l | 20–80 mg/l | not indicated |
The measurement in degrees of hardness is as follows: less than two °F is soft water, from two to ten °F of medium hardness is a normal level, more than 10 is hard. However, in an aquarium, 15 degrees of hardness can be considered normal. It all depends on what kind of inhabitants live in it.
The decrease in calcium in aquarium water occurs due to the consumption of ions necessary for life by plants, shellfish and fish. To reduce the level of temporary rigidity, various methods and devices can be used.
Water is boiled for drinking. The effectiveness of the method is clearly evidenced by the level of scale in the kettle. The pool can use a membrane filtration method or magnetohydrodynamic resonance.
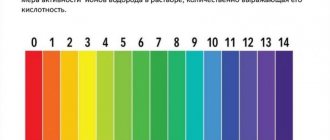
What is pH
The two-letter abbreviation originates in Latin. It stands for “hydrogen power” and means a measure of the activity of charged particles of a given element. To calculate the pH value, the concentration of hydrogen ions is measured. Then the decimal logarithm is taken from the resulting number and multiplied by (-1). The mathematical formula looks like this: pH = -log[H+].
Essentially, the hydrogen index is the ratio of H+ and OH– ions in a liquid, which are formed during the breakdown of water molecules. The ideal ratio is 1:1, i.e. pH=7. Distilled water has this value.
The value of the indicator is directly related to the temperature of the water and its interaction with air. If the pH in a closed vessel is 7, then as carbon dioxide enters the liquid, the value will drop to 5.2.
The pH value is also affected by substances that dissolve in water. The addition of some substances increases acidity, while others decrease it. This phenomenon allows you to evaluate the purity of a liquid, even when visually it does not have impurities.
How to determine compliance or non-compliance with the rigidity standard
As in the case of the level of hot water heating, the consumer has the right to make claims against the supplying organization if we are talking about temporary rigidity. The abundance of magnesium or calcium ions above the norm not only changes the taste of drinking water, but also has a harmful effect on human health and damages household appliances.
The supplier may have one of many water softening devices at his disposal. However, unscrupulous companies ignore existing regulatory requirements. In order to talk about the inadmissibility of an indicator existing in drinking water, it is necessary to make certain measurements and compare it with the hardness standard.
In this case, home-grown criteria, such as soap that lathers poorly even in hot water, or scale that quickly forms on a kettle, are unacceptable.
Water samples can be taken to the SES, where pathogenic microorganisms, organic impurities, and toxic inclusions such as nitrates will be identified. For home express analysis, you can use test strips, the cost of which does not exceed 500 rubles.
If we are talking about independent water supply to a mansion, cottage or country house from improvised sources, such as an artesian well, you can do a comprehensive analysis in a specialized laboratory, the cost of which varies.
In the laboratory of Moscow State University, an analysis of water hardness will not be cheap, but at a local one it can range from 1200 to 4500 rubles, if an extended one is required. But having all the indicators in hand and having identified inconsistencies with any hardness standards in the source used, you can choose one of the many water purification systems.
This will help protect your own health from future troubles and feel comfortable. These measures will also ensure the safety of household appliances.
Try test strips
What you will need
- Test strips for determining water hardness. They can be purchased at pet stores and home appliance stores. An alternative is strips for determining the acid-base level (pH) of a liquid.
- Cup.
What to do
Pour the water you want to measure the hardness into a glass. Dip a paper indicator strip with reagent squares applied to it into the liquid.
Shots: @Prosto Sidorov / YouTube
Pull out the strip and wait about a minute (the exact duration is indicated in the instructions). Under the influence of mineral salts, a chemical reaction begins, and the color on the dough indicator squares will change.
Shot: @Prosto Sidorov / YouTube
To determine water hardness, compare the color in the indicator windows with the sample in the instructions.
If you use pH strips, remember the general rule: the harder the water, the more alkaline it is - that is, the higher the pH value. Typically, soft water has a pH less than 7, while hard water has a pH above pH Levels in Drinking Water / ATS Environmental 8.5.