When purchasing a home pond, many aquarists first think about planning the decorations and stocking the fish, forgetting about such an important aspect as filling the tank with good water. As a rule, tap liquid is most often used for an aquarium, the parameters of which do not meet the requirements of fish and vegetation. Neglect of measuring indicators is a serious mistake of many novice aquarists, and has a detrimental effect on the condition of underwater inhabitants.
General definitions
A dirty and cloudy liquid spoils the overall appearance, but crystal clear liquid is also not always useful. After acidity, the second most important parameter is the level of hardness. Its too high or low values will primarily affect the plants.
Calcium cations and, to a lesser extent, magnesium cations have the greatest impact on the level. Manganese, iron and strontium, present in small quantities, are not taken into account in the measurement.
Hardness is divided into 3 types:
- Total (gH). Consists of two values given below.
- Non-carbonate. This is a constant value of the level of magnesium and calcium chlorides and sulfates dissolved in the liquid. Does not change when boiled at home. However, it may fluctuate within 24 hours. This is facilitated by the presence of plants or the time of day.
- Carbonate (kH). Concentration of bicarbonate salts (Mg and Ca). At a pH greater than 8.3 and boiling, they form a flocculent sediment, settle in crystals on the walls of the container and a film on the surface of the water.
Photo gallery of means for measuring water hardness:
kH is the most important for aquarists; this is due to several aspects:
- The level of carbon dioxide that is formed when fish breathe. At high kH, the CO2 value can reach a critical level of over 30 mg/l, which will lead to the death of the inhabitants. However, a low concentration below 15 mg/l will not allow plants to develop normally.
- pH stabilization. There is a direct relationship between the two values.
- Water for spawning of some fish species. This is a liquid with low kH and acidity in the range of 5.0-7.0.
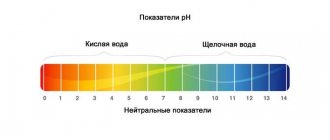
The acidity of the water inside the aquarium, also known as pH
This indicator reflects the reaction of water (acidic, alkaline, neutral) at a certain concentration of hydrogen ions.
In a chemically pure liquid, molecules decompose into OH- (hydroxyl ions) and H+ (hydrogen ions). This process is called electrolytic dissociation. 10-7g*ion/l - this is the stable amount of these ions at a water temperature of 25°C. The reaction of such water is characterized as neutral. To indicate the pH value, use the negative logarithm of the concentration of hydrogen ions. Under the conditions under consideration, it is equal to 7. If the liquid is not chemically pure, but contains acids, the number of hydrogen ions will exceed the number of hydroxyl ions. Thus, the water reaction will be characterized as acidic with a lower pH value. In a liquid with an alkaline reaction, on the contrary, an increase in pH and a predominance of hydroxyl ions will be observed.
According to pH, water is usually classified as follows:
- strongly alkaline - 10-14;
- slightly alkaline - 7-8;
- neutral - 7;
- slightly acidic - 5-6;
- sour - 3-5;
- strongly acidic - 1-3.
Depending on the time of day, pH parameters vary. This occurs due to fluctuations in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the liquid. This process can be stabilized through permanent aeration.
If pH values change too sharply, this will negatively affect aquarium animals and vegetation. From 5.5 to 7.5 - this pH is favorable for most fish.
Normal and critical rigidity indicators
The lifespan of the inhabitants depends on the hardness of the water in the aquarium. Salts of the alkaline earth metals magnesium and calcium, for example, affect growth rates, the formation of bones in fish skeletons and shells in mollusks. They also act as a mineral fertilizer for plant development. In too soft an environment, leaves curl and shoots die.
The unit of measurement for hardness is often taken to be the content of milligram equivalents of calcium and magnesium ions per liter of water (mg-eq/l). In aquarium keeping, for convenience, German and Russian degrees are used (1 ° = 0.36 mEq/l).
| Degree | Meaning | |
| Degrees | mEq/l | |
| Soft | 0-8 | 0,36- 2.88 |
| Average | 9-12 | 3.24-4.32 |
| Quite tough | 13-18 | 4.68-6.48 |
| Tough | 19-30 | 6.84-10.8 |
Normal kH is in the range of 4-8°. In older aquariums, the value drops below this level over time due to water oxidation.
Some species require a soft environment, while others, on the contrary, prefer higher degrees. This needs to be taken into account in several cases:
- When initially forming an aquarium: for snails, a more rigid one is preferable, for neon fish 6-8 °, for guppies 5-10 °, angelfish 18 °, for ferns 10-14 °.
- When completely replacing the liquid and transplanting fish into it.
- Preparing water for spawning. Some species reproduce in any conditions, for others it is necessary to pre-prepare the liquid.
For most aquarium fish, the norm will be values from 3-15°. A reading below three indicates a lack of rigidity.
What affects the living conditions of aquarium fish?
A considerable amount of impurities are dissolved in water:
- minerals;
- gases;
- organic.
Some of them help the aquarium population thrive, while others can be harmful.
Whether fish and algae can adapt and create a viable ecosystem depends on the nature and concentration of these contaminants.
Oxygen
Without oxygen dissolved in water, the normal functioning of an aquarium is impossible.
Animals use it for respiration, plants for respiration and photosynthesis ; with its participation, the processes of oxidation of organic matter occur.
Both a lack and an excess of gas are harmful to the inhabitants of the aquarium.
Reduced oxygen concentration leads to slower growth and changes in fish behavior.
Attention! The defect is visible to the naked eye: the fish rise to the surface and swallow air.
Increasing the concentration changes the course of chemical reactions, causing acidity to increase. Oxygen enters the water column in different ways:
- Diffusion on a surface. The process is common in natural bodies of water, where the surface is in constant motion.
- Plant photosynthesis. If there are a lot of them, a situation is possible when the environment is oversaturated with oxygen. The lower the temperature, the faster the O2 concentration increases, which is dangerous for fish.
- Artificial saturation. The water is blown through by an air stream. For this, compressors or filters are used.
Acceptable oxygen content is determined by the following figures:
- A concentration of 5 mg/l (or slightly more) is considered the norm.
- The lower and upper boundaries may shift depending on the fish species. On average, the permissible range stretches from 3 to 15 mg/l. If the aquarium is inhabited by plants and sedentary inhabitants, 1-2 mg/l will not harm.
Oxygen levels are checked using test reagents sold at pet stores.
There are several ways to normalize the oxygen content in water:
- Use aeration equipment. During uninterrupted operation, the water layers are mixed and evenly enriched with oxygen.
- Use drugs that increase oxygen levels.
- Increase the number of plants that will release O2 during photosynthesis.
Reference! The process of photosynthesis with the release of oxygen (nutrition) occurs only in the light. At night, plants breathe like other organisms, releasing carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide
The carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide) present in the aquarium is a product of the respiration of fish and plants.
If there are a lot of plants, its concentration can change cyclically , increasing in the dark.
Carbon dioxide is involved in two important processes. It is one of the plant nutrients.
In addition to photosynthesis, the gas helps acidify water (lower pH) by participating in the formation of carbonic acid. Only a small fraction is involved in the process - 0.1-0.2% of the gas dissolved in water.
It is important to monitor the balance of carbon dioxide, since it dissolves in water several times better than oxygen and easily exceeds acceptable levels.
Important! Excess CO2 concentration increases acidity, which leads to poisoning of fish and shrimp. A reasonable amount of it stimulates the development of plants, and a deficiency leads to a stunting of the growth of the aquarium flora.
Saturation tolerances are determined by the following figures:
- Normal concentration: 2-10 mg/l.
- Minimum: 3-5 mg/l.
- Maximum: up to 30 mg/l.
To measure the concentration of carbon dioxide, a drop checker is used - a device with an indicator liquid that shows the gas level in color.
Usually, aquarium owners are faced with excess carbon dioxide. To remove excess, instrument aeration and manual mixing of the top layer of water are used. A balloon system or lime tablets will help saturate the aquarium with carbon dioxide.
Acidity
The most important characteristic is acidity (pH), which affects many chemical processes.
A comfortable existence for fish is possible if this parameter is stable. A neutral environment has pH=7.0 units ; it is familiar to most fish and plants.
Acidity often decreases due to an increase in CO2 concentration. In real life, the pH value fluctuates in the range of 6.0-8.0. Many freshwater inhabitants adapt well to water with a pH of 5.5-8.5.
Acidity adjustment occurs in conjunction with alkalinity (carbonate hardness); these are interconnected processes. There are three ways to measure acidity: purchase a test (test kit) from a specialized store, a measuring device, or an aquarium controller.
To increase the pH, special preparations or a calcium-rich mineral are used, which is immersed in water. As they dissolve, they will increase the pH level and hardness.
Saturating the aquarium volume with carbon dioxide will help lower the pH level (acidify). For a slow decline, adding natural materials (for example, peat crumbs) to the aquarium filter is suitable.
Attention! The change in acidity must occur slowly so that the fish do not go into shock or osmotic stress.
We analyze the pH indicator in detail in this article.
Rigidity
Like acidity, it refers to the parameters on which the other properties of water depend and whether fish and plants will take root in the aquarium.
Hardness indicates the presence, type and percentage of salts and minerals dissolved in water; measured in degrees of hardness.
Based on the concentration of dissolved impurities, H2O is divided into:
- Very soft: 0-5.6 degrees.
- Soft: 5.6-11.2.
- Average: 11.2-16.8.
- Hard: 16.8-22.4.
- Very hard: above 22.4.
There are three types of it:
- Permanent (non-carbonate, residual, insoluble) hardness (GH). It does not change after boiling (hence the name), is an unchangeable feature, and therefore serves as an indicator of the suitability of water for living creatures. It is specified by calcium and magnesium salts (sulfates, silicates, chlorides).
- Carbonate (variable, soluble) hardness (KH). Indicates the presence of hydrocarbonate and bicarbonate anions in the solution. It has a second name - alkaline. The optimal content is 4-15 degrees.
- General hardness. Sum of soluble and insoluble hardness; clearly shows how soft or hard the water is. The aquarium norm is 3-5 degrees.
Information! Pet stores offer kits for measuring water hardness.
To bring rigidity back to normal, the following methods are practiced:
- Boiling reduces hardness, but not mineral content. To soften, add water from an external source: rain, distilled.
- Softening using ion exchange resins or chemicals.
- Demineralization. Impurities are removed using a reverse osmosis filter.
A detailed article on the hardness of water in an aquarium can be found here, and additional methods of softening can be found here.
Temperature
To keep fish and plants, certain temperature conditions are necessary, and they must be monitored.
Excess of water beyond the optimal temperature is destructive for many species of fish (tropical).
For most aquarium inhabitants, a favorable temperature range is 22-26°C.
Some species (for example, labyrinth fish) are more thermophilic; for normal life they need an environment with a temperature of 28-30°C. Less demanding fish (goldfish) are content with a range of 18-23°C.
Reference! During the day, temperature fluctuations within 2-4°C are allowed. The inhabitants of the aquarium may not be able to tolerate sharper changes. To avoid temperature fluctuations, the aquarium is placed away from direct sun, air conditioners, drafts and heating appliances.
Temperature is measured with a thermometer and maintained in different ways:
- For heat-loving fish (especially in winter), the best solution would be a water thermostat. Its design includes a heating element that automatically maintains a preset heat level.
- In order to raise the temperature , there are temporary solutions: a heating pad with warm water leaned against the wall, or a plastic bottle with warm water placed in water.
- To reduce the temperature during the hot season, lower a container of cold water into the aquarium. It is necessary to ensure that in the first 20 minutes the temperature drops by a maximum of 2°C, and in the next half hour - by no more than 1-2°C.
- A more gentle way to reduce the temperature: increase aeration (using a compressor) until the readings drop to normal.
What else you need to know about the need and methods of heating water in an aquarium, read the link, and this article will tell you about cooling water in an aquarium.
What else should you consider?
Water quality is determined not only by basic, but also by additional parameters:
Ammonia. Formed during the decomposition of organic matter. It is a life-threatening poison for fish: it causes damage to the gills and leads to death. The ammonia concentration must be zero, which is verified by testing. When gas appears, part of the water is replaced and the bottom is siphoned at the same time. Additionally, neutralizing drugs are used.- Nitrites and nitrates. They are formed at different stages of organic decomposition and are toxic to fish (signs of poisoning are lethargy, poor appetite, darkening of color). The optimal nitrite content is zero. Nitrates are consumed by plants, so their content is allowed in the range of 5-15 mg/l. A test helps to find out the exact indicators. The problem of excess is solved by changing the water, reducing the density of fish, and increasing the number of plants.
- Chlorine. A gas that is highly soluble in water and poisonous to fish. A concentration of no more than 0.25 mg/l is considered non-hazardous. Chlorine is used for disinfection in water supply systems, so before adding water to the aquarium, it is left to sit for 2-3 days. The most convenient way to check the concentration of chlorine is with a test; There is no need to rely on smell. Additional filtration of water through activated carbon will help normalize the indicator. A quick way to remove chlorine is to use a dechlorinator.
- Phosphates. Inorganic salts of mineral origin that are consumed by plants. Favorable concentration is 0.3 mg/l. Excess leads to algae growth. For a fish aquarium (without plants), the lower the phosphate concentration, the better. The presence of phosphates in the water is checked by strip or drop test systems. The content is regulated by changing water or applying fertilizers.
Mr. Tail recommends: methods for determining hardness
To find out the value of tap water, use several methods.
Using a TDS meter
Compact device that measures salt concentration. To check, lower the device into the liquid and wait, the result will be shown in milligrams per liter. Service life 1-2 years. However, the measurement can be considered relative, since, in addition to calcium and magnesium, the final number will also contain a small amount of impurities of other substances.
Strips with reagents applied to them
They can be purchased at the store. To determine hardness, you need to dip litmus paper in water and wait for the color to change. Then compare the result obtained with the table proposed in the instructions. The method is simple and affordable and can be done directly in the aquarium. But the units of measurement will have to be converted from foreign to Russian degrees.
Drip tests
Sold in pet stores. To check: take 5 ml of water and add a chemical reagent from the bottle. Next, the color of the liquid will change from red to green. After the reaction has completed, the number of drops of the reagent will be equal to German degrees.
Chemical reagent Trilon “B”
This method is considered the most accurate; the disadvantages are the complexity and duration of the experiment. A buffer mixture, a chemical reagent and a special indicator are added to the water taken from the aquarium. As the reaction proceeds, the color of the solution changes from cherry to blue-green.
Using laundry soap
It is considered the most affordable way. Required: 1 gr. crushed soap (60 or 72%) and heated distilled water. A solution is made from them and added to a jar containing 0.5 liters of tap water. After a head of foam appears—a signal that the salts in the liquid are bound—the remainder of the soap solution is measured with a ruler. This value is subtracted from the original quantity. Each centimeter obtained by subtraction is equal to 2 degrees of hardness. The result is found in the table.
Sometimes it happens that the solution is completely poured into the jar, but no foam has formed; in this case, it is generally accepted that the hardness is above 12°. the liquid must be diluted with distilled water 2 times and repeat all the steps, multiplying the resulting figure by two. The error of the method is 1-2 °.
The average tap water reading is 20°, the highest acceptable limit for many fish species.
Quality checking
The reason for poor health of fish and slow growth of plants is poor water quality. It is impossible to identify the problem by eye; the content of impurities is checked using tests or instruments.
Tests offered by pet stores are a proven (and quick) way to monitor water quality. They are special indicators that record the degree of concentration of a chemical substance.
It is important to understand that:
Diagnostics are not needed if the inhabitants of the aquarium feel well. Tests are needed in a new aquarium where the ecosystem is not yet established. Testing is also necessary for those who regularly use fertilizers (to avoid overdose).- There are tests separately for fresh or sea water, as well as universal ones.
- Drop tests provide reliable results. Test strips are less accurate, but they are good at diagnosing a problem.
- If there are problems with fish, first of all they test for acidity, ammonia, nitrates, nitrites.
- An aquarium with plants is additionally tested for phosphate, total and carbonate hardness.
- Periodic testing for metal impurities (copper, iron) is useful.
Reference! Tests can be purchased individually or in the form of kits, which is much more profitable. For diagnostics, it is convenient to use special instruments (for example, a chlorometer for determining chlorine), but purchasing a “collection” of meters is only advisable for owners of several aquariums.
A complete overview of aquarium tests can be found here.
Practical tips for using aquarium tests in the video:
How to increase water hardness in an aquarium
If the tests carried out reveal values that do not meet the required values, you can adjust the hardness to the desired value. However, there should not be a sudden change in values, as this can cause stress in the fish.
If you need to increase the level of rigidity, the following methods are used:
- Add the bottom layer of boiled liquid rich in salts.
- Mix water with harder water.
- Pour coral or dolomite chips into the aquarium filter.
- Place marble, limestone containing calcium carbonate or colored glass on the bottom. You can dissolve pieces of chalk by increasing the level by 2-4 °. The disadvantage of this method is the difficulty of controlling the rigidity. It is better to pass the liquid through a filter with the addition of marble chips.
- Decorate the bottom of the aquarium with shells.
- Add calcium carbonate 2 tsp. for 50 l.
- Use dissolved soda, 1 tsp. per 50 l, or 0.2-5 g per liter. This method is suitable for water with a temperature of at least 8 °.
- Add a 10% solution of calcium chloride and magnesium sulfate: dilute 50 g, obtaining a volume of 750 ml. Use each at 1 mg per liter.
- Pour 1 ml of 25% magnesia into 1 liter of water.
Almost all of the above methods change the stiffness index by 4 °.
Temperature for the herbalist's aquarium = 24-25°C
It is possible for plants to exist at lower or higher temperatures.
However, there is a known pattern: the warmer the water, the less solubility of gases in water. If its temperature is 24–25°C, it contains much more dissolved carbon dioxide (during the day) and oxygen (at night). And this is a direct benefit for the closed ecosystem that is the aquarium. Plants require oxygen for respiration and help oxidize organic matter and nitrogen compounds . And accordingly, plants assimilate more carbon dioxide necessary for growth.
In any aquarium there is always ammonium NH4 and ammonia NH3, which pose a danger to the inhabitants. They are formed from waste products of fish, including the decay of organic matter. If the water temperature is raised or the pH level is increased, the toxicity of nitrogenous compounds will increase.
Solubility of gases in the temperature range
Additionally, we note that Takashi Amano recommended at the very beginning, after starting the herbalist, to even reduce the temperature to ~ 21-23 degrees, that is, thereby preventing nitrogen imbalances from “hitting the plants” and the aquarium as a whole. An “increased amount” of O2 in the dark promotes oxidation and “fast work” on nitrogen, and promotes better respiration of the plant. During the daytime, CO2 acts to the same extent in its profile.
The most common mistake made by grass-fed aquarists is to ignore or minimize the O2 value at night - in the dark. The supply of aeration to the aquarium should be commensurate with the daily supply of CO2. It should be of the highest quality, finely dispersed (like from a CO2 diffuser). This effect can be achieved by raising the flute above the water level, with a powerful pump, or, for example, with a thing like the H 2 Show BubbleMaker , through which, by the way, it is possible and even awesome to supply CO2 in large herbalists - the bubbles are extremely finely dispersed and they are carried far and wide *50*50.
How to reduce water hardness in an aquarium
When the hardness level is high, it needs to be lowered. This is somewhat more difficult to do; the following steps will help to mitigate it:
- Add distilled liquid. After mixing, additional enrichment of the aquarium with oxygen and remineralizing salts is necessary.
- Pour in melt or rain water, which reduces the number of degrees of hardness. However, caution is required due to the possible presence of harmful impurities. To disinfect the environment, a special conditioner should be added.
- Bring water to a boil, cool, and stand for 24 hours. Pour only the top part into the reservoir.
- To reduce hardness, use peat by pouring it into the filter, after disinfecting it by boiling or calcining. The liquid is also left outside the aquarium by placing a peat tablet in it in a bag for 4-5 days.
- Freeze in a shallow container. Once frozen, melt the ice and add it to the aquarium.
- Another method of reduction is filtration, for example, through reverse osmosis.
- Plant plants such as aegropile, hornwort, nayas or elodea.
When choosing plants, snails, crustaceans or fish for your aquarium, a beginner and even an amateur should not forget about the hardness parameters. And be able to measure and adjust, at home, the indicators of tap water.
Aquarium water standards
Cloudy water in an aquarium is a clear sign that something is wrong and the fish are not feeling well there. But perfectly clear water is not always good either. Distilled water is considered absolutely pure, but it is unsuitable for fish. The norm is to maintain a balance of each of the following indicators:
- General hardness;
- Carbonate hardness;
- Nitrites (NO2);
- Nitrates (NO3);
- Acidity (pH);
- Phosphates, iron, chlorine and others.
The difficulty is that different fish need different conditions. Therefore, the task of the aquarist is to bring the life of fish at home as close as possible to natural conditions.
How to downgrade?
Lowering the stiffness is a little more difficult. You need to be careful, most species of fish and plants die in an acidic environment.
Home Recipes
The following traditional methods are used to reduce the amount of salts:
Make a mixture of tap and distilled water.- Boiling. Boil tap water over a fire for 1 hour. Only the top layers are added to the aquarium, since salts precipitate at the bottom.
- Freezing.
Water is added to the container and sent to the freezer. They wait until it is covered with a thick crust. A hole is punched in it, pouring out the liquid contents. Ice is melted by pouring it into the aquarium.
These are the simplest methods that anyone can use. No need to buy additional ingredients.
Filters
Chemical methods include a filtration system. You can use both different substances and electronic systems.
The following types of filters are used:
- osmotic;
- deionizing;
- peat.
The first 2 methods are applied using a ready-made system.
If a peat filter is used, the water is pre-boiled. After filtration, it will acquire a yellow tint. It is removed with activated carbon.
What it is?
Water hardness is a parameter that reflects the concentration of salts formed due to alkaline earth metals. These include magnesium, calcium, and auxiliary elements .
The more substances concentrated in water, the higher its hardness. This does not mean that the parameter should be eliminated completely.
A high-quality balance of substances is needed to maintain the normal functioning of plants and fish.
General
Total hardness is the total amount of calcium and magnesium salts present in water. It is divided into the following types:
- Carbonate or temporary.
- Non-carbonate – permanent.
The general parameter reflects the entire number of elements that form an alkaline environment. It is constantly changing as trace elements are deposited and fish and vegetation release metabolic products.
Carbonate
Carbonate hardness indicates the presence of bicarbonate and bicarbonate anions. The acid-base state increases greatly.
The following features are distinguished:
- formation of sedimentary particles;
- during the boiling process, sedimentary substances are formed to a greater extent, and gas is additionally released;
- ph is less than similar indicators.
Non-carbonate
Non-carbonate hardness does not change under the influence of various substances and thermal regulation. It appears due to the following properties:
- permanent salts;
- content of Cl, SO4.
The substances maintain the environment at an optimal level. Both types of stiffness interact. But the last parameter is always there, regardless of the conditions.
How often to measure?
The ratio of substances changes gradually . It takes a long time for salts to accumulate or decrease.
If a person uses indicator systems, measurements are carried out no more than once every 1-2 months.
If a large number of fish are grown in an aquarium, the microelement composition changes faster. Purchase high-quality instruments that measure hardness with greater accuracy.
It is determined at least once a month . Before replacement, clean water is immediately checked.
Peat-based preparations
Water softening compounds made from peat are on sale. One popular product is Tetra ToruMin. It gives the water a characteristic dark tint. This has a beneficial effect on the behavior, well-being, and coloration of some species of fish. Light penetrates into water less well, which prevents water from blooming.
Another peat-based product is JBL Tormec active. This is a granular filler for water softening. The effect of using this product is long lasting. It has a beneficial effect on fish whose natural habitat is dark water. The composition reduces the amount of algae in fresh water.
Another granular peat-based product is Sera Super Peat. It also softens water and reduces the acidity of the environment.