Beginning aquascapers, when starting a home pond, think through many nuances: where to put it? Which fish should I let in? What plants should I plant? However, these are not the main features of aquarium farming. First of all, you need to take care of the water parameters and understand that not every liquid in the aquarium will be appropriate. In each home, the water can be different, most often it is hard, and this is one of the main points in raising pets, affecting their health, growth and comfort.
What is water hardness
Before populating a home pond with fish, crustaceans, and plants, you need to assess the possibility of their coexistence. The chemical boundaries of their habitat must be identical. Water hardness is one of the most important parameters, which implies the degree of saturation with dissolved minerals. There are two indicators of hardness:
- Constant hardness (GH) is the presence of magnesium and calcium sulfates and chlorides dissolved in a liquid. This indicator determines the degree of suitability of water for an aquarium. The density of Mg and Ca can be reduced by distillation or chemical methods. Minerals are needed for the skeletal tissue of fish and are of great importance for the life of underwater flora and fauna.
- Carbonate hardness (KH) of aquarium water is determined by the level of carbonates and bicarbonates. This value changes several times per day. During the day, plants, due to the ongoing processes of photosynthesis, take away the carbon dioxide accumulated during the night. When there is not enough carbon, plants begin to synthesize it from bicarbonates.
Carbonate hardness differs for different aquarium inhabitants. Failure to comply with the correct parameter will definitely lead to a deterioration in the well-being of the fish and impaired ability to reproduce.
Definition of the concept
Water is an excellent solvent; it contains a large number of different elements (gases, salts) that determine its chemical and physical qualities, for example, hardness. Let's take a closer look at what this property is.
The hardness of water is determined by the content of various elements in it, mainly metal salts, of which calcium and magnesium salts have a greater influence on the structure and density.
Ions of these elements are present in all natural water sources, getting there from soil, especially rich in limestone, gypsum and dolomite. A high salt content makes the water structure hard, a low salt content makes it soft.
The amount of salts depends on the body of water itself, for example, fresh water bodies change the indicator during the period of rains or melting snow to a softer one, and oceans and seas have a very high value.
Did you know? The most expensive bottled water is sold in the USA, Los Angeles. In addition to purity and taste balance, taking into account acidity indicators, this precious liquid has an unusual packaging. Manufacturers decorate glass containers with rhinestones from
"
Swarovski
"
, the price of this magnificence is $ 90 per liter.
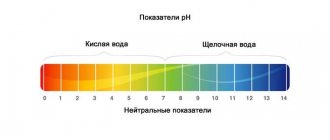
Hardness standard
The general hardness of the aquatic environment is measured in German degrees: 1 dH is equivalent to 10 mg of calcium oxide per liter of water. The following levels of water hardness are conventionally distinguished:
- 0-4.5 - very soft.
- 4.5-11.2 - soft. This water lacks minerals.
- 11.2-22.4 - medium hardness. Characins, small barbs, and corydoras catfish feel good.
- 22.4-33.6 - hard. Suitable for the life of African cichlids, cichlids, sagittaria and fern growth. A high concentration of minerals is vital for crustaceans, because in soft water the shells gradually break down. Viviparous fish species live well and leave offspring in such an environment.
- More than 33.6 - very hard. This environment is unsuitable for most aquatic life.
There is no single norm. Fish and plants have different preferences. We can talk about critical values that need to be excluded when preparing water for a home pond. The hardness should not fall below 6 or rise above 33 degrees.
Parameters, what should be
Different species of fish survive and reproduce in certain conditions. For some, low hardness is optimal, for others - medium.
But the most optimal parameters are highlighted:
- 3-6 mEq/L carbonate hardness for freshly poured water.
- up to 15 mEq/l when the water sits for a long time.
The vital activity of the internal environment of the aquarium is negatively affected by excessively reduced or increased hardness. These are critical parameters.
| Type of critical parameter | Description |
| Short | Occurs due to lack or absence of calcium. Without it, vegetation cannot exist, since its growth stops. Therefore, the minimum value is 4 mEq/L |
| High | Leads to sedimentation and gradual death of fish. In such an environment, breathing, reproduction, and other basic functions are difficult. Criticality appears above 15 mEq/l |
Soft or medium indicators are considered optimal. They fluctuate when external and internal factors change. Therefore, they periodically take measurements with a test system.
How to determine the hardness of water in an aquarium
There are simple techniques to measure the presence of minerals in water at home:
- TDS - meter or salinity meter is a simple device. The operating principle is based on measuring the degree of electrical conductivity of the liquid. The dH value of an aquarium can be checked approximately.
- Test - strips. The method is suitable for inexperienced users. Adding a reagent to a certain amount of liquid changes the color of the water. Hardness is determined by color. It is difficult to find strips on sale. When purchasing, be sure to take instructions for use.
- Laundry soap. With its help you can find out the exact parameters. Stir one gram of soap in a regular faceted glass with a small amount of warm distilled water. Add distillate for 72% soap at a level of 70 mm, for 60% 10 mm lower. Slowly pour the solution in portions into a liter jar of aquarium water. If a reaction occurs when a 10 mm solution is injected, the hardness level is 2℃ dH. If you need to pour 40 mm, then 8℃ dH. The indicator is above 12 if foam still does not appear when pouring the entire glass.
The testing method using the Trilon B chemical reagent is the most accurate, but overly complex and requires special chemical equipment. The most affordable is soap. Deviations in test results are insignificant.
Often the results of hardness measurements produce disappointing results. It is necessary to either increase or decrease the water hardness to a normal level. This must be done gradually so as not to create a stressful situation for aquatic inhabitants.
Water hardness: total gH and carbonate kH in the aquarium
The hardness of aquarium water or, in other words, gH and kH in an aquarium is the content in the liquid of magnesium, calcium and other alkaline earth metal salts (gAsh) or the amount of carbonate [CO3-] and bicarbonate [HCO3-] ions (keiAsh). The level of hardness is also affected by some rare chemical components that are of little importance to most aquarists. Water will be soft when the volume of dissolved salts is low, and hard when their amount is high.
For reference: gH and kH of water in an aquarium are the values of total and carbonate hardness, respectively.
The importance of aquarium water hardness
Sometimes water hardness is no less important for the entire aquarium ecosystem than the pH of the liquid. In particular, it is reflected:
On plant growth and their ability to absorb nutrients. Plants may die in water that is too hard or too soft; On the hardness and strength of the shells of mollusks and crustaceans; For the health of the fish. For example, calcium and magnesium salts take part in the construction of the skeletons of the inhabitants of the bowls.
It is necessary to remember that different types of fish and plants, and any other aquarium inhabitants, require water of varying degrees of hardness. Before you think through the design, set up and launch your new aquarium with fish and live plants, you should ask this question in advance.
Optimal hardness values
The optimal hardness of aquarium water is one that is at least approximately close to the hardness of the liquid in the natural habitat of your plants and fish. It is impossible to provide specific universal indicators here.
In an aquarium with fish and/or shrimp, attention is most often paid to the general hardness of the aquatic environment. Its unit of measurement is general hardness – gH. One gH will be equal to 10 mg of calcium oxide in one liter of liquid. In a planted aquarium, kN is an equally important indicator; it is closely related to pH and determines the buffering properties of water.
Levels of water hardness in an aquarium, which are determined only conditionally:
Over 33 gH – excessively hard. For most fish and plants, this habitat will result in death;
From 22 to 33 gH – hard. In such an environment, Vallisneria, some ferns, Cryptocoryne ciliata, Echinodorus rubinum, Limnophila aromatica and sagittaria, Alternatera violet will grow, some African cichlids and the neon iris will happily live. The increased amount of minerals will have a positive effect on the health of some crustaceans. Since in a soft liquid their shells slowly but steadily collapse. Tetraodons also like hard water - you can count on large offspring;
From 11 to 22 gH – medium hardness. Favorable environment for some livebearers (mollies, guppies, platies for example), corydoras catfish;
5-11 gH soft water. Suitable for most fish species (characins, barbs, American cichlids) and most plants in the herbal aquarium (optimally 6-8);
0-5 gH – extremely soft water. Perhaps the water needs mineralization. 2-5 is suitable for killifish and Thai and Congo ferns, pistia, many cryptocorynes and echinodorosas with sufficient fertilizer and CO2.
There are no general standards. However, it is necessary to at least ensure that the total and carbonate hardness of the water environment does not reach critical values.
Total water hardness gH in the aquarium
Total hardness or gH in an aquarium is the total volume of magnesium and calcium salts dissolved in the aquatic environment.
According to many aquarists, the question of what the overall hardness should be in an aquarium with live plants is not as important as the topic of carbonate hardness. However, we would like to say that if gH is extremely low, this will negatively affect the health of the plants. Moreover, at minimum coolant values they may even die.
Water hardness gH in a planted aquarium is really significant: magnesium and calcium are required for the development and growth of aquatic flora. They, along with the nutrients in fertilizers, are vital macroelements. Accordingly, it is necessary to think about what gH is in an aquarium only when the indicator level is low.
If you are interested in the general hardness of the water in the aquarium, the norm should be as follows:
4-8 mg. per liter - the recommended value for most inhabitants; 3 mg. per liter - be prepared for the fact that certain types of plants will begin to suffer from a lack of calcium; Less than 3 mg. per liter – lack of hardness. The aquatic environment requires attention.
Now you know what the water hardness gH in the aquarium should be. Read our article to the end and you will understand how you can change it - by raising or lowering it.
Carbonate hardness kH in an aquarium
Before we tell you what kH should be in an aquarium, we will explain what is hidden under this abbreviation.
Carbonate hardness or kH of water in an aquarium is the volume of HCO3 (bicarbonate) and CO3—(carbonate) ions in the aquatic environment. These ions are the main components of alkalinity. Alkalinity depends on the amount of carbon monoxide in the water. Therefore, the carbonate hardness of water kH in an aquarium can also be called temporary hardness, or it would be more correct to say alkalinity. The relationship between this parameter and pH acidity is direct.
How important is kH of water in an aquarium?
Most of the plants and fish living in aquariums actually come from rivers with their soft and slightly acidic environment. Therefore, for normal living they require a liquid with an acidity of approximately 6.5. Acidic and soft water is especially important for fish spawning.
At low kN, the aquarium can boast of low acidity of the aquatic environment. It will be possible to correct the indicators, for example, through the supply of carbon dioxide.
Also keep in mind that if the carbonate hardness kH in a saltwater aquarium becomes high, then it will not be possible to reduce the acidity level without minimizing the first. To put it simply, a decrease in acidity is equal to a decrease in carbonate hardness.
Carbonate hardness kH in aquarium: normal
Possible kN values in aquarium water:
Less than 3 mg. per liter and more than 15 mg. per liter – critical values of carbonate hardness; 3-6 mg. per liter – optimal values that do not need adjustment.
Approximately 15 mg. per liter kH will be the liquid acidified from a long stay in the bowl.
How to check the hardness of water in an aquarium?
You can measure the water hardness in an aquarium yourself, using special devices or “improvised means”. Let's look at the most popular options.
Application of tests
You can purchase test strips or drops for measuring the hardness of aquarium water at a pet store. In the case of strips, we are talking about pieces of paper with a reagent present on the surface. The strips must be placed in a glass of aquarium liquid, waiting for the color to change. The color scale determines the water hardness. The drop test works in a similar way - you count the number of drops until the liquid changes color.
Advantages of test strips: low cost of tests, the ability to find out the parameters in a short time. By the way, the reagent is safe for the aquarium ecosystem. Therefore, the strips can be lowered directly into the bowl.
The downside is that the results will be quite inaccurate. The pieces of paper will receive a shade that will have to be matched “by eye” with the color palette. Moreover, it is necessary to convert foreign degrees that comply with European standards into Russian degrees.
The drop test has higher accuracy!
Check out our detailed Aquarium Test Review
Buying a TDS meter
The device is compact in size, convenient and easy to use. It can be used to measure the volume of impurities in the aquatic environment.
The essence of the TDS meter is based on creating an electric field in the liquid, in which salt ions and other chemical elements can be easily detected. The device will need to be dipped into a separate bowl of aquarium water. And within a couple of seconds it will demonstrate the volume of impurities in ml. per one liter.
Advantages of salt meters: work on AA batteries, no need for special care or knowledge for proper use. And also an affordable price, which can start from 300-500 rubles. Even the most expensive TDS meter models cost no more than three to five thousand rubles.
A couple more ways for those who liked to do experiments in chemistry lessons))
Determining the hardness of water in an aquarium using household equipment. soap
The method is based on the fact that in 10 mg. calcium oxide dissolved in one liter of water can be neutralized by 0.1 g. laundry soap.
For measurements you will need:
Transparent flask or glass jar. Glass, syringe. 60-72% laundry soap. Distilled and aquarium water.
You need to cut and grind a one-gram piece of soap. After preparation, the crumbs need to be poured into a glass with 10 ml. heated (but not brought to a boil) distilled water.
The next step is to pour half a liter of aquarium liquid into a glass flask. Then, using a syringe, add 1 ml. soap mixture, continuously shaking the transparent vessel. Initially, flakes will appear on the surface of the solution, then bursting bubbles will appear.
It is necessary to add the soap mixture to the flask until the bubbles are stable and have beautiful multi-colored tints. This will indicate that the components of the laundry soap reacted and were bound by calcium oxide.
To find out the degree of hardness, you will need to multiply the number of ml used. soap mixture for two. This will reflect the parameter in degrees. The error level will be no more than one percent (plus or minus).
For example: if you had to pour 5 ml into the flask before stable rainbow bubbles appeared. aquarium water, which means the hardness level is 10 degrees.
It is worth considering: the accuracy of such measurements decreases if the hardness is over 12 degrees. We recommend performing several tests, doubling the ratio of components and multiplying the results obtained not by two, but by four. Those. take one liter of liquid and two grams. laundry soap.
Use of Trilon B (chemical reagent)
Not the easiest way to measure water hardness in an aquarium. It should be recommended only to those who love experiences and experiments.
The amount of magnesium and calcium salts present in the aquatic environment will be determined by the sodium salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, presented in the form of a simple white powder - Trilon B. You will also need a buffer mixture of NH4Cl and NH4OH, which maintains the pH level at approximately 10. The need for it is due to the fact that The color change of the indicator depends on the pH of the liquid.
So, for measurements you need:
Indicator and Trilon B solutions; Buffer mixture; Aquarium and distilled water; 200 mg conical flask.
Let's move on to how to determine the hardness of water in an aquarium. From distilled water and 9.3 g. Trilon B needs to be made into a liter solution.
Next, you need to obtain a buffer mixture by adding 20 grams to a small volume of distilled liquid. NH4Cl (ammonium chloride), after – 100 ml. NH4OH (20% ammonium hydrate). Then you need to pour in such a volume of distilled water to ultimately get exactly one liter of chemical liquid.
To create an indicator, you will need 10 ml. buffer mixture, 0.5 g. black T eriochrome and the volume of ethyl alcohol that will allow you to get 100 ml from all this. solution.
You need to add 15 drops of indicator, 5 ml, to a glass flask. buffer solution and 50 ml. aquarium liquid. The color of the mixture should be deep red. The flask should be titrated with a solution of Trilon B, constantly shaking, until the color of the liquid changes to purple. After this, the titration should be performed more slowly and continued until the color changes to greenish-blue.
At the next stage, it will be possible to carry out measurements using the following formula:
X = (V multiplied by 0.05 and multiplied by 1,000) divided by V1
In the example: V1 is the amount of aquarium liquid, V is the volume of Trilon B used, X is the volume in ml. per liter of water-soluble magnesium and calcium salts.
To obtain values for further measurement in degrees, the calculation results must be multiplied by 2.8. You can directly find out the level of rigidity by comparing your numbers with the information in the Datskevich table (can be found on the Internet).
The method is very complex and painstaking, however, it is the one that is highly accurate. We also note that Trilon B can be purchased in quantities of 25 kg. You simply do not need such a volume of substance.
How to reduce the overall water hardness gH in an aquarium?
Owners of planted aquariums most often have to think about how to lower gH in an aquarium. Regular tap water often has a fairly high overall hardness. To accommodate fish and plants that prefer soft water environments, the parameter must be seriously reduced.
Recommendations for those who are planning to reduce the water hardness gH in the aquarium:
Make sure there is no coral sand or limestone in the bowl.
Some soils and aquarium decorative elements contain components that increase liquid hardness. Inert stones and gravel should not contain lime.
The best way is to use reverse osmosis filtered water to fill containers with live plants and fish.
This is the most effective method of reducing the overall water hardness in an aquarium. As a result of cleaning, the liquid from the tap is deprived of minerals, chlorine, phosphates and nitrates.
Pour settled water into the aquarium and do this regularly.
The solution is suitable if the aquarium liquid has high hardness, as a result of water evaporation - the water evaporates, the salts remain, while tap water has a lower hardness. It is necessary to add settled water systematically. You can also use distilled water as a replacement.
Water softeners.
Water change can also be filtered by passing through peat or boiling (for one hour and then allowing it to sit for at least one day).
There are natural softeners - plants that actively consume dissolved salts from water: vallisneria, nayas, hornwort, elodea (fast-growing plants).
Special preparations for water softening, look here.
Important! Not the best way to reduce water hardness gH in an aquarium is to replace the aqueous medium of the bowl with rainwater. Every drop of rain can now be filled with a huge amount of impurities dangerous for any fish and plants.
To summarize: the overall hardness of water gH can be reduced using clean, settled or distilled water free of impurities and turbidity, an osmotic RO filter, and special preparations.
How to increase the overall hardness gH of water in an aquarium?
Finding out how to increase the overall water hardness in an aquarium will also be useful for every aquarist planning to keep African cichlids or rainbowfish. In some regions of the Russian Federation, tap water has low mineralization.
Signs indicating the need to increase the water hardness gH in the aquarium:
Holes appeared in the snail shells; The appearance of crustaceans and invertebrates has deteriorated; the inhabitants cannot “molt” normally.
Separately, let’s say that high rigidity may be required not only by the fauna listed above, but also by fish.
Several options for increasing water hardness gH in an aquarium:
Use of special fillers for external filter or soil.
This method can increase not only gH, but also carbonate hardness (alkalinity) in aquarium water. Coral chips and marble chips can be used as fillers - they both contain the necessary magnesium and calcium carbonates.
The solution has one significant drawback: it will not be possible to understand in advance to what level you will increase the water hardness. On the other hand, you can carry out the tests that we talked about just above.
The advantage of the method is that the level of rigidity set by the soil and fillers slowly increases and then remains unchanged.
Mixing the aquarium aquatic environment with hard water sediment.
Boil hard water in an enamel saucepan for an hour. After this, leave it to cool. And then pour out about two-thirds without stirring up the sediment at the bottom. Your next goal is to pour the sediment, filled with the necessary minerals, into the bowl with the fish.
Use of shells and marble.
This decor will increase gH by approximately three to four degrees. One handful of marble chips will be enough for a small bowl. The solution has a drawback - uncontrollability. The hardness may rise to too high values. Therefore, do not rush to “fill” the aquarium with marble. Act gradually, taking measurements and observing the condition of flora and fauna.
Add baking soda or calcium carbonate to the aquarium.
The optimal ratio of components: per 50 liters of aqueous medium, one teaspoon of baking soda. A household product will also make it possible to increase hardness by about 4 degrees.
If you want to use calcium carbonate, you will need two teaspoons for the same amount of aquarium liquid. For the same purposes, you can purchase a 10% calcium chlorine solution (sold in pharmacies) and mix it with sodium sulfate. The ratio of components is one ml per liter of aqueous medium. chemical products.
Using magnesium solution.
For every liter of aquarium water, one ml is required. 25% magnesia solution. The procedure will increase the level of rigidity by four degrees.
How to reduce the carbonate hardness of water kH in an aquarium?
Let's move on to how to reduce the carbonate hardness of water in an aquarium:
Using reverse osmosis water.
Before removing kN from the aquarium, you will need to purchase a special reverse osmosis filter. You can buy it for 3-4 thousand rubles, but the cost varies widely. It is necessary to dilute the resulting water with tap water to the required carbonate hardness.
An important rule: clean water after treatment through a reverse osmosis filter should not be used to fill an aquarium. Since its gH and kH indicators will be zero. But you can use hard tap water - mix it with purified reverse osmosis liquid.
In addition, clean water passed through the filter can be remineralized with magnesium and calcium salts. For example, the mineral mixture “Remineral pH / kH Plus” - the composition in a sufficient proportion restores both carbonate and general hardness. In the absence of chlorine, which is dangerous for fastidious plants, the mixture will give the water the same salt components that are found in the natural aquatic environment.
Alternative professional solution.
Purchase of specialized aquarium products such as “kH Minus”. They will leave the overall hardness unchanged, but will lower the level of carbonate hardness.
Important! If the carbonate hardness is zero, pH fluctuations can be critical - this will lead to the death of the fish.
Freezing water.
A not very expensive way to lower kH in an aquarium. Place the water in the freezer and let 50% of it harden. Then pour out the liquid that has not yet frozen, and defrost the piece of ice. Pour the melted liquid into the aquarium bowl.
This is not only an affordable, but also a quick method of how to lower the kH of water in an aquarium. It takes about 12 hours to freeze 50% of the liquid in a one and a half liter plastic bottle. High kH in an aquarium can be reduced by half.
Boiling.
We mentioned this method only for general information. Since this is far from the most effective option on how to reduce kN in an aquarium. Basically, the total, and not the carbonate hardness we need, will drop.
How to increase kH in an aquarium?
If your problem is low kN in the aquarium, use dolomite chips. Along with coral chips, dolomite must be poured inside the filter. The advantage is an increase in the level of liquid hardness, the disadvantage is complicated cleaning of the filter element.
Limestone contains an impressive amount of calcium carbonate. Using a large piece of limestone, you can solve several problems at once - decorate the bowl with an element of “wild nature”, increase and maintain a high level of carbonate hardness.
You can raise kN using the following limestone rocks:
Aragonite; Travertine; Dolomite; Tuff; Oolite.
Which type should you prefer? In our case there is no difference. The number of pieces should be determined independently until the required water indicators are obtained.
If you can't get your hands on limestone, you probably have regular baking soda at home. For 100 liters of aquarium liquid, one teaspoon of powder is required. But you should prepare a “soda + water” solution in advance. Using the powder, the kN level can be raised by two degrees.
Important Safety Instructions
Be especially careful when increasing the hardness. While fish and plants can at least somehow cope with an excessively soft aquatic environment, an excessively hard liquid can simply kill them.
If you are sure that the parameters of the aquatic environment must be changed, do not rush. Make gH and kH changes very slowly. “Take a step,” look at the state of the inhabitants of the bowl. If the plants and fish are doing well, further adjustments to hardness may not be necessary.
For those who are afraid to use soda, chemicals, limestone and other rocks, we can recommend store-bought products. For example, the already mentioned Remineral allows you to increase the carbonate and general hardness of water. There are many other special formulations, the use of which can be obtained from pet store consultants.
How to increase water hardness in an aquarium
To increase the hardness in the aquarium, no complex manipulations are required. The most popular methods:
- Enrich the soil with marble chips and shells, measuring and increasing the hardness to the required parameters. Connecting filter systems allows you to regulate the flow of water that passes through the minerals.
- Place calcium carbonate in the reservoir. Two teaspoons per 50L will raise dH values by 4 notches.
- A 25% pharmaceutical preparation of magnesia at the rate of 1 ml per liter of liquid will raise dH by 4 notches.
To increase the saturation of magnesium and calcium sulfates and chlorides in the tank, the easiest way is to partially replace the aquarium water with a harder one.
Types of hardness
Hardness can be different, so to more accurately determine the values, it was divided into three main types.
General
Total is the sum of the values of constant and variable hardness, that is, the total indicator of calcium and magnesium salts.
Carbonate
Carbonate hardness in an aquarium, or temporary one, is determined by the presence, in addition to calcium and magnesium, of hydrocarbonate anions. Temporary hardness can be eliminated by boiling (in this case, hydrocarbonates will disintegrate into water, carbon dioxide and poorly soluble sediment), which is why it is called temporary.
When planning to keep fish, you should take into account the requirements for the conditions of a particular species - be it mollies, barbs, veiltails, clown fish, zebrafish, gourami, platies, astronotus, betta fish, lalius, ancistrus, parrotfish, surgeonfish, thornets.
Non-carbonate
Constant or non-carbonate hardness is due to the presence of compounds of alkaline earth metals with strong acids: sulfuric, hydrochloric, nitric and others, which do not decompose under the influence of high temperatures, but dissolve in water without forming scale.
How to reduce water hardness in an aquarium
Softening the water in an aquarium is a more labor-intensive process. Carry out one of the following procedures:
- Add rainwater to the fish tank. When collecting rainwater, its purity must be taken into account as much as possible. Do not collect water running off the roof.
- Add distillate. Buy ready-made or purchase special equipment to do it yourself.
- Boil the liquid, let it settle and pour the top layer into a home pond in which you want to make the water softer.
- Freeze the water in the refrigerator by 50%. The unfrozen part of the liquid is disposed of, the ice is melted and poured into the aquarium.
- Place peat purified by boiling in a bag into a filter container or use as a substrate for plants. To remove the yellow tint from water, add activated carbon to the filter.
- Hornwort, egrosaw, and elodea planted in the ground can soften the aquatic environment.
Sometimes aquarists use water where alder cones have been boiled to soften them. The method is extremely unsuccessful, because the decoction dramatically changes all other parameters of the water.
On a note! You can reduce the amount of dissolved minerals using EDTA or Trilon B, following the instructions.
How to prevent the indicator from being distorted again?
To prevent the water from becoming hard again, you need to monitor the indicators and periodically carry out the necessary measures:
- when using peat and special preparations, add them to the water every 2-3 days;
- when softening water with soda or soap, as well as by freezing or boiling, the hardness indicator will not increase if special plants are additionally planted or products are used;
- Filter cartridges or the filtrate in them must be changed regularly.