Any hydroponic solution, regardless of composition and origin, has two important indicators that the grower absolutely must be able to measure and control. The first indicator is the concentration of the solution
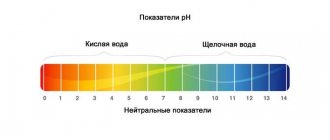
, i.e. the total density of substances dissolved in it. (The second indicator is pH, i.e. acid-base balance, which is the subject of the following essay).
Why is it necessary to measure and control the concentration of a nutrient solution?
• If the concentration of the solution is insufficient
, your plants will receive less nutrition and, as a result, grow slower and bear fruit worse;
• If the concentration is excessive
(for example, 2-3 times higher than normal), this can cause root and leaf burns, growth retardation, flower dropping, deformation and damage to leaves and fruits, diseases, etc. Young plants are especially vulnerable to overdose.
Therefore, knowing the concentration of your solution, you can correctly adjust its saturation and provide your plants with an optimal (i.e., consistent with their stage of development and species needs) nutrition regime.
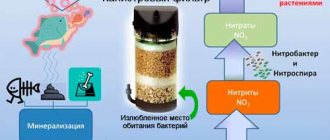
What affects water hardness in an aquarium?
In short, the overall stiffness of the GH can be ignored. It is enough that its value is not prohibitively high.
For fish, it doesn’t really matter what level of general GH hardness is in the aquarium.
All you have to do is make sure that it does not have prohibitive values.
For aquarium fish and plants, carbonate hardness KH and pH levels are more important.
These two parameters directly influence each other, and therefore they should be considered together.
The pH level parameter determines the acidity of the aquarium water, and the connection with the level of carbonate hardness KH is very simple.
Just remember not to plunge into the abyss of hydrochemistry.
Water with a carbonate hardness of more than 12 degrees of hardness will have an alkaline reaction.
Water of average carbonate hardness in the range of 8-12 degrees of hardness will be close to neutral with a pH level of approximately 8.
Water with a carbonate hardness of less than 6 will tend to be acidic.
What does this mean and how does it affect fish?
Excessive acidity of aquarium water, in other words, low pH level, can lead to damage to the body and eyes of the fish with subsequent damage to internal organs.
Excessively hard and alkaline water with a pH greater than 9 leads to an increase in the concentration of ammonium and ammonia in aquarium water.
Ammonium and ammonia cause severe poisoning in all inhabitants of the aquarium. Up to the death of all living things in the aquarium.
Also, excessively alkaline water causes burns and damage to the outer skin of the fish, making the fish more susceptible to infections.
The question arises, what hardness parameters should aquarium water have?
How is the concentration of a solution measured?
Concentration is measured using a device called an EC meter or TDS meter; sometimes manufacturers call them not “meter”, but “tester”. Despite the mysterious technical name, they are no more difficult to use than a regular medical thermometer and in their simplest form they look like this:
More advanced combined measuring instruments “4-in-1” or “5-in-1” are also sold, combining the functions of an EC and TDS meter, pH meter, thermometer and even a water salinity meter:
About Us
Stroitelnaya has been carrying out construction work in all regions of Russia for many years. During this time, we have accumulated vast experience and acquired reliable suppliers of building materials, machinery, and equipment. We employ only qualified specialists who are guaranteed to complete all necessary construction work with high quality and on time.
To complete our facilities, we use the most modern construction equipment from the world's best manufacturers. We approach each client individually and select exactly what best suits the customer’s wishes.
By choosing a construction company, you get a reliable partner, the result of joint cooperation with whom will delight you for many years.
At the same time, from us you can get professional advice on the design, configuration and construction of swimming pools, water parks, houses, cottages, baths, saunas, fountains.
If necessary, our specialists will visit the site of the proposed construction completely free of charge and make all the necessary measurements and calculations.
Construction offices are located in Moscow, St. Petersburg and Omsk. The full address and location of offices, as well as contact numbers, can be found on the official website of the construction company in the contacts section.
What is the difference between EC and TDS meters?
Both of these devices measure the same physical indicator - the electrical conductivity of a solution, i.e. its ability to conduct electric current, by which one can judge the concentration of salts in the solution. The difference between them is that they measure this indicator in different units:
• EC meter
(EC,
English
electrical conductivity) measures electrical conductivity in standard units - mS/cm (millisiemens per centimeter);
• TDS meter
(
English
Total dissolved solids, “total amount of dissolved solids”) first measures electrical conductivity, and then converts it to another unit of measurement -
ppm
(
English
parts per million, “parts per million”). For example, 200 ppm means that in a given solution, per million particles of water there are 200 particles of some substance capable of conducting current.
Notice the word “someone.” The thing is that the TDS meter really doesn’t have the slightest idea about the chemical composition of the substances in solution! It only shows the number of particles of an electrically conductive substance, but does not know what kind of substance it is. Therefore, controlling the composition of substances in the solution is the task of the grower himself.
Optimal water hardness in an aquarium
As we have already found out, it is impossible to talk about water hardness alone in isolation from its pH level.
The following water parameters can be recommended for any home aquarium.
The water should be of medium carbonate hardness 8-10 degrees hardness with a neutral pH level of 6-8.
These water parameters will be optimal for most aquarium fish.
Problems will arise only when breeding some fastidious spawning fish, which require water with different levels of hardness and acidity for spawning.
That's sorted out.
I'll move on to the next point.
Why is EC more practical than TDS/ppm?
EC is more practical because it is a standardized physical indicator that is understood in the same way all over the world
. That is why, having received a recommendation to bring your solution to EC 1.2, you clearly understand that this means 1.2 mS/cm (millisiemens per centimeter).
But when using a TDS meter, not everything is so simple, since this device uses a different unit of measurement - ppm (eng. parts per million
, "parts per million"). And, depending on where and for whom the device was manufactured, it can use one of three standards to convert from EC to ppm:
- The American standard
, promoted by measurement equipment manufacturers Hanna Instruments and Milwaukee, uses sodium chloride (NaCl) as a reference for conversion from EC to TDS. According to this standard:
1 EC = 500 ppm
- The European standard
, promoted by the manufacturer Eutech, uses potassium chloride (KCl) solution as a reference for conversion from EC to TDS. According to this standard:
1 EC = 640 ppm
- The Australian standard
, promoted by the New Zealand manufacturer Bluelab, for conversion from EC to TDS uses as a reference the average electrical conductivity of a solution of three salts present in drinking water (sodium sulfate, sodium bicarbonate, sodium chloride), taken in a 40/40/20 ratio. Therefore, according to this standard:
1 EC = 700 ppm
So, if you measure in EC, then the resulting values will be clear to anyone without further clarification. And if you use TDS, then when reading applied literature or exchanging data obtained using a TDS meter on a forum, you will have to clarify each time which of the three ppm standards you are talking about, which is unproductive and tedious.
How to change pH value
Water pH is an unstable indicator. When it is changed with the help of reagents, it returns to its previous level over a short period of time.
To maintain it at 7.0 and above, you can use marble or limestone as decoration or filter material. But keep in mind that this method increases water hardness.
You can add baking soda to the water. In this case, the pH value changes quickly and for a long time.
If it is necessary to make the pH below 7.0, then peat-based fillers are used. They are installed in the filter.
It is not recommended to lower or increase the pH value using special reagents, as this is financially expensive.
EC to TDS/ppm conversion table
| EC (mS/cm) | TDS American | TDS European | TDS Australian |
| EC 0.1 | 50 ppm | 64 ppm | 70 ppm |
| EC 0.2 | 100 ppm | 128 ppm | 140 ppm |
| EC 0.3 | 150 ppm | 192 ppm | 210 ppm |
| EC 0.4 | 200 ppm | 256 ppm | 280 ppm |
| EC 0.5 | 250 ppm | 320 ppm | 350 ppm |
| EC 0.6 | 300 ppm | 384 ppm | 420 ppm |
| EC 0.7 | 350 ppm | 448 ppm | 490 ppm |
| EC 0.8 | 400 ppm | 512 ppm | 560 ppm |
| EC 0.9 | 450 ppm | 576 ppm | 630 ppm |
| EC 1.0 | 500 ppm | 640 ppm | 700 ppm |
| EC 1.1 | 550 ppm | 704 ppm | 770 ppm |
| EC 1.2 | 600 ppm | 768 ppm | 840 ppm |
| EC 1.3 | 650 ppm | 832 ppm | 910 ppm |
| EC 1.4 | 700 ppm | 896 ppm | 980 ppm |
| EC 1.5 | 750 ppm | 960 ppm | 1050 ppm |
| EC 1.6 | 800 ppm | 1024 ppm | 1120 ppm |
| EC 1.7 | 850 ppm | 1088 ppm | 1190 ppm |
| EC 1.8 | 900 ppm | 1152 ppm | 1260 ppm |
| EC 1.9 | 950 ppm | 1216 ppm | 1330 ppm |
| EC 2.0 | 1000 ppm | 1280 ppm | 1400 ppm |
| EC 2.1 | 1050 ppm | 1334 ppm | 1470 ppm |
| EC 2.2 | 1100 ppm | 1408 ppm | 1540 ppm |
| EC 2.3 | 1150 ppm | 1472 ppm | 1610 ppm |
| EC 2.4 | 1200 ppm | 1536 ppm | 1680 ppm |
| EC 2.5 | 1250 ppm | 1600 ppm | 1750 ppm |
| EC 2.6 | 1300 ppm | 1664 ppm | 1820 ppm |
| EC 2.7 | 1350 ppm | 1728 ppm | 1890 ppm |
| EC 2.8 | 1400 ppm | 1792 ppm | 1960 ppm |
| EC 2.9 | 1450 ppm | 1856 ppm | 2030 ppm |
| EC 3.0 | 1500 ppm | 1920 ppm | 2100 ppm |
Chemical composition of water
Rigidity
In most cases, people can tell whether their tap water is hard or soft by the effects it produces in their home. In hard water, more soap is required to obtain foam than in soft water, and in addition, hard water causes the formation of plaque on the inner surface of plumbing parts and metal kettles. This plaque is mainly calcium carbonate (CaCO3). Water hardness is determined by the concentration of certain dissolved minerals, mainly calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) salts. In nature, they enter water as it flows through rocks and soil containing the corresponding minerals. Likewise, aquarium water can become harder if limestones and other decorative elements containing appropriate soluble mineral salts are used in the design. Water containing little or no such salts is called soft.
The ratio of hardness and mineral content
Hardness is an important parameter for the aquarist, but it is especially worth noting that it is determined only by the amount of certain dissolved minerals. There are other substances that contribute to the total mineral content, but do not affect water hardness, which is defined above and can be measured using special tests. Based on the same criterion, it can be said that although water purified from minerals (that is, with a minimum content of them) is soft, such water does not necessarily have to be completely devoid of minerals. It is very important to remember this because some water softening methods (see below) do not reduce mineral content, but simply convert the salts that make the water hard into other salts that do not affect the hardness.
The ability to distinguish between water parameters such as hardness and softness is necessary if you have to deal with some “difficult” species of fish that places high demands on the environment. An example is the special species of fish found in some rivers of the Amazon, where the water is surprisingly soft and contains almost no minerals. If you keep unpretentious fish, then in this case it is usually enough to take into account only the hardness of the water.
Measurement of hardness and mineral content
Kits for measuring water hardness can be purchased at pet stores. They can be used to test both tap water and aquarium water (for example, to determine whether aquarium design elements are affecting the water hardness). Kits from different companies designed to determine water hardness sometimes use different units of measurement - parts per million (ppm), as well as English, French and German degrees. Using the aquarium literature as a guide, which often provides examples of how hardness is determined in accordance with each of these systems, you can identify the system and relate the data given in the literature to the readings of your measuring set.
Aquarium measuring kits are not suitable for a complete comprehensive analysis of the chemical composition of water. You may be able to obtain such data for your local tap water from your water utility, or you may be able to submit a sample of the water to a laboratory for testing. The amount of mineral content can be accurately determined by measuring the ability of water to conduct electric current, i.e. its electrical conductivity. The higher the electrical conductivity, the higher the concentration of minerals. However, this method does not give an idea of what kind of mineral substances we are talking about. If the aquarist keeps fish for which mineral content is critical, then it is better to purchase a special device that measures electrical conductivity - it can be purchased where laboratory equipment is sold. Books that provide biotope data for aquarium fish usually also contain electrical conductivity measurements.
On a note:
Units of water hardness expressed in parts per million (ppm) of dissolved calcium salts*
1 English degree (Clark) = 14.3 ppm 1 German degree (dH)** = 17.9 ppm 1 American degree = 17.1 ppm 1 French degree (fh) = 10.0 ppm 1 ppm = 1 milligram per liter
* English, French and American degrees of hardness express the content of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), while German degrees indicate the content of calcium oxide (CaO).
**Nominally the designation "dH" applies only to German degrees of hardness, but in recent years it has become universally applicable. Water softening and demineralization
If the tap water where the aquarist lives is too hard or so low in mineral salts that it is unsuitable for the fish he wishes to keep, a number of measures can be taken:
How to use an EC or TDS meter?
Elementarily simple! I said that these devices are no more complicated than a thermometer, right? Now you will see this.
• Turn on your EC or TDS meter by pressing the ON/OFF button.
• Remove the cap protecting the electrodes and immerse them in the solution to a depth not exceeding the dotted line (see photo).
• The HOLD button is needed to freeze the measured value on the screen. This button is convenient to use in cases where measurements need to be carried out in a cramped and dark container (for example, in an opaque jar with a narrow neck), where the EC meter screen becomes inaccessible for direct viewing. To return your meter to continuous measurement mode, press the HOLD button again.
• The measured value displayed on the display indicates the concentration of salts in your solution. For a TDS meter it is displayed in ppm, for an EC meter it is displayed in millisiemens per centimeter (mS/cm) or microsiemens per centimeter (uS/cm).
• After measurement, rinse the electrodes in clean water and put on the protective cap.
Example:
the device in the photo above measured 298 ppm. Is the concentration of this solution high? Answer: for hydroponics - not especially. Because this is the amount of salts contained in ordinary tap drinking water of high hardness, which (surprise!) is poured into the bowl.
Redox potential of water
The oxidative process in an aquarium is the combination of nitrites with oxygen, and the reduction process is the breakdown of nitrites and the release of oxygen.
Options:
- rH 40-42 – maximum oxidation (pure oxygen)
- rH 35 – strong oxidation
- rH 30 – slight oxidation
- rH 25 – weak oxidation
- rH 20 – weak recovery
- rH 15 – slight recovery
- rH 10 – strong recovery
- rH 5-0 – maximum recovery (pure hydrogen)
Most fish and plants feel good at rH 25-35. There are species that like higher or lower rH. To measure the redox potential of water, special instruments are used. You can increase the parameter by changing the water, siphoning the soil and constantly blowing air.
The importance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the aquarium and the change in their quantity.
Water is a good solvent for many compounds, including the gases in the air: oxygen and carbon dioxide.
1.1. Oxygen O2 and its significance
The oxygen content in water depends on many factors: the depth of the tank, water temperature, the presence of plants and animals. Water that is in motion is usually better oxygenated than water that is standing. The dependence of temperature on the degree of oxygenation is inversely proportional - with increasing temperature, the saturation of water with oxygen decreases. The water in the aquarium is saturated with oxygen primarily from the air. If it remains motionless, only its upper layers are saturated with oxygen. An additional oxygen producer is the healthy plants we grow. Recipients of oxygen are fish and other aquarium animals, microorganisms living in water (mainly in the substrate, in the filter) and at night (in the dark), as well as in plants. Hence the need for additional ventilation at night (setting the water in motion). In a well-oxygenated aquarium, oxygen decomposes organic pollutants and oxidizes organic compounds (proteins, carbohydrates or fats) into simple compounds that are easily digestible by fish and plants. Anaerobic decomposition processes (lack of oxygen in the aquarium) lead to the formation of toxic substances harmful to the aquarium inhabitants (for example, hydrogen sulfide, organic acids, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons), which cause, among other things, an unpleasant odor.
To increase the amount of oxygen in the aquarium, you need to install an additional filter or aerator, replace it with a new one, or introduce more plants into the aquarium.
1.2. Carbon dioxide CO 2 and its significance
During the day, carbon dioxide is released by fish and other aquatic animals, occurs during the decomposition of organic compounds, and at night is also released by plants. An excess of this gas in the water is promoted by an aquarium with few plants, insufficient ventilation and excessive fertilization of the substrate. An excessive number of plants in relation to fish in an aquarium is also not recommended - during the day this leads to a deficiency of carbon dioxide and oxygen at night. This is also the cause of biological decalcification of water (plants extract carbon dioxide from calcium bicarbonates and calcium carbonates). Only an aquarium maintains a biological balance (number of fish in relation to plants, optimal temperature, pH, water hardness, amount of light, systematic cleaning and replacement of water, appropriate filters and aerators, loose substrate) is able to function effectively for the benefit of our fish and plants. It should also be mentioned that excess carbon dioxide can cause a decrease in pH. If we exaggerate the amount of this gas when supplied to the aquarium (above 50 mg/litre) then the pH may drop to a level where the fish may begin to die. I will give here some examples of the dependence of the pH value on the amount of carbon dioxide dissolved in water:
| Carbonate hardness kH [° dKH] | Amount of carbon dioxide in water | ||
| more than 50 mg/liter | about 30 mg/liter | less than 15 mg/liter | |
| 2 | pH 6.1 | pH 6.4 | pH 6.7 |
| 5 | pH 6.4 | pH 6.7 | pH 7.1 |
| 10 | pH 6.7 | pH 7.1 | pH 7.4 |
| 20 | pH 6.9 | pH 7.4 | pH 7.7 |
The most recommended dose of carbon dioxide is 20-30 mg/l and must be maintained to ensure plant growth. It is also important that the amount of light is within 0.5 W so that plants can use CO 2 in the process of photosynthesis.
What is a measuring device and how to use it?
As a rule, this is a compact analyzer of a convenient shape with a display for displaying readings and buttons for turning on and off and recording readings. These options are located on the front panel of the TDS meter.
At the bottom of the device, under a protective cap, there are two electrodes that must be immersed in water to collect the required readings.
On the back of the analyzer there is a fixing clip and a calibration screw.
There is a built-in battery compartment at the top of the device. The TDS meter runs on two LR44 batteries.
The device is quite easy to use.
Having turned on the device by pressing the “on” button, we look at the display, where the control value “000” is shown. We lower the device with the electrodes into the liquid/water and wait for a summary of the calculated value. The indication indicator (assessment of condition and quality) is three-segment and if the value is greater than 999, then the designation X10 will be displayed below. According to sanitary and hygienic standards, the permissible standard for water hardness concentration should not exceed 350 ppm.
Below are the purity values for the hardness of tap water:
• 50 ppm – impeccable purity, suitable for drinking and cooking;
• 170 ppm – water after carbon filtration, so to speak, acceptable;
• 300 ppm – hard water with limited use;
• 400ppm – unsuitable water with high hardness and the presence of foreign impurities;
• 500 ppm – water of increased hardness is not suitable for eating or drinking, so-called “technical” water.
The temperature of the water measured by the TDS meter is not significant and does not in any way affect the measurement characteristics of the water.