What is pH
Hydrogen index or pH is a value that denotes the logarithm of the concentration of hydrogen ions with a negative sign. To put it simply, the hydrogen index is the number of moles per liter of hydrogen ions. The pH value depends on the number of moles, which means the pH level drops, because. the number of moles of ions decreases and the pH level increases as the number of moles increases.
A low pH level in an aquarium means there is a high concentration of hydrogen ions, and a high level occurs when there is an excess of hydroxide ions, causing the water to become alkaline.
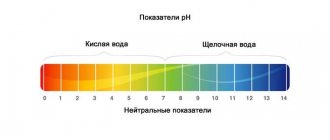
pH scale
The pH of water in an aquarium ranges from 0 to 14.
| Name | Acidity |
| Strongly acidic | 0–2 |
| Sour | 3–5 |
| Slightly acidic | 5–6,5 |
| Neutral | 6,6–7,5 |
| Slightly alkaline | 7,6–8,5 |
| Alkaline | 8,6–10 |
| Highly alkaline | 10–14 |
Carbonate hardness kh
Carbonate hardness is a measure of the hardness of a liquid, determined by the amount of carbonate anions, calcium and magnesium carbonates dissolved in water. The relationship between pH and kh is direct and close, because the carbon dioxide indicator depends on it. Carbon dioxide accumulates and causes fish diseases. If there is insufficient aeration or overcrowding, the concentration of carbon dioxide becomes dangerous for fish. The carbon dioxide rate is 2–3.5 mg/l.
How to test the pH of tap water?
Many aquarists immediately test their tap water for pH. However, these are not entirely accurate readings. To correctly measure the pH of tap water, you need to pour tap water into a container and place a spray bottle in it to stir it for 24 hours. After this you can take measurements. It would be a good idea to take a second reading 48 hours later to see if there are any further changes. These values, measured after 24-48 hours, are an accurate indicator of the pH of tap water. The sprayer is installed with tap water in order to mix it and cause gas exchange on the surface of the water. This exchange reduces the amount of carbon dioxide in your water and causes the pH to rise. This pH will actually be the one you will measure in your aquarium.
Tip: First calibrate your pH meter
Many beginners in the aquarium hobby often make the mistake of buying a pH test and immediately measuring it. If you bought a controller or electronic pH meter, do not rush, calibrate it before use. If calibration powders or solutions are not included in the package, you need to purchase them. Remember, the first step is to examine the test set you are using to see if it is accurate or not.
Most droplet tests have a life of their own (usually 6 months). If your test kit is older than its expiration date, it may provide inaccurate results.
ph meter
What is the normal pH of water
The normal pH value is considered to be the approximate indicator of fish blood acidity (7–7.5). Approximately this indicator corresponds to the pH of a pure liquid without impurities.
Freshwater aquarium
In freshwater aquariums, some parameter is changed gradually. To do this, part of the fresh liquid is poured into a separate tank and allowed to brew for some time. If fresh water has low acidity, then baking soda is added to the liquid, which is thoroughly stirred and settled in advance.
To oxidize aquarium liquid, orthophosphoric or hydrochloric acid is used in small doses.
Seawater aquarium
For marine life, the pH level of aquarium water is important and even small deviations will lead to disruption of the normal condition of the fish. The optimal pH is 8.2. A change in pH not only directly affects fish organisms, but also indirectly. When alkalinity decreases, calcification occurs, inhibiting the construction of the skeleton.
Alkalinity is increased using a calcium reagent along with carbon dioxide.
The influence of pH on vegetation and aquarium inhabitants
Effect of pH on Vegetation
Acceptable indicators of the active reaction of water for hydrobionts and plants are in the range from 5 to 9.5 units. Exceeding the specified data means death. But the optimal limits are considered to be 6-8 for fish and 6.8-7.2 for plants. Specific numbers depend on the type of inhabitants and plants. Moreover, fish can adapt to the acidity of the water, but will not tolerate its instability. This applies to the artificially created environment. In natural bodies of water, there are aquatic organisms that can live well outside this range.
In a closed biosystem of an aquarium, all elements are interconnected with each other. The number of fish and other inhabitants, the density of planted plants, and the operation of equipment affect the properties of water. Most often, this influence leads to souring. When this process is slow, fish and plants adapt to hydrochemical changes, but a sharp jump ends in death.
In aquariums where there is no soil or plants, the oxidation process occurs much faster than in tanks with vegetation. Over the course of a week, the pH value can drop by 1 point.
A decrease in the pH level leads to the following consequences:
- the digestibility of food deteriorates, causing the fish to increase their appetite;
- signs of suffocation appear;
- movements become monotonous or jerky;
- plant growth slows down;
- leaves fall;
- the activity of nitrifying bacteria fades away.
The following signs indicate an increased pH level:
- the fish are lethargic and get stuck in the thickets;
- coordination of movements is impaired.
When moving fish, for example when purchasing, from one aquarium to another, an important point should be taken into account: the fish adapts more easily if it changes hard and alkaline water to soft and acidic.
The immunity of aquatic organisms living in conditions with elevated pH and pH values is stronger than that of those living in an acidic environment.
For the above reasons, control of the pH level must be constant. pH levels are measured using aquarium tests. Drip tests provide more accurate results. They can be selected for each parameter. The required amount of indicator (indicated in the instructions) is added to the test water and the resulting color of the liquid is compared with the attached color scale.
In addition, they produce special devices - electronic pH meters, powered by batteries in the range of 0-14 and having an error of +/-0.1 pH.
pH controller
In aquariums with rich vegetation and powerful lighting, which require a CO2 supply, experienced aquarists actively use a drop checker. This device maintains the pH level by varying the supply of carbon dioxide. It is also called a long-term test. It is a small vessel with water and indicator liquid. Carbon dioxide penetrates the indicator liquid and changes its color, by which the pH level is determined. It should be taken into account that real values appear only 1.5 hours after the test starts.
Dropchecker
A drop checker on aquarium water informs about a sharp drop or increase to critical pH levels. But there is a developed so-called standard solution in which the KH level is 4.0. Such a device monitors not only the exact pH level, but also the CO2 concentration, regardless of carbonate hardness.
Ways to increase pH
A simple way to increase the acidity of water is to add rocks and gravel to the bottom, which raise the pH value. Typically, such stones are recommended for tropical inhabitants.
The photosynthesis process also raises the pH level. If a lot of light enters the aquarium and a large number of plants are planted, the acidity level quickly increases. But it is better not to choose photosynthesis when it is necessary to increase the pH in the aquarium, because this process is not easy to control.
Raising acidity levels with aragonite is much easier. This mineral is rich in calcium and will begin to dissolve at a pH level of 7.8.
Coral sand also increases the pH value, but it dissolves at pH=8.
Why is pH important for your aquarium?
Maintaining a constant pH can greatly affect the water in your aquarium. For example, if your pH drops below 6, the bacteria that hold ammonia and nitrites in the aquarium (toxic compounds to fish) begin to die off.
If you do not maintain a constant pH level, the ammonia level in your aquarium will fluctuate. Total ammonia is a combination of ammonium (NH4+) and ammonia (NH3) ions. The pH value of the water used is a major factor in the relative concentrations of these two compounds. More ammonia (the more toxic of the two compounds) will be present in alkaline water, while more ammonium ions (the less toxic of the two compounds) will be present in acidic water. In any case, after the cycle is completed, there should be no ammonia left in your aquarium.
Ways to lower pH
Natural peat will help lower the pH of the water in the aquarium, but only dark brown peat is suitable. Boil in clean water before adding.
Phosphoric acid, which is often included in commercial products for maintaining acid-base balance, is good at lowering pH.
More popular ways to reduce the pH of water are the use of oak bark or alder inflorescences. They are boiled and pH tests are performed frequently to ensure that the pH in the aquarium does not drop too low.
You can also lower the pH by using peat crumbs or placing driftwood at the bottom.
Take a look at this post on Instagram
Additions, expansions Pavel (@cihlids) 14 Tra 2021 r. about 11:04 PDT
How to raise the pH in an aquarium?
There are certain steps you can take to raise the pH level in your aquarium:
- Substitutions. If you do not change your aquarium water, the pH in your aquarium will decrease. The most effective method to bring it back up to tap water level is to make regular changes. Siphoning the soil will also help counteract the tendency of the pH to decrease over time.
- Rocks – Add rocks or driftwood to your aquarium to raise the pH. Crushed coral is used as a substrate in many African cichlid aquariums (African cichlids prefer a high pH). Limestone and fossilized corals also help raise the pH.
- Aeration - Increasing the oxygen concentration in your water will serve to reduce the CO2 concentration, lowering the pH. The less carbon dioxide, the higher the pH. Thus, you can increase the aeration in the aquarium to increase the pH.
- Baking Soda - Adding baking soda will also increase the pH, but if you add baking soda once and just forget about it, there will be no effect. You must add baking soda to your aquarium constantly. You also need to be careful not to add too much at once as... this will cause the pH to spike and can kill your fish. The pH level should change gradually, in any direction. The general rule is 1 dissolved teaspoon of soda per 20 liters of water. Results measured by device or tests
Water pH measurement
Checking the pH of the water is a must to ensure healthy fish life. These tests are especially helpful when checking tap liquid, because it often does not meet safety standards.
Basic ways to measure pH:
- Litmus paper. These test strips detect acidity/alkalinity by changing color. In an acidic environment, litmus paper turns red, and in an alkaline environment, it turns blue.
- pH meter. Used in situations where it is important to more accurately determine the pH of water.
Phosphorus
Availability of Phosphorus ions for plants depending on pH value
The most important macronutrient, which plants need in relatively large quantities, is phosphorus. This element takes an active part in the processes of storing and spending energy and, accordingly, in the synthesis of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, enzymes, as well as in the processes of respiration and plant nutrition. Let me remind readers of only one well-known fact: phosphorus is the main part of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the main energy substance of a living organism. Phosphorus accumulates in the greatest quantities in young shoots of plants.
Signs of phosphorus starvation are darkening of the color of young leaves, curling of leaves and shoots, and the appearance of brown and reddish-brown spots on old leaves.
Calcium, potassium and magnesium salts of orthophosphoric acid are most often used as phosphorus fertilizers. The most widely used calcium salt of this acid is superphosphate (Ca(H2P04)2 x H2O).
It is quite difficult to determine by external signs that the plants in the aquarium lack phosphorus. Therefore, when signs of a lack of minerals appear, complex fertilizers, which also contain phosphorus, are added to the water.
Molybdenum
Availability of Molybdenum ions for plants depends on pH value
A trace element that also affects plant metabolism is molybdenum. Its main function is nitrogen fixation in plant tissues, normalization of phosphorus nutrition and carbohydrate metabolism. Molybdenum is involved in many redox reactions occurring in the plant body. In molybdenum aquarium conditions, hunger, as a rule, is not observed. A lack of molybdenum in water can only be detected using chemical analysis. It should be noted that all complex mineral fertilizers produced by industry contain molybdenum. A slight addition of such fertilizers to the aquarium water can compensate for the lack of this element.
It should be noted that preparing fertilizers for aquarium plants is a complex task; it is necessary to maintain a certain order of dissolution of individual components, add substances that promote good absorption of microelements by plants. Therefore, we recommend that aquarists who are interested in growing aquatic plants use special fertilizers.
Magnesium
Availability of Magnesium ions for plants depends on pH value
Magnesium, like calcium, is a macronutrient. This element plays a significant role in metabolism, especially in young plant organs. Its deficiency in water is much more common than calcium deficiency.
The presence of magnesium ions, as already indicated, affects the degree of water hardness. But hardness in artificial reservoirs and aquariums is often increased by adding only calcium salts to the water. In this case, plants may experience magnesium starvation, which is expressed in the appearance of white spots between the veins of the leaf and the subsequent disintegration of the tissues of the leaf blade. Therefore, once again I would like to remind lovers of aquatic plants that when artificially increasing water hardness, they should definitely use a combination of magnesium and calcium salts.