From this article you will learn:
- What is water hardness
- Why is it necessary to determine water hardness?
- How to determine water hardness at home
- How to determine water hardness using special means
- How to soften hard water
In recent years, we have been increasingly told about the effect of hard water on the body and its harmful effects on household appliances. Where does this water come from, and why is it called hard? From a scientific point of view, the level of hardness is determined by the concentration of magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca) ions. The less of them there is in a liquid, the softer and healthier it is. Then a reasonable question arises: how to determine water hardness?
What does water hardness mean?
The most important property of tap water is hardness. This quality is imparted to it by calcium and magnesium salts, called hardness salts. The fewer of these inclusions, the softer the water will be. A unified measure of hardness on a global scale has not yet been established.
According to the state standard GOST 31865-2012, the measure of hardness in the Russian Federation is a degree (º F) equal to 1 mg-eq/l (equal to the calcium or magnesium content at a concentration of ½ millimole per liter).
In order to correlate the degree measures of different countries, the unit propromille (ppm – part per million) was adopted as a conventional unit, i.e. part per million (1·10−6) of the base mass: 1ppm=0.0001% (1 mg/kg).
As for household appliances, their indicators are usually indicated in manufacturer's units. To compare these characteristics with the standards established in our country, they are converted into Russian units of measurement.
Conversion of degrees of hardness to ppm:
- 1 dH (Germany) = 17.8 ppm;
- 1 f (France) = 10 ppm;
- 1 (England) = 14.3 ppm;
- 1 A (US) = 1 ppm;
- 1 mEq/l (1ºZh, Russia) = 50.05 ppm.
Three types of hardness are known:
- Temporary (or carbonate), which shows the content of carbonic acid salts (Ca and Mg bicarbonates). At boiling point they disintegrate, creating an insoluble precipitate of CaCO3 (calcium carbonate) and Mg(OH)2 (magnesium hydroxide).
- Permanent (or non-carbonate), which does not dissolve when boiled. In this case, water contains metal salts with valency 2 (Ca, Mg, Ba, Sr), based on strong acids: HCl (hydrochloric), H2SO4 (sulfuric), HNO3 (nitric). When establishing the level of water hardness, strontium (S) and barium (Ba) salts are not taken into account, since their quantities are minimal;
- Total, which is calculated as the sum of the concentration of magnesium and calcium ions in water.
In our country, water is grouped according to the degree of overall hardness:
- soft – up to 2°F;
- average – 2-10 10°F;
- hard – from 10°F.
You may also be interested in: Drinking water analysis: from taking samples to deciphering the results
What methods of determining the degree of hardness are used in everyday life?
If it is not possible to send a water sample for analysis, you can try to determine on your own whether the water is coming from your tap. The following methods are suitable for this:
- Pay attention to scale in the kettle. If, after boiling water, scale forms on the walls of the kettle, and over time it becomes more and more, this indicates that the amount of calcium and magnesium salts is clearly exceeded, therefore, the water is hard.
- Carry out the following experiment: apply a few drops of rain, boiled and unboiled tap water to the glass. When the drops dry, we can conclude that they are hard. Rainwater is very soft, as it contains practically no calcium and magnesium salts. The sediment after evaporation of unboiled water will give an idea of the overall hardness, and the sediment obtained after evaporation of boiled water will allow us to draw a conclusion about temporary hardness. If after the water evaporates there are no stains left on the glass, then the water is clean and closer to soft.
- Use soap to assess the level of hardness. It is known that soap does not lather well in hard water. If you soap your hands after soaking them in water and cannot achieve foam, then the water is very hard. If foam appears easily, then the water is not considered very hard. When good foam has formed, but it is not washed off with water, the water is considered soft. To determine the level of hardness using soap, you can purchase special test water, the packaging of which will indicate the degree of hardness. For example, you can buy soft and very hard water, and also take tap water for testing. You will need to place a small amount of soap into these liquids and lather. Then look at the resulting foam and measure its height in centimeters. For example, the foam height in soft water with a hardness of 1 mEq/l will be 10 cm, in hard water with a hardness of 15 mEq/l - 1 cm, and in your sample - 5 cm, then the hardness after calculations will be approximately 8 mEq/ l. But this is only an approximate calculation that will give a general idea of the level of hardness of the water that flows from the water supply.
- Do another experiment using soap and warm water. For it you will need distilled water, laundry soap, scales, a ruler, a cylindrical glass, and a transparent liter jar. To perform the experiment, you need to measure out 1g of soap and grind it, then put it in a glass. Heat distilled water, but do not boil, after which it must be carefully poured into a glass with soap shavings. The soap will dissolve. Then you need to add more distilled water to the glass. If 60% soap is used, then you need to add up to a total liquid height of 6cm, and if 72% - then up to 7cm. In each centimeter layer of the solution, an amount of soap is obtained that is sufficient to bind all hardness salts in one liter of water, if their concentration is 1 ° dH (you can convert the degree to mEq/l using a special table). After these steps, you need to pour 0.5 liters of tap water into the jar. Next, pour the soap solution from the glass into the jar, stirring until white foam becomes visible in the jar. Its appearance will indicate that the soap has bound calcium and magnesium salts. After this, you need to measure the height of the soap solution remaining in the glass and subtract it from the original height. Each centimeter of the solution sent to the jar bound hardness salts in 0.5 liters of tap water, the amount of which corresponds to 2°dH. If 2 cm of soap was poured into the jar and foam appeared in the water, then the hardness of the water being tested is 4°dH. This will be approximately 1.5 mEq/L.
- Determine the level of water hardness by taste properties. Hardness salts present in water change its taste. Soft and hard water taste very different. Therefore, the whole family can conduct an experiment at home, studying the taste characteristics of water of varying degrees of hardness. To do this, you need to purchase soft and hard water from the store. Then pour purchased water and tap water into a glass for tasting. This option will help you roughly determine which option your home water is closer to—hard or soft water that was purchased in a store.
- Determine the degree of hardness using reagents, which can be purchased in stores offering products for aquariums. Depending on the manufacturer, tests using reagents differ somewhat, but in general, one should follow the same scheme. You must first pour the required amount of water into the container, add a certain amount of solution 1 and solution 2, add drops of solution 3 until the color changes from reddish to purple. Next, you will need to count the number of drops and use the formula to find out the hardness of the water. Test strips for determining hardness can be used as reagents. To find out the level of hardness, you need to apply a reagent to the paper, which will replace the water upon contact with water. The strip must be immersed in water and monitor the intensity of its coloring, which will be related to the concentration of substances in the liquid. This method has low accuracy, since it is difficult to interpret the results by determining “by eye” the intensity of water coloring.
Often, in order to find out the level of hardness, a TDS meter is used - a device that measures the electrical conductivity of water. But this indicator is influenced not only by the presence of calcium and magnesium salts, but also by other parameters, which can cause some difficulties in measuring the level of water hardness. Therefore, it is better to use this device by professionals who can give the correct answer regarding the degree of hardness of tap water in your home.
Why is it necessary to determine water hardness?
Excessively hard or very soft water poses a danger to household appliances and our health. The latter helps remove calcium from the body, which weakens the structure of bones and teeth. In soft water, corrosion of metal parts of household appliances accelerates, to prevent which an inhibitor is used.
What harm does hard water cause?
- Creates an increased salt load on the human genitourinary organs. As a result, kidney stones form, skin and hair deteriorate, problems arise in plumbing and heating systems, and irreparable damage is caused to household appliances.
- More energy is required to heat water, since scale (precipitates of hardness salts) on heating elements has low thermal conductivity. Therefore, heating elements tend to burn out due to poor heat dissipation.
- It is necessary to use additional portions of detergents because surfactants (surfactants) in their composition form insoluble compounds with calcium and magnesium salts, which prevents the creation of a sufficient volume of foam to remove stains.
- The inner surface of the pipelines quickly becomes covered with limescale, which reduces the water pressure, and the pipes have to be replaced.
Do not forget to determine the hardness of water obtained from a tap or other source. To significantly extend the life of your heaters, dishwasher and washing machine, use affordable water softeners.
Before purchasing expensive devices and reagents, find out what salts and how much the water from your tap contains. It should be noted that the general hardness parameter is not constant and is determined by the amount of precipitation, snow melting and other natural phenomena that change the density of salts. To select the right softeners, do a preliminary water hardness test.
For everyday use (water procedures, cleaning, washing), it is enough to determine this indicator once and, if necessary, buy the necessary products. With increased hardness, it is better to use high-quality bottled water for cooking and from time to time check its condition with a simple portable device for the total content of salts and carbonates.
The influence of water hardness, regulatory requirements and recommendations
What kind of water can be used for cooking and drinking? Liquid hardness requirements depend on local conditions. Please note that too hard water has a bitter taste and negatively affects the functioning of the digestive system. WHO does not give specific figures, although studies on the connection between water quality and diseases of the heart, blood vessels and other organs of the body have been carried out repeatedly. Too soft water is also bad, since it disrupts the water-salt balance. A liquid with a hardness of 4 mg-equiv/ is fraught - the main cause of scale formation on the internal parts of heating systems. It is also harmful to skin and hair.
6 more options for determining water quality at home
How to determine water hardness at home? There are six simple methods:
- The most accessible way is to evaluate the quality of water by appearance and taste. It should be transparent, odorless and sediment-free.
- To determine the purity of a liquid, it is poured into a washed transparent glass to a height of 20 cm and placed on a sheet of paper with text. If it is read through water, this indicator is normal.
- The color of the water is determined in the same way, but only 100 ml is poured and the glass is placed on a clean white sheet. If water has organic impurities, then it darkens on paper.
- The purity of a liquid can be determined by its smell. First, the water is heated to 20 °C, then brought to 60 °C. The appearance of a putrid odor indicates the content of hydrogen sulfide in the water.
- Individual properties of the liquid can be determined by taste. A little water is poured into a clean container and boiled for 5 minutes. Then cool to 20 – 25 °C and taste. A sweetish taste indicates the presence of gypsum inclusions, a bitter taste indicates the presence of magnesium salts, and iron salts add a slight tartness to water. The putrid tint is caused by the content of animal and plant organic matter in the water. If you filter it, you can find solid impurities. However, before this, the water is allowed to settle for some time.
- If you drop water on a mirror or glass and let it evaporate, you can also evaluate the degree of its purity. The presence of stains indicates poor water quality. Look into your aquarium, whoever has one. Fish, as a rule, react subtly to water quality.
Methods for eliminating hardness
To combat excessive salt content, the following methods are used:
- Boiling completely eliminates temporary hardness. This process is accompanied by abundant sedimentation on the bottom and walls of the tank where boiling occurs.
- Chemically - you can reduce the amount of salts using slaked lime. If soda is added to lime, you can get rid of constant hardness.
- Freezing - this method makes it easy to deal with constant hardness. To soften water, it is enough to freeze it to a state where it is no more than 10% water, but 90% ice. Then the unfrozen liquid is drained, and the solid water is melted and used for its intended purpose.
- Distillation - all salts are non-volatile substances, so it is enough to first turn water into steam using heat and then condense it.
- Electromagnetic method - an electromagnetic field is used to soften the liquid. This method of reducing salts in water is most often used in boiler installations.
- Cation exchange is a highly effective method of purifying water from excess salts. Purification occurs by passing water through a layer of cation exchanger.
Any of the proposed methods of water softening can cope with a high level of this indicator, but a chemical method is usually not used to remove salts from drinking water.
How does hardness affect water quality?
The hardness of drinking water primarily affects its taste. The taste threshold for calcium ions in drinking water is 2-6 mEq/l. The taste threshold for magnesium ions is much lower, so the most pleasant-tasting drinking water is considered to be the one in which this indicator is from 1.6 to 3 mEq/l.
In some cases, water with a hardness of up to 10 mEq/L can be used as drinking water, but long-term use can negatively affect human health. Too hard water is undesirable for use in liquid heating devices . Electric kettles, boilers, washing machines and dishwashers necessarily have a heating element in their design, which quickly becomes overgrown with deposits, and the process of heating the liquid is less efficient.
Long-term operation of an electric heater with a significant layer of scale leads to overheating of the element and its failure. Fortunately, to descale it, it is enough to dissolve 2 bags of citric acid in 1 liter of water and thoroughly boil the kettle or any other water heater. Then you should thoroughly rinse the device and use it further for its intended purpose.
How to determine water hardness at home using soap
The high salt content of water also negatively affects the washing process. Dissolving detergent in water rich in potassium and magnesium ions leads to excessive foam formation. Foam contributes to the formation of plaque on the elements of the washing machine, which can also negatively affect the performance of some components of this household appliance.
Consequences for human health
With prolonged use of hard water in the human body, serious deviations from the norm are observed, which primarily manifest themselves in the functioning of the following organs:
- Gastrointestinal tract (GIT) - when the salts contained in hard water combine with animal fats, salts of fatty acids are formed, which envelop the walls of the stomach and intestines, preventing normal fermentation and significantly inhibiting peristalsis. As a result, harmful substances and waste accumulate in the body, and dysbiosis develops.
- The work of joints - some types of salts entering the human body form inorganic substances, which over time displace synovial fluid from the joints. As a result of this replacement, the joints become overgrown with crystals, which cause severe pain when moving. Long-term consumption of hard water can lead to arthritis and polyarthritis.
- Cardiovascular system - with a significant increase in the hardness of drinking water, heart function worsens, up to the manifestation of severe arrhythmia.
- Condition of the skin - hard water leads to premature aging of the skin. Negative effects are observed both when ingesting liquid and when washing dishes. When dishwashing detergent comes into contact with hard water, a film is formed, which, when deposited on the skin, has a negative effect on the upper layers of the epidermis for a long time.
- The formation of kidney stones - this statement is a myth that has been debunked thanks to the work of scientists. The process of stone formation does not depend on the quality of drinking water. Kidney stones are formed mainly due to a lack of calcium in the body. As a result of a deficiency of this element, it is washed out of the bones and deposited in the urinary system.
GH, water hardness, water hardness measurement, hard water quality in aquarium, hard water, water
All of the listed ailments and painful conditions can be avoided if you use multi-stage water filtration. The use of such devices will not cost too much, but the treatment of various pathologies can cost significant amounts of money.
Methods for determining water hardness
To avoid the negative effects of hard water on health, as well as to extend the life of heating devices, it is necessary to determine the approximate amount of potassium and magnesium salts dissolved in the liquid. Doing this by taste is quite problematic, because changes can only be detected in this way if a certain value is exceeded.
To determine high levels of potassium, magnesium and sodium salts at home, you can use the following methods:
- Try to dissolve the soap in water; if foam does not form, then the water is very hard and should not be used.
- If a large amount of scale forms in a kettle and other appliances over a short period of time, then the water definitely exceeds the safe values for this value.
- Using indicator strips, you can more accurately determine the amount of salts in a liquid, but this method will require small financial expenses. To carry out the experiment, it is enough to immerse the indicator strip in water for a few seconds, and after a minute compare its color with the table in the instructions.
GH, water hardness, water hardness measurement, hard water quality in aquarium, hard water, water
Conclusion
It is very important to know what hardness the water is used for drinking, as well as in heating boilers and other water heating devices. The need to use precise units of measurement to carry out calculations at home is not always necessary.
In the chemical industry and other high-tech industries, on the contrary, you will need to know the amount of salts dissolved in water up to a milligram, so you can use any units of measurement of this indicator proposed in this article to determine and, if necessary, reduce the amount of salts in water.
Review of Xiaomi Mi TDS Pen water tester (determining water quality, hardness)
How to determine permanent and temporary water hardness
Temporary water hardness, called carbonate hardness, occurs in almost every case. To accurately confirm its presence, special methods are used.
How to determine carbonate hardness of water:
- perform a chemical analysis for this indicator;
- use laboratory services;
- purchase a special test to determine hardness;
- contact specialists.
Temporary hardness of water occurs due to the content of calcium, iron and magnesium cations, as well as hydro- and bicarbonate (II) anions. This indicator is established as follows: when water is heated, bicarbonates decompose to form a slightly soluble carbonate precipitate, carbon dioxide and water.
To determine the constant hardness of water, you need to find the concentration of magnesium and calcium salts in it - phosphates, sulfates and chlorides, which are completely dissolved in water without sediment when boiling. They can be removed using ion exchange resin filters, electrodialysis or reverse osmosis. To calculate the total hardness of water, the coefficients of permanent and temporary hardness are added.
How to measure hardness
The following methods are used to assess water hardness:
- Complexometric titration with Trilon B. The method is complex and the most accurate.
- Purchased tests. Not 100% accurate, but simple and inexpensive.
- Electrical conductivity measurement. Use a conductivity meter.
- Using an ionometer and ion-selective electrodes.
- Using the method of titrating water samples with hydrochloric acid. A complex and not very accurate method. The same can be said about tests using laundry soap.
Titration means adding a reagent of the required concentration to water. The concentration of hardness salts is determined depending on the reaction of the reagent with water. Preparing the reagent is simple - just mix the acid with distilled water in the given proportions. The prepared solution is not dangerous.
The easiest way is to use ready-made texts. To do this, 5 ml of water is poured into a glass, then the contents of the dough are added dropwise to the liquid, after each drop the water is mixed. You need to do this until the color turns green instead of pink.
How to determine water hardness using special instruments and tests
Of course, any water must have optimal hardness, otherwise it will be harmful to humans due to the absolute absence of salts. Thus, with a minimum content of carbonate salts, diseases of the cardiovascular system occur.
In terms of heating tanks, soft water encourages corrosion. Therefore, in heat power engineering, after working on soft water, the surface of the equipment is treated with a special solution that slows down this process.
Water from any source has a certain hardness index. At the same time, it is good if it is average in size, because an excess of salts, like their lack, causes undesirable consequences.
How to determine water hardness? Today it is not difficult. You can buy special devices to monitor this indicator at work and at home. The most suitable option is the TDS-3 device, which is found on the shelves under different names.
You can use another, relatively cheap device - an electrolyzer , which also allows you to evaluate water hardness .
He will not be able to calculate the degree of hardness in numbers, but he will color the water a specific color, taking into account the salt content in it. By electrolysis, you can determine by the color of the water exactly what impurities are present in it.
The most accurate method for finding rigidity is laboratory. Submit the water for analysis, for example, to a sanitary and epidemiological station. There they will not only check the accumulation of hardness salts, but also measure the proportion of nitrates, pesticides, iron, hydrogen sulfide, organic impurities and other substances characteristic of groundwater. When choosing a treatment system for a cottage, water analysis is extremely necessary.
Test strips can be used to evaluate water hardness. They are offered in pet stores, coffee machine shops, and sometimes in large household appliance chains. This test will allow you to approximately determine the hardness of your water. The paper contains a reagent that changes color when it reacts with water. The strip is immersed in water for a short time, and the brightness of its color depends on the concentration of salts in the water.
The disadvantages of this method include inaccuracy and difficulty in interpreting test results. First you need to roughly establish the intensity of the color in comparison with the “palette” of the proposed shades. Then convert the hardness indices indicated on the palette from foreign degrees to Russian ones, since high-quality test strips are mainly produced in Europe.
Hard and soft water - what's the difference?
The amount of salt in water is affected by the presence of calcium and magnesium elements dissolved in it. This indicator can also be significantly increased by the presence of iron hydrate, the content of which in artesian waters can be excessive.
In the case when such impurities contain a small amount, it is called “soft”. This indicator is usually divided into 3 categories:
- Soft.
- Average.
- Tough.
Soft is the liquid obtained from rain or distillation.
There are practically no mineral impurities in such water. In most cases, it can also be obtained as a result of prolonged boiling or the addition of special chemical reagents.
Medium - found most often in water supply systems, as well as in spring and artesian water.
Hard - this category includes sea, ocean, and water flowing from rock layers rich in mineral deposits. A large amount of salts can be dissolved in it. If taken as a percentage, the salinity can reach up to 33% of the total volume.
How to create a device yourself to determine water hardness
You can make a device for determining water hardness with your own hands. To do this you will need:
- stainless steel size 50×50cm;
- transparent tube;
- purifying water filter;
- plastic container with a capacity of 1.5 liters;
- liquid check valve;
- nuts and washers;
- bolts M6×150;
- fittings.
The base of the future electrolyzer will be a stainless steel sheet. Imported steel AISI 316L or domestic grade 03Х16Н15М3 is perfect for this.
The metal is marked and cut into 16 equal squares, one corner of each is cut off and a hole is made in the opposite corner. It will come in handy later. The principle of operation of the device is the directed flow of electricity between oppositely charged plates, which causes the breakdown of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
To improve the flow of current, the plates are connected alternately: first a positive charge, then a negative one. The tube is used for insulation purposes. A ring is cut off from it and an incision is made to obtain a strip 1 mm wide.
The plates are secured with washers. First, a washer is screwed onto the bolt, then a plate is put there, then three washers and again a plate, etc. Each charge will require 8 plates. All operations should be performed carefully to avoid contact of the cuts with the electrodes.
Next, to create a device that allows you to determine the quality of water, tighten the nuts and insulation of the plates. The resulting structure is placed in a plastic container of the appropriate size.
Two holes are drilled at the points of contact between the bolts and the walls of the box. If the bolts do not fit into the container, they are shortened and tightened with nuts to make the connection tight. Then holes are made for the fittings in the lid. To ensure the tightness of the seam, it is coated with silicone sealant.
Before measuring water hardness with this device, it is a good idea to check its functionality. The device is plugged in, filled with water to the level of the bolts, and closed with a lid. A tube is connected to the fitting, the second end of which is lowered into water. The occurrence of current can be observed visually.
Now the current is gradually increased. Purified distilled water has poor electrical conductivity, so to obtain an electrolyte, an alkali is added there, for example, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), which is found in compositions for cleaning pipes such as “Mole” or others. A check valve prevents excess accumulation of gases. So, you have assembled a device with your own hands that will help determine the hardness of water.
You may also be interested in: How to test water quality: yourself and in the laboratory
Does aerating water somehow affect hardness? Why is water even aerated in hydroponic systems?
Solutions are aerated mainly to saturate them with oxygen.
Because the roots of plants in these systems are not protected by anything and, if there is not enough oxygen, then parasitic microorganisms will multiply on them, which, at a minimum, will reduce the yield, and, at a maximum, will lead to the death of the plant. The second moment during aeration is the saturation of the solution with carbon dioxide from the air. Carbon dioxide, although contained in small concentrations, can form various carbonates and bicarbonates (K2CO3, KHCO3) with the salts included in fertilizers, as a result of which the pH of the solution will increase. To stabilize the pH, it is necessary to use pH correctors; they contain buffering agents. They, in turn, will smooth out (ideally, prevent) the pH shift.
Third, this is a purely physical point (if we are talking about DWC systems). When the plant has just been planted and has not acquired a powerful root system, the substrate is sprayed with a solution from below to remove bursting air bubbles. This amount of water is enough for a young plant and also stimulates the roots to grow down to where the water is.
As you can see, aeration does not affect the hardness. (Editor’s note: Read more about aerating a nutrient solution in our article)
If ORP and pH are related, can ORP be influenced by changing pH?
ORP and pH are indeed related to each other according to the formula rH2 = Eh/0.029 + 2 pH. ORP depends not only on pH, but also on the equilibrium redox potential under current conditions - Eh, which in turn depends nonlinearly on pH.
In other words, out of three unknowns, we only know two. There are special instruments that measure Eh. Having the pH and Eh values in hand, we can calculate rH2. There are also instruments that determine the ORP indicator itself. To measure redox potential, redox meters, redox meters or rH meters are used, which are essentially the same thing.
Are there really such concepts as “living” and “dead” water? What does it mean?
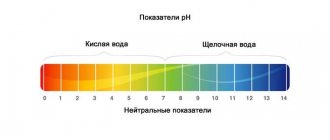
In natural water, the ORP value can have both positive and negative values and ranges from - 400 mV to + 700 mV.
When the ORP value is positive, then the properties of water are oxidizing. Such indicators are most often found in surface waters. Water that has pronounced acidic properties is called “dead” water.
. Its ORP can reach +800+1000 mV. “Dead” water is a strong oxidizing agent and this explains its disinfectant and bactericidal properties.
The more reduced the water, the more easily it gives up electrons, the lower the ORP value, and the lower the water’s properties. This is typical for underground mountain springs, melt water. This water is called “living” water.
. “Living” water (alkaline) is an excellent stimulant, tonic, source of energy, gives vitality, stimulates cell regeneration, improves metabolism, and normalizes blood pressure. Negative ORP of natural water is an extremely rare phenomenon. There are only a few places on the planet where such water exists. The ORP of the human body usually ranges from -90 mV to -200 mV, and the ORP of ordinary drinking water is almost always significantly above zero:
— tap water from +80 mV to +300 mV; — water in plastic bottles from +100 mV to +300 mV; - well, spring water from +120 mV to +300 mV.
This information means that when drinking ordinary drinking water, the activity of electrons in the internal environment of the body is higher than the activity of electrons in it. Those. Such drinking water takes free electrons from the biological environment of the body, i.e. is an oxidant. This leads to premature aging, chronic diseases, and chronic fatigue.
Conversely, the negative ORP of drinking water provides energy charging to cells, organs, and systems. The electrical energy of cell membranes is not spent on correcting the activity of water electrons and water is immediately absorbed, because has biological compatibility in this parameter. Drinking water with a negative ORP is an ideal antioxidant.
By the way, for the most part, aquarists use rH to measure ORP. I think this same indicator will be very convenient for hydroponics. Here are the indicators:
- rH 40-42 – maximum oxidation (pure oxygen);
- rH 35 - strong oxidation;
- rH 30 – slight oxidation;
- rH 25 – weak oxidation;
- rH 20 – weak recovery;
- rH 15 - slight recovery;
- rH 10 – strong reduction;
- rH 5-0 – maximum reduction (pure hydrogen).
Almost all plants feel comfortable at rH 25-35. rH is measured by special meters called rH tests. I haven't seen them in grow shops yet.