biofiltration in an aquarium
Click on the photo to find out what discus fish do.
An airlift filter for an aquarium is not at all difficult to make with your own hands. If you fill it with zeolite, then at first it will be a device for removing ammonia from the aquarium by absorbing it with zeolite, and over time you will get a super-efficient biofilter that can be installed anywhere: in a nursery, in a quarantine aquarium, in a decorative aquarium. It will reliably insure aquarium fish from unexpected ammonia poisoning.
The soil in an aquarium is its biochemical kitchen. It is in it, and even on the filter material of the filter, that beneficial nitrifying bacteria settle, without which the fish quickly die, poisoned by ammonia and/or nitrites. But the problem is that in many cases the aquarium ends up without soil, or there is too little soil there. For example, there is often no or little soil in nursery aquariums, quarantine hygienic aquariums, in commercial aquariums of pet stores and wholesale centers that keep fish, in aquariums where discus and angelfish are bred. It is also not always possible to equip these containers with external filters, and the small sponges of the internal filters have to be washed too often, thereby washing away nitrifying bacteria. So it turns out that nitrifying bacteria simply have nowhere to live in such “banks”, and therefore it is difficult to maintain the basic parameters of aquarium water at an acceptable level. In fact, many amateur aquariums with soil, but too small internal filters, also periodically suffer from ammonia “strikes” (peak ammonia concentrations) due to overfeeding or unsuccessful water changes combined with a soil siphon. The problem is especially aggravated in spring and autumn, and even in summer, when there is heavy rain and the quality of tap water drops. What can I do to avoid problems with ammonia and nitrites?
At one time (back in 2000), this question was very acute for me. It was not possible to maintain dense plantings at the aquarium fish holding facility, and the imported discus fish, accustomed to living in very clean water, did not want to live with us at all. I was able to quickly deal with ammonia poisoning of fish using a very simple device, which, under the pressure of circumstances, I had to quickly come up with. Many years of practice have proven its exceptional effectiveness. Here's what a homemade airlift filter looks like and how to make it :
Photo 1. Take a plastic bottle with a capacity of 0.5 liters or more, use a soldering iron to burn several rows of holes in its lower part. The holes should not be too large so that the zeolite does not fall out. Next, all that remains is to pour zeolite into the bottle. What zeolite should I use? In fact, this is a question that requires further study. There are many varieties of zeolite. Here we note the importance of the zeolite being sufficiently hard and not dusty. Zeolite from AquaEL Zeo MAX and API AMMO-CHIPS, as well as other natural and synthetic zeolites by weight, are suitable, but the properties of the latter can vary significantly, so they must be used with great caution in aquariums with live plants. Next, lower the bottle with zeolite into the aquarium and insert an air tube with a spray into the neck. That's all, the airlift filter started working:
Such an airlift filter initially works simply as a device that adsorbs ammonia, methane, hydrogen sulfide, and small organic molecules due to the physical property of zeolite to absorb these substances. The description for Polish zeolite ( Zeo MAX ) states that it also absorbs phosphates, nitrites and nitrates. However, the sorption capacity of the zeolite in the filter is depleted over time and it can be expected that the filter will stop purifying water (only the mechanical cleaning function will remain). But practice shows that, at least with regard to ammonia and nitrite ions, this is not the case. It turns out that zeolite is an excellent substrate on which nitrification processes proceed well. When colonized by nitrifying bacteria, our airlift filter quickly turns into a biofilter, and a very effective one at that. A possible mechanism of action is as follows: zeolite (often called clinoptilolite in foreign literature) physically binds ammonia and ammonium ions very well. At the same time, it is a good substrate for the life of nitrifying bacteria. These bacteria find abundant nutrition on zeolite. Even if there is not a lot of ammonia in the water, the zeolite accumulates it during ammonia emissions. There is every reason to believe (and this assumption is confirmed by experiments described in a special article) that ammonia-oxidizing bacteria are somehow able to extract it from zeolite. For bacteria of the second stage of nitrification, such a zeolite airlite filter also has something to profit from: the product of ammonia oxidation is nitrite. Nitrite is oxidized by these bacteria to nitrate. Thus, in this zeolite airlift filter, nitrification processes effectively occur, ridding the water not only of ammonia, but also of nitrites. One such zeolite is superior or equivalent in efficiency to the entire aquarium soil. This happens due to the forced flow of water and due to the sorption properties of zeolite. The zeolite biofilter, protected by a sponge, works without cleaning for many months, you just need to remember to wash the sponge. The main population of bacteria remains completely undisturbed. But you can’t turn off the filter - the bacteria will die from suffocation, deprived of the oxygen that water brings as it passes through the filter. The device will not work as a biofilter if it does not contain beneficial nitrifying bacteria. Accordingly, treating fish with antibiotics in an aquarium with a biofilter greatly reduces or negates its effectiveness, since nitrifying and other beneficial bacteria will partially or completely die. The death of beneficial microflora can be determined visually: the zeolite pebbles will turn gray and become covered with abundant mucus. The sorption properties of zeolite can be washed and restored by soaking (for 24 hours) in a 10-15% solution of table salt and subsequent rinsing in running water. The idea I proposed of using zeolite as a substrate for biological filtration in aquarium filters has in fact proven its usefulness and has been successfully implemented for more than fifteen years. In addition to its use in airlift structures, zeolite has shown excellent performance in external filters. In aquariums with a high population density, it makes direct sense to use zeolite. In this case, the filter will work more efficiently.
The use of zeolite in aquarium farming is a very interesting and not so simple topic, because there are many brands of zeolites and they can absorb not only ammonia, but many other substances. This circumstance must be taken into account when using zeolites in quarantine and treatment tanks, as well as in aquariums with live plants. Medicines and micro- and macronutrients needed by plants can be removed from the water, which can lead to the death of sensitive species. You can discuss all this and ask your question on the Aquarium forum. Come in, don’t be shy - it’s interesting there!
You can also read the following materials about the use of zeolite as a filter substrate in biofilters: “Which biosubstrate is better, or where do nitrifying bacteria live?”
Popular manufacturers
Among the most common manufacturers are:
Aquael filters FAN series
They are characterized by a powerful pump, low energy consumption, simplicity, reliability, and efficiency.
The filter material is a phelon-free sponge containing bacteria that process organic residues and nitrogen compounds. Capacity 260 l/hour. This model has an increased noise level;
Sera
Internal filters from this German manufacturer are reliable, affordable and easy to use. They are suitable for home aquariums with a volume of 30, 60, 120, 150, 300 l;
Tetra
They are distinguished by high quality and affordable price. Their fillers are double-sided biosponge and coal. When used, three cleaning methods are available - biological, chemical, mixed. Every month (once) it is necessary to replace the cartridge. Capacity 100 l/hour;
Eheim Pickup
It has a biological and mechanical cleaning method. The sponge is a filter material. There is a sprayer. Eheim Pickup is able to set the direction of the water stream during the filtration process. It is suitable for sea and fresh water. The model is safe, silent, easy to clean and maintain. Productivity up to 570 l/hour;
Juwel
This model is characterized by a biological filtration method. Fillers include synthetic padding, charcoal, large-porous, fine-porous, and nitrate sponges. If desired, they can be swapped. But here it is necessary to regularly change the adapter so that over time the pump does not create noise. This filter has high productivity - about 1000 l/hour;
Barbus
Characterized by mechanical filtration, low price, small size, easy to install. The model is designed for small tanks up to 20 l. There is a water aeration function. Capacity 150 l/hour. But it makes a lot of noise and does not have a flow control.
When choosing a model, it is important to familiarize yourself with all its characteristics and determine its functions.
How to make it yourself
The cleaner is created from scrap materials that are sold in hardware stores. One device is used in containers up to 500 liters. For a larger aquarium, two units are needed. Before manufacturing, it is worth understanding the principle.
How does it work
Homemade external aquarium filters provide biological filtration. Cleansing takes place according to the following scheme:
- Water is pumped through a tube using a pump.
- In the device, liquid passes through filter parts. Bacteria convert ammonium into nitrates.
- Clean water returns through the outlet tube.
After starting, the filter works like a mechanical one, after 2–4 weeks the number of beneficial bacteria inside the filler increases, and natural cleaning of the aquarium environment occurs.
Necessary materials
To design an external filter, you will need:
- base (bottle or canister);
- material for filter cassettes (plastic pots);
- hoses or flexible pipes;
- electric pump;
- fitting;
- padding polyester or cotton wool;
- foam sponge.
For an aquarium with a volume of 100 liters, a plastic bottle is suitable, for spacious vessels - a canister or a plumbing pipe with plugs. The material for filter cassettes can also be a kitchen mesh, a vegetable drawer or a container of suitable diameter. New components are purchased, since the old ones contain toxins accumulated during operation. Materials must be non-toxic. Metal elements without lubrication and protected from direct contact with water are suitable. It is better to choose hoses that are durable and without kinks.
The following devices will be useful:
- silicone sealant for aquarium;
- spanners;
- drill;
- bolts.
Various filter materials are suitable:
- bioballs;
- biofilm;
- Activated carbon;
- peat;
- filter wool;
- zeolite;
- ceramic rings.
Instructions
You can construct an external filter with your own hands in five steps:
- Make a hole at the bottom of the canister into which the fitting is inserted. Make two holes on top of the base of the purifier for the outlet hose and the wire from the pump. Using a fitting, secure the pump to the inside of the cover.
- Coat all joints with aquarium silicone.
- Make filter cassettes. To do this, holes are made in a previously shortened garden pot. The diameter of the cassettes should be slightly smaller than the canister. A layer of foam rubber is laid at the bottom. The second container contains a padding polyester. The third is filled with filter material, for example, carbon. Combining several types of media will provide more effective filtration.
- Secure the inlet and outlet hoses using sealant. Carefully measure the length of the hoses. If the tubes are too long, water purification will occur more slowly, and if the hose is not long enough, it will be impossible to install the unit correctly. The sealant dries for at least 24 hours; equipment cannot be tested ahead of schedule due to the risk of leaks.
- Before putting it into the aquarium, the filter is checked for leaks. The base is filled with settled water. If no leaks are detected within 24 hours, use equipment to maintain cleanliness in the aquarium.
Why does water flow through the air tube in aquarium filters?
- this happens because high resistance is created at the outlet of the pump. It may be due to severe blocking of the water flow regulator, or the installation of a flute.
The main hydrodynamic indicators of pump performance are the flow and pressure of water created by it.
Consumption
– this is the amount of water (in liters) that is pumped by the pump per unit of time at a given pressure. It should be remembered that due to design differences, even with the same electricity consumption, the ratio of pressure and flow will differ. In the passport data, the manufacturer sometimes displays in the form of graphs or tables the dependence of the flow rate and pressure of water passing through the pump and filter on the height of the liquid rise.
The movement of water through the pump certainly generates an increase in its specific energy, called pressure
. This indicator determines the height to which the water rises when moving vertically upward, and, therefore, affects the location of the external filter relative to the aquarium. Pressure is usually measured in meters, or units of pressure in a column of liquid.
When choosing a high-performance pump, it should be borne in mind that the maximum flow and pressure of water is achieved by its location at the level of the interface. Water consumption naturally depends on the height of the rise and will decrease as it increases. During the operation of the filter, contamination of the filler and the internal walls of the pump inevitably occurs, which leads to a decrease in water consumption. The aquarist needs to monitor the condition of the pump, and if the water flow weakens, immediately begin cleaning. Otherwise, the pump will overheat and fail. All components of the filtration system should be checked and cleaned: hoses, flutes, flow-through carbon dioxide reactors, the canister and the filler itself (which may need to be replaced regularly).
If you are planning to install a filter in your aquarium and make a preliminary calculation, then you should remember that the practical water pressure created by the pump will be slightly less than the theoretical one. There are several explanations for this. Thus, due to the design features of centrifugal pumps, not all the water entering them experiences the pressure of the rotating blades of the impeller, which leads to a drop in the speed of water movement near the outlet pipe. Part of the energy must be spent on overcoming the inevitable hydraulic resistance of water and friction by the impeller. Additional resistance to water flow is due to the design features of the filters, as well as the presence of any devices that the water has to overcome. The nominal difference between the actual and theoretical pressure only increases over time, which is due to the formation of mineral and bacterial plaque.
However, the effect of changing the speed of water flow, which occurs as it passes through different sections of the system, each of which has a specific cross-section, is used by aquarists to create filters.
Other models
In addition to external filters, there are other filters for aquariums.
Airlift
Such devices purify water using air. They are gradually losing their popularity due to low efficiency. Inexpensive, they can be made at home. You can make an air filter from a plastic tube. At the upper end there is a square that supplies water. A hose is inserted at the bottom of the tube, on which a sponge is placed.
Mounted
For a small aquarium, you can make a hanging filter with your own hands. A glass or plastic container in which partitions are made is suitable for manufacturing. The first compartment contains padding polyester, the remaining compartments are filled with filter media. Water is supplied by a compressor.
Carbonic
Purifies water chemically, destroying foreign odors and cloudiness. Along the way, useful substances disappear, so constant use is undesirable. This type of device is made independently from metal mesh. Two cylinders of different diameters are made, and plugs are attached to the bottom. The smaller cylinder is placed inside the larger one, the structure is fixed with a self-tapping screw. Coarse coal is poured in, and a padding polyester prefilter is placed on top.
Advantages and disadvantages
Aerofilters have many advantages:
- They operate silently, with only the sounds of running air bubbles;
- The sponge, which fits well to the tubes, is absolutely safe not only for large, but also for small inhabitants (shrimps, snails, fry);
- Compact device effectively saves space;
- the filter part is easy to disguise among stones and algae;
- the device can be easily transferred from one tank to another;
- energy and space are saved by using an additional water aerator device;
- if desired, you can make a design that will look beautiful in the interior of the aquarium;
- an airlift can be made independently with a minimum of investment and labor costs.
Common mistakes
- When assembling the external filter, the component elements are not properly sealed, which increases the likelihood of a leak. Do not skimp on the sealant when gluing.
- Neglecting to check leaks or not taking enough time to identify defects can lead to leaks. The adhesive curing time and conditions must also be fully observed.
- Lack of pump power will not provide the necessary filtration of spacious containers. For an aquarium with a volume of 100 liters, a pump with a capacity of 500 l/h or more is suitable.
If you have doubts about your skills, it is better to buy a ready-made external filter. Poorly made equipment will cause a lot of problems for the aquarist and the fish.
AIRLIFT AQUARIUM FILTRATION SYSTEM
An airlift filter is the most suitable option for water filtration in small aquariums. These types of filters have successfully proven themselves among aquarists.
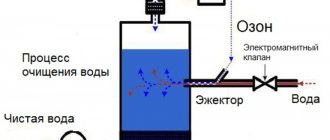
In our aquarium literature, filters are usually divided into two types - external and internal. Abroad, there is another division of filters according to the types of filter materials and methods of water purification. These are mechanical mesh (removing dirt from water by straining it onto a mesh screen), biological (dirt is retained in a special chamber and biological processes are accelerated due to the flow of water through the chamber), chemical (use of ozone) and adsorption (electrostatic adsorption). In this article we will look at the advantages and disadvantages of water supply systems to filters. Three systems are most widespread: airlift, mechanically gravity and injection. The first two of these systems are well known to Soviet aquarists.
Photo of a bottom filter with air-lift water supply
The airlift filtration system is based on atomizing air from a compressor through a special porous nozzle. Air bubbles rush to the surface of the water, carrying with them the water and dirt particles suspended in it.
This system is productive inside the aquarium, in the water. This principle of supplying water for purification is used, as a rule, for internal filters. Foam rubber filters from the GDR and glass filters with a foam screen (Germany), which are sold in our chain of pet stores, work on this principle.
The sprayer is placed inside the foam rubber (it should be noted that special foam rubber is used, with through pores), the water carried by the air goes up, new water enters through the foam rubber in its place, and the dirt settles outside and in the internal channels of the foam rubber. The simplest flotation filters also have a certain drawback: they do not remove large dirt particles from the water, but only absorb particles suspended in the water from small ones.
The performance of airlift filters depends on the air pressure and regular washing of the foam rubber.
Airlift filter systems (in Russian transcription sometimes - airlift systems) are also widespread. To lift water, air from a compressor is also used here: air bubbles move through a special system of vertical tubes, and the water between them is supplied upward, like on an elevator. At the outlet of the tube, air comes out and water flows out.
The airlift filtration system is used on both internal and external filters. Water can only rise in the system - while the filter is at depth; can be supplied above the surface of the water - in this case, the water flows by gravity again into the aquarium. Sometimes in internal filters, air enters the lift tube system through a nebulizer, as in some machines from Hong Kong sold in pet stores; More often, it is fed into the tube in large bubbles, between which doses of water are drawn in and raised. In internal filters, the air lift pump is placed after the cleaning chamber (in its center) so that the water rises already clean. Water is taken in through the cracks in the cleaning chamber. These are plastic filters of domestic and foreign production.
Photo airlift filter
Airlift filtration system is widely used for water supply and external filters. There are two design solutions for these filters. In the first case, water enters the cleaning chamber located outside the aquarium by gravity through a curved adapter tube, and the airlift filter system discharges already purified water into the aquarium. These were the glass filters of the GDR and Poland in the 50-60s and domestic plastic filters.
The disadvantages of these filters include some difficulty in filling the curved adapter tube and the need to place the filter cleaning chamber at the water level of the aquarium.
If the water supply through the adapter is stopped, the water level in the chamber drops. Water leaves through the airlift, and the flow of new water through the adapter tube stops and the filter runs idle. Sometimes the flow of water stops for a short time due to a snail crawling along the transition tube, but the system is already disrupted and the intervention of the aquarist is required.
The air lift tube in these filters is usually not fixed, and there are situations when the water drain valve is not above the aquarium. In this case, the filter pumps water to the floor until the reduced water level in the aquarium causes the transition pipe to turn off.
A more advanced method is to use an airlift to remove dirty water from the aquarium. In this case, the airlift system is in the water, the intake mesh is at the bottom, and the water raised into the chamber by gravity passes through the cleaning screens and flows back.
An example of this are external filters from Hong Kong. Here you don’t need to mess around with connecting the adapter tube (fill the filter chamber with water, then the tube, then, holding both ends to prevent air from getting in, lower them into the water of the aquarium and chamber), just hang the chamber outside with the airlift lowered into the aquarium and connect the air : The chamber will fill with water, which will flow into the aquarium after cleaning.
If you do not clean the filter material for a long time, the flow of clean water will weaken, and the flow through the airlift will naturally not change, and the amount of water in the chamber will increase. To prevent water from overflowing, the chambers of such filters have an emergency drain that removes excess water back into the aquarium without purification. Because clean water is coming back. into the aquarium by gravity, the water level in the chamber is constantly higher than its level in the reservoir.
This allows such airlift filters to be used to raise water 10 cm above the level of the reservoir. So, one of the Hong Kong filters raises water above a pond in my greenhouse, it is cleaned in the filter chamber and flows out onto a tray where it washes the roots of coastal plants on the way to the pond. This type of airlift filter is now popular in the USA, Germany and other countries. Of all the filters where water movement is carried out using air, in my opinion, this is the most advanced system.
The performance of all airlift systems, of course, depends on the strength of the air supply, but up to a certain limit: with a very high supply, the air does not capture water and the filter runs idle.
At the outlet of water into the chamber, aeration occurs; a stream of water flowing by gravity from the chamber vibrates the leaves of plants at a depth of 30-40 cm and, therefore, ensures the movement of water in the aquarium. The disadvantage of this system is that the water movement occurs only at the wall where the filter is hung; Therefore, dirt is removed mainly from this corner of the aquarium.
Structure and principle of operation
Although the name of this filter may seem unfamiliar to an inexperienced person, many are familiar with it. Typically, such a filtration system consists of a sponge and plastic pipes attached to it for air circulation. The principle of operation of an aerofilter is quite simple - pipes for supplying and pumping out air are connected to a compressor, which, in addition to air, also draws water into them. Subsequently, the water is filtered through the sponge and poured back into the aquarium, leaving dirt and harmful bacteria in the sponge. Such filters are not only cheap, but also easy to manufacture and install.
If you use them correctly and clean them in a timely manner, they will become good protectors of your aquarium.
Not long ago, new generation airlift filters appeared in specialized stores; they have a different structure, but work in the same way. The filter is a small plastic container in which various filtration materials are arranged in several layers. Most often, these containers are made of a corner type, which saves space as much as possible , and therefore is suitable for small aquariums. The principle of operation is still the same, but the presence of several filtration materials allows the airlift filter to work as a full-fledged biological one.
In addition, this system allows you not only to purify water, but also to saturate it with air, which makes it possible to do without an additional compressor with oxygen.
Homemade aquarium filters
To create optimal conditions for the inhabitants of the aquarium, it is necessary to have water filters. It can be cleaned by external and internal devices. In this article we will look at how to make external and other filters for an aquarium with your own hands.
Depending on the volume of the aquarium
Video “How to make an external filter”
Pump “scourge” – cavitation
Cavitation is a physical phenomenon that occurs in a liquid when it boils due to a change in pressure. In relation to pumps, the phenomenon occurs at the liquid inlet into the pump impeller. In the event that the absolute pressure of water turns out to be equal to or less than the vapor pressure at a given temperature, the water begins to “boil”, which results in a break in the flow and the cessation of pumping. In the place where the pressure is less than the saturated vapor pressure or equal to it, the release of gases and water vapor dissolved in water with the formation of microscopic bubbles. The bubbles are carried away by water flows into an area of high pressure, where they collapse, causing mechanical damage. The working areas of the pump receive microscopic damage from collapsing bubbles, which, with prolonged exposure, leads to rapid wear of the pump and its failure (mainly the impeller blades). The occurrence of cavitation during pump operation is accompanied by a significant and sharp decrease in efficiency.
Cavitation is accompanied by characteristic noise and vibration of the pump and is typical for any pump filters, both external and internal - with aeration connected at the filter inlet.
A characteristic noise may also arise for another reason, signaling that the pump cannot pump water because an “air lock” or simply a bend has formed in the hose of the external canister filter, through which the flow of water is extremely difficult or even impossible. As a rule, this problem occurs due to an excessively long hose, which, if not secured, falls below the pump outlet level.
External filter
Located outside the aquarium. It is more convenient to use, does not take up space in the aquarium, and works efficiently. It is necessary to filter the water in the aquarium. However, it is not necessary to spend money on buying an expensive device. Making an aquarium filter yourself is not difficult.
A homemade external filter for an aquarium can be made from scrap materials. For the base, you can use a plastic canister or pipe. You can’t do without fanfare when creating it. It is with its help that water is pumped out of the aquarium and, after being cleaned, returned back. Another important part is the filter element.
Depending on the type, it carries out chemical, biological or mechanical water purification. You will need synthetic winterizer, foam sponges, ceramic and glass-ceramic fillers, coal, peat, expanded clay, bioballs, zeolite. If you use several fillers, the degree of cleaning will increase. To take water in and return it, you will need hoses or tubes.
Also prepare taps, plugs, nuts, fum tape, separator, silicone. Tools you may need include wrenches, a screwdriver, a knife, and a drill. You can also come up with your own version of the device and use other materials.
Instructions
Let's look at how to make an external filter for an aquarium with your own hands using a specific example. Take a plastic pipe of the required diameter and length. At the top and bottom of the pipe you need to make covers with holes for the water inlet and outlet hoses. You can use fittings for this. The pump is secured inside using a fitting.
Next we make cassettes with filter material. The selected elements are laid in layers, separated by separators (pallets from pots, kitchen mesh). For pre-cleaning, use foam rubber or padding polyester. Then we lay ceramic rings, a biofilter or other materials. Hoses are attached to the fittings, and taps are cut in to release air.
The entire structure is sealed using silicone or other sealants. It should be checked before installation.
Aggressive environment. Recommendations for materials
Although today the market provides the aquarist with a wide range of products to choose from for his hobby, there is often a desire or need to either customize some equipment to suit your needs, or make a filter system yourself, from scrap materials, the list of which will be limited. Recommended materials for equipment that comes into contact with aquarium water are glass and ceramics, and most but not all types of plastics. Metal, if necessary, must simultaneously meet several stringent requirements. In addition to strength, a necessary condition for its structural suitability, it must also be chemically resistant. The reason for this is not only that a part exposed to metal corrosion will quickly fail, but also that for fish living in an aquarium, most metal compounds that can enter the water due to corrosion are poisonous. And here it would be useful to remind you that aquarium water is an aggressive environment. There are many different factors that make it this way, although water itself is a solvent. Many substances that can interact chemically with water can form acid or alkali as a result, thereby changing its pH. An example is carbon dioxide, a by-product inherent in aerobic respiration. All living beings that use oxygen for breathing produce carbon dioxide, which is easily soluble in water, which reacts with it to form unstable, weak carbonic acid. It is constantly present in water, due to its instability, breaking down back into carbon dioxide and water and forming again.
Decaying remains of food, plants and the excrement of the fish themselves are a source of nitrogen compounds (nitrates, nitrites, ammonia, etc.), phosphorus and sulfur. They are also chemically reactive and can cause corrosion. By entering into chemical reactions with water, gases dissolved in it, and aquarium sludge, they can form organic and inorganic compounds (including acids) contributing to the destruction of parts, both metal and some types of plastic.
Bacteria, which inevitably inhabit any, even the most seemingly clean, aquarium, are the main “suppliers” of hydrogen sulfide, which is a by-product of their vital activity. When it gets into water it also forms acid and is poisonous. The role of bacteria in the destruction and premature wear of aquarium equipment is also great. They settle in the pores of filter substances, reducing their efficiency and, over time, rendering them completely unusable. They form bacterial deposits on all parts of the aquarium submerged in water and simply on wet surfaces; such growths in hoses and other parts of existing filter systems are the main reason for the decrease in their efficiency. In any case, if you are a novice aquarist and are not sure of the chosen material , refer to ready-made designs and time-tested designs and materials, examples of which can be found in printed publications or on the Internet. —— based on materials: www.aqa.ru/filtraciya_akvariumnie_filtri
Internal filter
Suitable for small containers. They perform mechanical cleaning and are easier to manufacture than external ones. You will need a plastic bottle, a hose, a suction cup, a compressor, filler (pebbles), and a piece of sponge. Tools that will come in handy include a knife, screwdriver or drill.
Instructions
Making an internal aquarium filter with your own hands is very easy, even for beginners. Holes are made in the bottle cap to allow untreated water to enter. A piece of sponge is placed on the lid for rough cleaning. A hole is made in the neck of the bottle to install the hose. The other end of the hose is attached to the compressor.
You also need to make a hole for attaching the suction cup. You need to place pebbles or other filler inside. Then we place what we got into the aquarium and attach it to the glass with a suction cup.
Depending on the volume of the aquarium
For a 100 liter capacity, you can use an internal model made from a plastic bottle. To do this, you need to cut it, leaving the part with the neck. A plastic tube is inserted into it, and holes are made on the outside for water to enter. Filter media are placed inside: sponge, padding polyester, gravel. Then a hose is attached to the tube at one end, and the structure is secured inside the aquarium using a suction cup.
For 200 liter containers, external canister or mounted models are usually used. How to make an external filter with your own hands was described above. For a hanging model, you will need a plastic or glass container. Partitions are made of plastic. A padding polyester or sponge is placed in the first compartment and water flows in.
Other compartments can accommodate other fillings. A hole is made in the last compartment for water to escape. It is supplied using a pump (compressor). For a homemade model, you can use a pump from a washing machine. The finished device is suspended from the aquarium.
In containers of 300 and 500 liters it is better to use external filters. The larger the volume, the more powerful the pump required, the larger the size of the structure itself and the amount of filler. Watch the video about the manufacturing technology.
How does an airlift filter work?
The work of creating a flow of water is created by rising air pumped by an air compressor (can be of any type - pump, rotary, etc.).
Air, according to the laws of physics, tends upward due to the difference in density. Entering a tube located in a liquid, the air flow quickly expands and creates a kind of “piston” that lifts a small portion of water.
If a filter element is installed at the inlet of the tube, the passing water flow will be cleared of mechanical impurities.
Thus, the airlift filter performs several functions at once:
- Enrichment of water with an air mixture.
- Providing water circulation inside the aquarium.
- Filtration of water from mechanical impurities.
VIDEO INSTRUCTIONS ” alt=””>
Airlift filter compared to a pump filter
As mentioned above, it is difficult to achieve high power from an airlift filter, this is due to the fact that the pushing force in the design is, in fact, air, and not the engine.
In pump filters, the movement of water flow is ensured not by an air “piston”, but by a real mechanical one.
This entails a significant increase in the power and stability of the pumped liquid flow.
Power is the determining factor in the difference between these types of aquarium filters.
For example, an airlift filter is very sensitive to excessive contamination. Even a slightly clogged filter element can stop the operation of the entire device.
Water will stop flowing into the tube and water circulation will stop, although air will still flow into the aquarium. And all because of the small traction force of the rising air.
A pump filter will be able to pump water through the filter element even with a fair amount of mechanical impurities.
The pump and filter of such devices are most often combined into one housing, so pump filters take up a lot of the usable volume of the aquarium (in airlift filters, the components are usually separated - the compressor is located separately outside the aquarium, and the filter is immersed in water).
How to make an airlift filter with your own hands
You can make a homemade airlift filter in different ways. Below we will consider one of the simplest and most accessible.
For this we need:
- Air compressor for aquarium;
- Air supply tube compatible with compressor outlet;
- The lifting tube (its diameter should be several times larger than the supply tube);
- 90° elbow for lifting tube;
- Filter element (for example, sponge);
- Aquarium suction cup compatible with one of the tubes used.
- A hole is made in the lower part of the lifting tube according to the diameter of the supply tube with air.
- From the lower end to the hole, a distance should be set aside that will be sufficient so that a sponge filter can be fixed to the lifting tube.
- A square is mounted at the upper end of the lifting tube, directing the flow of lifted water in the desired direction.
- Using a suction cup, the structure is attached to one of the walls of the aquarium. When the compressor is turned on, air will flow through the supply tube into the lower part of the lift tube.
- Rushing upward, the air will also create a water flow, drawn through the lower end of the tube, equipped with a mechanical filter. The sponge should not touch the bottom so as not to suck up the aquarium soil. And using the square at the top of the filter, you can direct the water flow in the required direction for proper circulation.
The design of the airlift filter may be different. It all depends on the required dimensions, performance and functionality.
Other models
To purify water, an internal or external filter of different models is used. The choice of a specific one depends on the size of the aquarium, its inhabitants, and existing problems. Moreover, any model can be made into an aquarium with your own hands.
Air
An airlift filter filters water using air. They are not expensive, but are very effective. It is necessary to use a compressor, a filter sponge, a hose, a suction cup, a plastic tube or a flask and electrical tape. A corner is placed on top of the plastic tube through which water will flow back. For better connection density, the tube can be wrapped with electrical tape.
A hole is made at the bottom of the tube. We insert the hose and place the entire structure inside the sponge. Using a suction cup we attach it to the glass of the aquarium.
Carbonic
A carbon filter helps to chemically purify water from unpleasant odors, yellow color, drugs and other substances. However, being an adsorbent, it absorbs useful substances from water. Therefore, their constant use with plants is not recommended. Coal can be either as part of a complex of fillers for external models, or separately.
Let's look at how to make an activated carbon filter yourself. Take a metal mesh with small holes. Make two cylinders from it, one larger and the other smaller in diameter. You can fasten the seams using wire. Plugs are placed at the bottom of the cylinders; they can be secured with rivets.
Then the smaller cylinder is inserted inside the larger one, secured with self-tapping screws. Coal is poured inside, preferably of a large fraction. Close the top with a lid. We put a padding polyester prefilter on top. It is recommended to change the carbon periodically; the longer it is used, the weaker it performs its function.
Canister
A canister filter is a type of external filter that is characterized by high performance. How to make such a device yourself? To do this you will need a plastic pipe or canister, pump, hoses, filler, fittings, plugs, rubber gaskets, tap, nuts. A hole is made at the bottom of the device to install the water inlet hose. The water then passes through the fillers inside.
For example, a prefilter (foam sponge), then a biological filter, then a ceramic filler. The pump is mounted on top under the cover. Holes are also made in it to attach a hose that releases purified water. Hoses can be secured with fittings and nuts.
Purpose and principle of operation
Ammonia and nitrites, toxic to aquatic life, gradually accumulate in a closed ecosystem. If a certain concentration threshold is exceeded, living creatures in the aquarium may die. Therefore, it is necessary to pay great attention to the purification of the aquatic environment from fish waste products.
Airlift filters for aquariums perform several functions at once:
- enrich the aquatic environment with an air mixture;
- ensure circulation of water flows inside the container;
- filter water from mechanical impurities.
The system includes elements such as a compressor, a sponge and a tube for air and water.
The air filter works simply. Tubes for supplying and pumping air are connected to the compressor. The air flow from the compressor is supplied to the bottom of the filter, where it unfolds and naturally rushes to the surface. Due to the created backdraft, water is sucked into the sponge, and along with it dirt. From the outside it looks like the movement of an elevator, hence the name. The water passes through the filter sponge, is retained and returned purified back to the aquarium. The air compressor is located outside, thereby saving space inside the aquarium.
New airlift filters have a more complex structure, but will work on the same principle. The filter looks like a plastic container with various filtration materials, which are arranged in layers. Corner containers save space. They are suitable for small sized aquariums. Such sophisticated airlift devices perfectly maintain the biological balance of the aquatic ecosystem and saturate it with oxygen.