4.6
(11)
When purchasing an aquarium, a person wants it to always please him and his guests at home. Of course, for the home underwater world to bring true pleasure, it is necessary that beautiful fish live in it, there are various decorative elements and plants are planted. But, of course, the aquarium must be kept clean, and for this you need to provide high-quality filtration.
Using special equipment, you can constantly purify water, making it safe for inhabitants. Pet stores offer many filter options. These are both inexpensive internal models and external units. However, the former are not particularly productive and are often used only for compact aquariums.
The latter, of course, are more optimal in their characteristics. They do not spoil the design, they simultaneously perform biological, mechanical and bacterial cleaning, and in addition, they need to be washed every few months, which is extremely convenient. But external filters have one caveat, namely their high cost. Not every aquarist wants or has the opportunity to spend a lot of money on equipment for an aquarium.
In this case, you can use alternative options. For example, in recent years the phytofilter has become especially popular.
Purpose and principle of operation
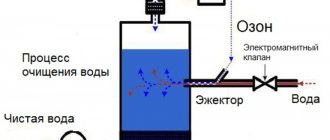
The purpose of the phytofilter is to purify water from nitrogen and phosphorus compounds that accumulate in excess in the aquatic environment. This is especially true for reservoirs where it is impossible to plant plants that would absorb these substances. For example, in an aquarium where there are goldfish that eat algae.
Operating principle:
- Using a pump, water from the aquarium is pumped into a container filled with substrate and plants planted in it.
- Water seeps through the substrate and plant roots, leaving accumulated elements harmful to fish there.
- Naturally purified water is discharged from the other side.
The performance of the phytofilter is high. Its installation will help out where it is not desirable to organize a strong flow of water from powerful filtering equipment.
What it is?
A phytofilter is a structure where certain types of plants are planted, flowing through the roots of which water is filtered from harmful substances.
In fact, this is one of the types of filtering equipment, the main advantage of which is exclusively natural water purification.
In this case, all nitrates and phosphates released from food residues, rotting plants and fish feces are absorbed by the roots of the plants.
A conventional biofilter has the ability to accumulate harmful substances that harm fish. Such a filter needs regular cleaning, and the aquarium needs to be replaced with fresh water weekly in order to avoid fish poisoning. But some species do not tolerate this procedure well. In this regard, a phytofilter is an excellent way out of this situation.
Sometimes it is not possible to plant plants in the aquarium itself due to the incompatibility of some fish with living plants and their desire to bury themselves in the ground. A striking example of this would be cichlids.
The devices described may differ in the materials from which they are made, the number of compartments and the plants with which the filter is filled.
Different models of phytofilters can be made from:
- plastic containers (the most popular material);
- glass;
- plexiglass;
- PET bottles.
The number of compartments depends on the wishes of the aquarist and the volume of the aquarium.
Suitable plants
In order for the device to fulfill its purpose, you need to choose the right plants for the phytofilter.
They must meet the following requirements:
- have the ability to grow and develop quickly, while consuming large amounts of microelements;
- the roots must be resistant to rotting in a very humid environment;
- be unpretentious in care and do not require frequent replanting.
The height of the plants must be taken into account. For voluminous ones you will need strong support. This factor must be taken into account, since the phytofilter is installed on a wall shelf or on the aquarium itself.
Plants that best meet these requirements:
- Spathiphyllum. It is classified as stemless, as large, elongated, shiny leaves immediately grow from the soil. The growth rate is high. In spring, beautiful flowering begins. Loves humidity and temperatures around 22°C. Some varieties grow more than one meter in height. For the filter, choose low varieties (Spathiphyllum floribundum, Spathiphyllum wallisii).
- Scindapsus. Flower growers everywhere grow this unpretentious vine; more than 30 varieties have already been bred. It has strong, elastic stems framed by foliage. Several vines planted side by side, differing in leaf color, look beautiful. The plant is tropical and loves water.
- Sankhetia. A moisture-loving shrub that attracts with its spectacular variegated leaves. It is unpretentious in care, grows quickly and consumes an increased amount of nitrogenous substances.
- Dieffenbachia. This upright plant with patterned leaves benefits from high humidity. He will like the place next to the aquarium. The only condition is that the stem should not be immersed in water, only the roots.
- Chlorophytum crested. A “fountain” made of leaves will look great in a natural area. In parallel with water filtration, it will also purify the air in the apartment.
- Tradescantia. This climbing plant will like running water at the roots, as it absolutely does not tolerate stagnation. It grows rapidly and consumes many microelements.
- Monstera. Aquarists choose this tropical plant for a filter with good reason - it grows rapidly and copes with the function of purifying aquarium water. But the dimensions of the plant are large; it can grow so rapidly that it will swallow up its neighbors. Numerous aerial roots will entwine everything around.
- Nephrolepis. This is an unpretentious, well-known fern with lush greenery that loves high humidity. There are many legends around it, in which there is some truth. For example, the fact that it is capable of absorbing harmful electromagnetic fields from a computer.
- Fittonia. Thanks to its bright foliage, it looks like an ever-blooming plant. Consumes a lot of nutrients and loves moisture. The bush needs constant pinching for lush branching.
Selection of plants is a fascinating and important stage in the design of a phytofilter. Before planting another bush, you need to inquire about the conditions of its maintenance.
On a note! Ficus benjamina is not the best option for planting in a phytofilter, as it grows tall, needs special care and does not like neighbors.
Types of filters
Based on their composition, the following types of filters can be distinguished:
- Biological. The basis is bacteria, which in the process of their vital activity produce a positive effect on the microflora of the aquarium as a whole.
- Phytofilters. Roots of non-aquarium outdoor houseplants.
- Mechanical. They help fight pollution exclusively through mechanical action. Structure: small generator, pump and sponges; Recommended for nano aquariums.
- Chemical. The composition includes coal or special resin.
- Combined. They combine several types at once. An ideal choice for large aquariums.
Based on the principle of operation, it can be divided into:
- Electrical.
- Airborne. Most often these are bottom or airlift filters.
- Of natural origin.
Regarding accommodation:
- Internal: “heads”; box-shaped, glass or bottom type; of natural origin.
- External: phytofilters, hanging waterfall, canister.
What should the substrate be?
According to the experience of aquarists, large expanded clay that does not float to the surface performs best. If one could not be found, pebbles are poured into the top layer, which will prevent the expanded clay pebbles from rising to the top. Ordinary crushed stone is also suitable as a filler. Sand should not be poured in; it will quickly clog the exits.
One option is to use a mixture of ceramic rings and expanded clay. Any minerals that do not interact with the aquatic environment and do not emit harmful substances are suitable.
Advantages and disadvantages
There are many advantages of such a filter system:
- simple design that can be made independently even from scrap materials;
- aesthetic appeal that complements the living area in the home;
- This device does not interfere with the inhabitants of the aquarium, as it is a remote device;
- aquarium water will not need to be changed frequently;
- the water is saturated with oxygen and microorganisms useful for the life support of aquatic inhabitants.
Another advantage is that it makes it easier to care for indoor plants, since you do not need to monitor their regular watering.
Disadvantages must also be taken into account:
- a rather cumbersome structure for which it is necessary to find a place;
- it is necessary to provide additional lighting for plants;
- water evaporates faster from the aquarium;
- If you choose the wrong plants, the roots will rot and the aquarium water will be filled with toxic substances.
If you make such a phytofilter for an aquarium, you will have to master not only the basics of aquarium farming, but also indoor plant growing. And whether this is a plus or a minus is something everyone understands in their own way.
How to make a phytofilter with your own hands
Self-assembly is not difficult. Such structures are made from plexiglass, or even from ordinary plastic containers. But the most ergonomic and aesthetic option is a phytofilter made of ordinary silicate glass.
Material and tool
To make a filter you will need the following materials and tools:
- silicate glass 5 mm;
- glass cutter;
- a piece of foam rubber (sponge);
- water pump;
- plastic corrugated tube;
- fitting;
- drill with a round attachment;
- roulette;
- marker;
- silicone sealant;
- building level.
To fill the container, you need to stock up on substrate and moisture-loving indoor plants.
Step-by-step instruction
Stages of making a phytofilter:
- Cut the glass to the required size to obtain a container frame 90 mm long, 20 mm wide and 22 mm high.
- Cut 6 glass partitions measuring 10 mm x 20 mm.
- Using a drill, cut a hole on one of the side walls 2-3 cm above the bottom of the filter into which the fitting for the supply tube from the aquarium will be inserted.
- Cut two outlet holes on the second side wall. One of them is working, the second is a safety overflow, which is located above the planned water level.
- Degrease all glass surfaces.
- On a flat table, glue the frame together using silicone sealant. We check the structure with a level for distortions.
- We glue glass partitions to the walls so that water bypasses obstacles from different sides. At the entrance and exit we place two partitions side by side, in increments of 3 cm, and glue the remaining two approximately in the middle in increments of 15-20 cm.
- Leave the filter for a day for the sealant to set.
- We install fittings with tubes into the holes. We put a sponge between the two partitions at the water inlet from the aquarium.
- Fill the structure with water and check for leaks at the seams.
- If the connections do not flow, we put the phytofilter in a permanent place, fill in the substrate and plant flowers.
- Install the pump in the aquarium. The pump model must cope with constant circulation of water.
The location is thought out in advance. The main requirement is that the filter device must be located above the fish’s home. This can be a shelf made from a plastic window sill and attached to the wall above the aquarium with metal brackets. This interior solution combines practicality and aesthetics.
Video material
In the video below you can clearly see one of the options for making a phytofilter from silicate glass.
Correct installation in the aquarium
At the very beginning, you need to take a container for plants, drill several small holes in the bottom, and two more larger ones at the ends.
You need to place the substrate in the container, and insert a hose or part of the filter into the side holes. Now the entire container should be secured to the back wall, partially submerged in water.
Thus, water will be supplied through the hose into the substrate, pass through the container, and pour out through the holes.
This is an example of the simplest version of a phytofilter. If you have time, energy and desire, you can do something more elaborate.
Phytofilter care
Such equipment does not require special care. Once everything is installed correctly, self-regulation processes are activated. This is exactly what is appreciated in this filter variation.
Care includes a minimum of manipulations:
- washing the substrate from sludge as it gets dirty;
- cleaning the foam twice a month;
- replacing plants that do not do well in the aquatic environment with others.
Sometimes aquarists make phytofilters from opaque containers. This is undesirable, since it is impossible to control the condition of the roots of indoor plants. If you liked the article, leave comments and share a link to it on social networks.