Home/AQUARIUM CARE/Bacteria for starting an aquarium: types, photos, videos
Live aquarium bacteria are used by experienced and novice aquarists when preparing the tank for use. They occupy leading positions in the ecosystem. After all, they are engaged in cleaning aquarium water from organic residues and harmful substances.
Types of filtration for aquariums
Several options have been developed for purifying aquarium water:
- Mechanical. This is done by sucking dirt particles into the filter. Residues of unnecessary substances settle on the materials of aquarium filters. Mechanical filtration also includes bottom siphoning, which is performed manually.
- Chemical. Removing unnecessary substances from the aquatic environment using numerous aquatic chemicals. For example, Sera-Toxivec or Tetra-CrystalWater.
- Biological. Water purification using natural beneficial bacteria. Microorganisms actively decompose organic compounds and waste products of fish to the state of gas.
Of all the methods of purifying aquarium water, the most effective and best is biofiltration.
When arranging biofiltration, the owner of an aquarium does not even have to invent anything - everything has already been created by nature. The main thing is to be able to reproduce the natural process at home. And external or internal biological filters will help in this arrangement.
Re-Mineralizers/GH Modifiers
Another geographical characteristic of water is its total hardness or GH. Total hardness is an indicator of calcium and magnesium salts dissolved in water. Hard water is responsible for the hard, whitish residue inside the kettle or on the lining of your aquarium. Some regions have hard water and some have soft water. Aquatic organisms that come from different parts of the world have adapted to a certain level of water hardness, which must be reproduced in order to facilitate adaptation. Some fish are sensitive to GH water, while others are completely indifferent. Whether they are sensitive or not, recreating natural hardness levels will help enhance coloration and encourage natural behavior in your fish such as breeding.
These medications are not always necessary and it is important to test the water before use. When using soft tap water and keeping fish from soft natural water, there is no need to use one of these drugs. However, if you are trying to keep African cichlids and you have soft water, then you would be wise to use these products in your aquarium such as Kent Cichlid Chemistry, Seachem Lake Salt and Sera Mineral Salt.
Many aquarists choose to use purified water (reverse osmosis) for their aquariums; such water is completely devoid of salts and can be very dangerous for fish if it is used without GH recovery! This “clean-de-salted” water literally sucks the salts out of your fish. Salts are extremely important for various biological functions and therefore water without some salts is not very good for fish or plants. Remineralizers are needed in such situations to restore the natural salt balance without adding phosphates, nitrates and heavy metals from tap water. These drugs include Seachem Equilibrium, Kent R/O Right and Seachem Replenish. When using Reverse Osmosis water in freshwater aquariums, the use of one of these preparations is not unnecessary.
The benefits of biofilters
Every home aquarium contains organic matter - it is left by the aquarium inhabitants. The decomposition of the remains of vital activity and foliage of aquatic plants, uneaten food and gas exhaled by the inhabitants leads to the release of ammonia.
Ammonia compounds pose the most important threat to aquarium inhabitants; ammonia is destructive to all living organisms.
Ammonia concentrations as low as 0.2 mg/l lead to the death of aquarium fish. And for many of their varieties, this indicator becomes destructive even when it decreases by 10-12 times. You can combat the formation of ammonia in other ways - for example, by regularly changing the water. But keep in mind that such manipulations:
- become a source of serious stress for fish;
- do not show effectiveness (after all, water is usually changed once a week;
- can destroy the fragile ecological balance.
The best and safest method for removing ammonia is beneficial microorganisms. Bacteria oxidize ammonia compounds and convert them into nitrites and nitrates.
Nitrates in high concentrations also harm the inhabitants of the jars, but these compounds become a nutrient medium for aquatic plants, which consume them.
There are two types of beneficial microorganisms that are effective as natural cleaners of aquarium water. This:
- Nitrifying. Microorganisms involved in the oxidation of ammonia compounds. After processing, ammonia is converted into hydroxylamine, which is subsequently converted by bacteria to nitrates and nitrites.
- Nitrobacteria. Microorganisms that process nitrites. The result of their activity is the appearance of nitrates. These substances are not harmful to fish and are absorbed by aquatic plants.
Biofiltration principle
Biological filtration occurs in several stages:
- Fish and other aquatic animals leave behind their waste products.
- Waste (remains of food, leaves, feces) decomposes and releases ammonia compounds.
- Beneficial microorganisms process ammonia.
- The nitrates formed after processing are absorbed by aquatic plants.
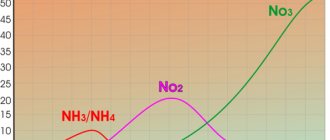
As the aquarium goes through the nitrogen cycle, bacteria begin to form on their own.
Microorganisms live in the aquatic environment, on the walls of the container, decorations, and soil.
Bacteria maintain and correct the eco-balance. But situations arise when there are not enough colonies of important microorganisms, which leads to an increase in ammonia and poisoning of aquatic life.
When such a situation arises, the aquarist is faced with the task of propagating beneficial denitrifying microorganisms. It is necessary for their populations to grow to large sizes and be able to cope with increased bioburdens. To strengthen and expand a colony of bacteria, three conditions are necessary:
- Favorable material (substances) for their residence.
- Oxygen.
- Proper filter care.
The principle of operation of an aquarium biofilter
The biofilter is found in various modifications. These devices may differ in the type of filler, body features and other technical characteristics. But regardless of the type of biofilter, all such devices work on the same principle:
- A special filler is placed in the device’s container. It has a porous structure, favorable for the colonization of bacteria.
- A hose equipped with an additional element (usually a compressor) is connected to the housing. The hose creates a simulated flow.
- Aquarium water enters the biofilter and is purified by beneficial bacteria.
- At the outlet of the filter, the water is already purified and safe for aquarium inhabitants.
- The nitrates that remain in it are absorbed by aquatic plants.
pH Modifiers and Buffers
The water that comes out of your tap has certain characteristics that are unique to your geographic location. The fish you find in the pet store are most likely not from your area; Freshwater tropical fish are mostly from the Amazon, tropical regions of Asia and the Reef Lakes of Africa. All of these regions have their own unique water characteristics. One of the most important characteristics of these bodies of water is the pH or “pH,” which is an indicator of how acidic or alkaline the water is. This is important for the most sensitive fish species, especially if you want to start breeding them. It is also important that the pH level remains stable throughout the day. There are two types of pH modifiers - with and without buffers.
Buffered pH modifiers change the pH of the aquarium water and its 'buffer', which simply means that the chemicals added will help keep the pH from changing from its original level. The pH in an aquarium becomes lower over time as a result of biological processes such as waste recycling through biological filtration. Buffered pH modifiers will prevent this. Products in this category include neutral regulators - API Proper pH 7.0 and Kent Cichlid Buffer.
Other pH modifiers change the pH only temporarily and if the water has any hardness, the pH will always return to its original value. Products in this category include API pH UP and pH Down, TetraAqua pH/KH Plus and Minus, Sera pH-Minus and Plus. They are most useful when paired with an appropriate buffer to stabilize the pH.
Keep in mind when using these products that fish are sensitive to sudden changes in pH and that it should change slowly. Most freshwater aquariums will do well with a pH of around 7.0, as this is neutral and falls somewhere between the extremes, while saltwater aquariums will need to be in the 8.0-8.4 range.
Types of biofilter fillers
For modern biofilters, various types of fillers are used. Each of them has its own characteristics:
| Type of filler | Description | Note |
| Sintepon (foam rubber) | one of the most common, this filler is universal and also provides mechanical cleaning; it is usually used for internal filters | not suitable for large aquarium tanks, as it cannot cope with increased load and immediately becomes clogged |
| Bioceramics | often used as a basic filler for biological filters and is already included in the kit, usually used for external biofilters, there is no mechanical cleaning | actively sprays oxygen, the bioceramic filler does not retain dirt, which ensures long-term operation without rinsing |
| Plastic balls | have a ribbed surface in which microorganisms accumulate | not as effective due to too small area of bacteria colonization |
| Porous glass | created using special technology and consists of small balls with a volume of 8-12 mm | ensures rapid growth of beneficial bacteria, innovative material |
Fertilizers for Plants
To maintain the health and continued growth of aquatic plants, it is essential to provide the necessary macro and micro nutrients required for the natural biological processes occurring in plants. Some of these substances and nutrients are: nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, calcium, boron, iron, molybdenum, zinc. Each element plays an important role and without these supplements there is a shortage. Symptoms of nutrient deficiency are lack of growth, poor color, yellow or discolored leaves, loss of foliage. Adding some in the form of CO2 is also an important part for plant growth and overall health. Carbon supplements such as Seachem Flourish Excel, Sera Flore 1 Carbo and TetraPlant CO2 Plus provide carbon for plants without the need for a complex CO2 system and are very easy to use. Tetra has created a complete line of products that include a wide range of additives: TetraPlant PlantaStart, TetraPlant PlantaMin, TetraPlant Crypto-Dunger - macro and microelements - Tetra PlantaPro Macro and Micro. Adding these nutrients and elements is essential to improve the health, appearance and growth of aquatic plants.
Additives for freshwater aquariums
designed to help you maintain and maintain your aquarium so your fish feel right at home. Whatever you choose, always be aware of how these supplements are used and what they are for; blindly using additives will lead to disaster and therefore it is always recommended to test the water before use. All of these Additives have changed the hobby for the better and will continue to change the hobby in dramatic and unexpected ways as modern technology and research allow for superior advancements in aquarium keeping.
How to choose a biofilter for a home aquarium
Modern aquarium farming offers a wide variety of ready-made devices that guarantee high-quality cleaning of the container. Of the entire huge range of biofilters, it is worth highlighting a few that have proven themselves the most.
When choosing the required design, take into account the performance of the biofilter - the best devices are those that show a performance of 2 full volumes of water per hour of operation.
Aquael brand equipment
Aquael is a Polish company that produces budget biofilters. But, despite the affordable price, this equipment is famous for its powerful performance and has proven reliability and quality:
- biofilters from Aquael are designed for cans of 100-700 l;
- the most powerful units are equipped with 2 pumps and 4 hoses (working for the inlet and outlet of a water jet), which allows you to achieve a good flow;
- Bioballs or ceramic rings are usually used as fillers.
Tetra-EX brand equipment
One of the most famous and popular manufacturers of aquarium equipment and accessories.
The German company meets the highest quality standards, and all their products undergo careful control and technical testing:
- biofilters from Tetra-EX are designed for cans with a capacity of 60-500 l;
- standard equipment includes biological balls and ceramic rings;
- Each device has instructions that describe the rules for assembly and installation.
All supplied fillers must be washed under running water before placing them. By the way, this applies not only to Tetra-EX equipment, but also to other brands. After all, during transportation, dirt and microscopic fragments settle on them.
In order for the Tetra-EX biofilter to be in working condition, the aquarist must independently create the necessary draft. This is done using the paging function (the button is located on the top of the case).
JBL brand equipment
Another equally famous German manufacturer of aquarium equipment. This company specializes in economical filters with a budget pricing policy. All models use bioceramic filler with a mechanical cleaning function.
Nitrification occurs in two stages
At the first stage, ammonium-oxidizing bacteria convert ammonium into nitrite. These bacteria include two phylogenetic groups:
1. In marine systems. The genus Nitrococcus, which belongs to the β subclass of Proteobacteria and is represented by two marine species (Koops and Pommerening-Röser, 2001); 2. In freshwater systems. Gamma subclass of Proteobacteria, represented by the clades Nitrosospira and Nitrosomonas (Michaud, 2007).
Ammonium oxidation has the following form: NH4+ + 3/2 O2 → NO2— + 2H+ + H2O + 84 kcal mol-1
First, ammonium is oxidized to hydroxylamine as an intermediate product, and then to nitrite. The process involves two enzymes: ammonium monoxide genase (AMO) and hydroxylamine oxide reductase (HAO) (Tsang and Sukuki, 1982; Bock et al., 1991). Hydroxylamine is the first product of aerobic oxidation. Under anaerobic conditions, nitrite formation from hydroxylamine is reduced (van de Graaf et al., 1996).
In the second stage, nitrite is oxidized to nitrate by various groups of microorganisms, nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB). These bacteria include four groups (Egli, 2003).
The main group belonging to the α subclass of Proteobacteria has only one genus Nitrobacter, which is divided into four species, two of which are marine (N. mobilis and N. gracilis, belong to the β and γ subclasses of Proteobacteria, Koops and Pommerening-Röser, 2001). Another genus, Nitrospira, includes two species, N. marina and N. mascoviensis (Ehrich et al., 1995), which are part of a phylum belonging to the δ subclass of Proteobacteria (Michaud, 2007).
The oxidation reaction of nitrite to nitrate has the following form: NO2— + 1/2 O2 → NO3— + 17.8 kcal mol-1
Several enzymes are involved in this process: nitrite oxide reductase (NOR), cytochrome a1 and a2, quinine and NADH dehydrogenase (Bock et al., 1986; Bock et al., 1990).
If the mechanisms of nitrification have already been comprehensively studied (van Rijn, 1996; Aoi et al., 2000; Koops and Pommerening-Röser, 2001; Egli, 2003; Tal et al., 2003; Sharrer et al., 2005; Michaud, 2007), The study of the flora of heterotrophic bacteria began relatively recently (Michaud et al., 2006, 2009). These bacteria play an important role in oxygen consumption, the formation of metabolic by-products after cell lysis, and the outbreak of fish infections. In addition, they compete with autotrophic bacteria for oxygen and substrate, and significantly inhibit nitrification (Zhu and Chen, 2001a; Léonard et al., 2002; Michaud et al., 2006). In fact, in a biofilter, heterotrophic bacteria develop faster and predominate on the outer layer of the media, directly consuming oxygen from the water. This has a detrimental effect on autotrophs, which grow more slowly and in deep layers of litter (Lewandowski et al., 1993; Zhu and Chen, 2002). Competition is critical to filter efficiency and ammonium oxidation. It is especially relevant when the availability of organic carbon for heterotrophic bacteria is high (Zhu and Chen, 2001b; Michaud et al., 2006).
How to make a biofilter yourself
A self-created biofilter is in no way inferior to ready-made analogues even from the most renowned brands. You just need to know how and what to make biological filters from. There are several options for making them.
From a plastic bottle (option 1)
We will need a plastic bottle, a PVC tube (its diameter must match the neck of the bottle).
For filler we use fine-grained pebbles with a diameter of up to 5 mm. You also need a compressor and padding polyester.
The manufacturing technology is as follows:
- Cut the bottle along the top edge of the label. It is necessary to ensure that the upper part of the bottle fits into the lower part with difficulty.
- In the created device (in the bowl) we make 10-12 holes measuring 3-4 mm.
- Insert the PVC tube tightly into the bowl, making sure it fits tightly. If a gap appears, use silicone glue to glue the joint to completely seal it.
- The height of the PVC tube will be slightly larger than the bottom of the bottle, but it should not reach the bottom.
- We put a 5-6 cm layer of pebbles into the prepared structure. We put padding polyester on top.
- The compressor hose is inserted and securely fastened into the pipe.
All that remains is to check the equipment and run it in the aquarium. This method is the most accessible and easiest to manufacture. When the compressor is running, air will flow through the PVC pipe and exit to the top.
The substrate will become actively saturated with oxygen, and a water stream will flow through the holes down to the pipe and enter the jar.
From a plastic bottle (option 2)
This method is similar to that already described, but has its own nuances. To make a biofilter you will need a 1.5 liter plastic bottle, foam rubber, substrate, sprayer, clamps and a compressor with a hose. The assembly diagram is as follows:
- We make several small holes in the lower area of the bottle.
- We tightly wrap the lower part with holes with foam rubber. For reliability, we tighten the foam layer with clamps.
- Pour the substrate into the bottle (about half the capacity).
- We connect a compressor hose with a sprayer to the top of the bottle (to the neck).
The biofilter is ready. We check it and install it in the jar. The principle of its operation is simple: the flow is formed by oxygen, the air combined with water exits through the neck of the bottle, and at the bottom the water stream enters the aquarium through the holes.
If your aquarium is large, then take a larger compressor. The bottle can also be larger in volume.
From glass
This version of a self-contained biofilter is the most complex to set up. But it is also the most effective in terms of characteristics and effectiveness. To create it you need glass, alcohol, a glass cutter, matches, a measuring tape and three types of filler. The manufacturing procedure consists of the following steps:
- We measure the aquarium in width and length. We need to cut glass of the same size (this is the bottom of the biofilter).
- We make the side walls in the same way. Their length will correspond to the length of the can. The height does not matter; 10-12 cm is enough for it.
- The back wall is also cut using the same method. The length corresponds to the aquarium, but it is necessary to provide a reserve the size of the thickness of the side aquarium glasses. We take 10-12 cm in height.
- We carefully treat all glass blanks with alcohol, and after drying, carefully apply glue (the adhesive layer is applied evenly to the edges of our future walls).
- Glass blanks are assembled and joined. They should be fixed until the adhesive composition dries completely.
- Let's start making partitions. They will be identical in length to the base already made, but their height is slightly reduced (by the size of a matchbox). It can be placed on the bottom when assembling the structure - it is important to ensure that water flows freely in this area along the bottom.
- We glue the partition structure according to preliminary markings. In total, we will have two similar barriers and three chambers in which the filler will be located. The walls of the partitions should be located at the same distance. To determine the measured width of the aquarium, divide by three and place markings at each point.
- We make the second partition in the same way and glue it to the aquarium.
- We cut out two more additional partitions from glass (with their help, the access of water to the edges of the jar itself (at the place where the filter is installed) will be limited). When making, take into account that the additional partitions are wider than the aquarium stiffeners. These models are glued to the free part of the main part, in the place water leakage.
- Cut out a small strip (its length is equal to the length of the filter, its width is 2 cm). We glue the bar to the end of our second partition in the form of a visor.
- We make the second bar in the same way (slightly shorter in size than the aquarium length, 6-7 cm in height). We attach it to the third building (the padding polyester filler will be located there). The bar will help the water flow freely into the jar.
- We make the next bar, slightly shorter in length than the aquarium bar and 2-3 cm wide. Glue it under the gap.
After making the entire structure, we proceed to filling it. The first compartment is filled with padding polyester, the second is filled with expanded clay (or pebbles, ceramic rings), the third is also filled with padding polyester. We attach a filter and a hose to the can (the hose is attached to the pump from the internal filter). All that remains is to check the design and launch it.
There are various biofilters for home aquariums. Both ready-made and created independently. Such devices are extremely important in creating favorable living conditions for aquarium fish and other aquatic inhabitants.
Next
EquipmentAquael Fan Mini Plus filter for cleaning your aquarium
Microelements
Fish uses elements contained directly in the water and in different areas of the planet there are different concentrations of trace elements and certain types of biological molecules. These elements include chromium, cobalt, copper, manganese, iodine, etc. You can find similar trace elements in multivitamins. These elements are important for various biological functions in fish. Adding a micronutrient supplement to your aquarium will enhance coloration, activity, immune system and reproductive function.
These drugs are used as conditioners that change water conditions to mimic the "black water" of the Amazon known as Blackwater. Products such as Sera Blackwater Aquatan, TetraAqua ToruMin and Kent Black Water Expert recreate the “black water” of the Amazon River and its tributaries. These extracts improve overall well-being, stimulate natural behavior and reproduction, and help in the incubation process of eggs of those fish that originate from these places. Such additives are known to inhibit algae growth by blocking excess light and can lower pH, making water more acidic.
What to do to prevent mycobacteriosis from occurring?
- Introduce only healthy individuals that have undergone adaptation into the common tank.
- Equip the container with aerators and mechanical filters.
- Maintain temperature conditions.
Cyanobacterial toxins
Cyanobacteria or blue-green algae differ from other pathogenic microorganisms in that they have the properties of bacteria, as well as algae, and are less susceptible to treatment. They actively reproduce if the appropriate conditions are created:
- Availability of organic matter and nutrients.
- Irregular water changes.
- No filter.
- Introduction of uncleaned stones, driftwood and other decorative elements.
- Using a powerful fluorescent lamp.
You can encounter cyanobacteria in an aquarium if you do not clean the container in a timely manner. All experienced aquarists carry out such actions for an aquarium with their own hands.
Blue-green algae can be eliminated if:
- Carry out manual cleaning of decorative elements, tank walls, and driftwood.
- Install a powerful pump, which increases the speed of water movement.
- Reduce the brightness level of the lighting fixture.
- Treat infected individuals.
- Excess feed in the tank is avoided.
- The substrate is mixed periodically. For this purpose, aerators are used, as well as pumps with the required power.
- Maintaining the temperature at 20–25 degrees. If necessary, this figure increases. It all depends on what phenotypes the mollusks live in the container.
- Regular water changes (every 7–10 days).
Universal methods of struggle
A bacterial outbreak can be suppressed if the following measures are taken:
- Introduction of a booster pump with skimmers and filters into the tank.
- Temporary exclusion of food in the form of granules or flakes. Reduce frozen and live feeds.
- Introducing ampoules into the container, which destroy the film. A bacterial outbreak is often suppressed by them.
- Introduction of activated carbon into the filter composition. It makes it easier to get rid of organic residues.
- Administration of medications. The capsule or drops are administered in a specific manner.
What causes a decline in the population of beneficial bacteria?
- Oxygen deficiency. It provokes not only the death of beneficial microorganisms, but also the rotting of plants.
- Increased acidity, excessive amounts of carbon dioxide. After all, these two parameters act as antiseptics. In order for beneficial microorganisms to develop, it is necessary to establish a balance.
- Introduction of disinfectant compounds into the tank. Medicines that are used to treat mollusc phenotypes have a detrimental effect on the condition of beneficial bacteria.
By maintaining anaerobes and nitrifying bacteria in excellent condition, you can protect the aquarium from an excess of organic matter and nitrates. Periodically, experienced aquarists introduce microorganisms. At the same time, appropriate conditions for development are created.
Principle of operation
Several types of bacteria live in aquariums:
- heterotrophs that convert organic substances into inorganic form, for example, into free ammonia, which is toxic to the inhabitants of the aquarium;
- autotrophs involved in the nitrification process.
Nitrifying bacteria in aquariums and biofilters are represented by:
- Nitrosomonas - they oxidize ammonium to nitrites;
- Nitrobacter – transforming nitrites into nitrates.
These genera of microorganisms include aerobes that require oxygen and facultative aerobes that can temporarily survive without it. The process of water purification is not complete without the denitrification reaction - the conversion of nitrates into nitrogen gas. It involves anaerobic (not requiring external oxygen) microorganisms. They obtain the O2 necessary for life as a result of the denitrification reaction.
Biofilters contain all types of bacteria, which ensures effective water purification from toxic substances. However, this does not mean that the concentration of dissolved oxygen in the water flowing through the system is unimportant for the biofilter. With good aeration, the number of aerobes predominates.
If O2 activity decreases, then the biofilm contains the majority of anaerobes, the waste products of which can also be toxic to fish. They become toxic because with a lack of oxygen, even anaerobic bacteria switch from oxidation processes to enzymatic biochemical processes, which result in the release of CO2, ammonium, hydrogen sulfide, methane and other substances toxic to living organisms.