Proper aquarium lighting is the key to the health and beauty of its inhabitants.
The variety of light bulbs, the availability of a wide selection of designs for lighting and illumination (including programmable electronic ones) allows you to solve the issue of light competently, efficiently and at the lowest cost.
A correctly selected lamp will not only provide comfort to the inhabitants of the aquarium, but also provide aesthetic pleasure to its owner.
Is lighting necessary in a fish aquarium?
Undoubtedly, if the owner is going to enjoy the aesthetic appearance of the fish in the aquarium, he will definitely need light.
Some species of fish, such as goldfish, may fade if there is not enough light. Moreover, fish need light to feed and engage in other fish activities. But they also need a few hours of darkness to relax and unwind.
It is important to remember that different freshwater fish have different lighting needs.
What to look for when choosing
- spectral composition;
- color rendering level;
- lamp power;
- plant type.
Spectral composition of light
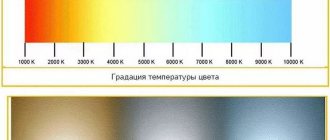
The spectrum is measured in “kelvins” (K), a unit of measurement that represents the number of degrees emitted by a hypothetical black body when heated.
In color terms, the body first becomes red, then turns yellow, green, blue and finally becomes violet.
If the degree Kelvin is low, the color of the spectrum will have a red tint.
The higher it gets, the darker its color. Eg:
- super warm white lighting – 2700 K;
- warm white – 3000 K;
- natural light – 4000 K;
- cold white light – 5000 K;
- full spectrum – 5500 K.
The use of overhead lighting, taking into account the spectral composition of light, is considered the most successful for aquarium plants, since it imitates natural growth conditions.
Color rendition
This parameter shows how natural the conditions in which the plants are located will look when illuminated by the selected lamp.
The value is denoted “Ra”, or called CRI (Color Rendering Index).
The ideal color rendering value is Ra=100. The higher the CRI of the lamp, the better the color rendering.
Based on this, the following CRI standards are determined:
< 51 – weak light transmission;
51 – 80 – average value;
81 – 91 – good;
91 – 100 best color rendition.
Modern aquarium lamps have a CRI value of at least 80. For correct color rendering of the underwater world, professionals recommend using lamps with a maximum CRI value and a color temperature from 5400 to 10000 K.
These parameters can be found on the lamp packaging. For example, /960 means that this is a fluorescent lamp with CRI=90 and CCT=6000 K.
How much light do plants need?
To understand this, let's look at the necessary concepts.
- Lumen - shows how much light a light source produces.
- Lux is the amount of light that hits the surface of something.
The amount of light falling on a certain area of the aquarium is calculated using the following formula:
Lm = S x lux
Where:
- S – bottom area of the aquarium;
- lux is the light needed by the plant.
- Lm is the number of lumens that the light source should produce (indicated on the lamp packaging).
Example:
Bottom area of the aquarium = 0.18 m2. Plants planted in it require 15,000 Lux. Which lamp should you buy?
0.18 x 15000 = 2700 Lm.
You need to purchase a lamp that says 2700 or more lumens.
There is an opinion in educational literature that the ideal value for comfortable plant growth is lighting of 50 - 70 Lm/m. We dare to challenge this fact and here’s why. Fluorescent lamps produce diffused light, which means the rays diverge in all directions and in some places may not even reach the aquarium.
LEDs, on the contrary, shine purposefully in the direction they are turned. If you hang such a lamp over the middle of the aquarium, its sides will be illuminated less than the center. And if you imagine an aquarium with a water column of 50 cm or more, 50 - 7-Lm/m are generally lost at such a depth.
Each aquarium with plants is individual, which means you should not become attached to the values proclaimed by printed publications. Only experience, independent calculations and taking into account individual characteristics will help you choose the ideal lighting.
A household lamp is not able to satisfy the photosynthetic needs of aquarium plants.
Daylight hours
Remember that fish and other inhabitants of your jar are practically not interested in additional lighting. It is required primarily by plants.
For them, the amount of daylight is as important as getting the right nutrition.
This is due to the fact that representatives of the flora undergo different processes day and night.
Japanese aquarist and designer Takashi Amano in his works uses not just the alternation of day and night, but creates for his wards conditions that are as close as possible to natural ones, according to the principle “dawn, zenith, sunset”. Moderate lighting lasts for 6 hours, peak lighting lasts for 3 hours, followed by sunset for 3 hours.
Lighting also depends on the age of the plantings. For example, for a newly formed aquascape, light is first applied for 3-5 hours without simulating zenith. From the second week, you can increase daylight hours to 6 hours on a regular basis, gradually bringing it up to normal.
Most plants need 5-6 hours of intense lighting to fully carry out photosynthesis.
Tips for setting up lighting:
- The lighting time in the aquarium should be between 8-12 hours depending on the inhabitants.
- At night it is necessary to turn off the lights in the aquarium.
- Vary the lighting spectrums – you can always try using lamps with different color spectrums.
- LED lamps are not a panacea for an aquarium, but only one of the options.
- We do not recommend leaving the aquarium without light for a long time, as this will result in a sharp growth of algae and green growths.
Light for tropical freshwater fish
The most common tropical fish come from rivers, streams and clear lakes in warm regions and are accustomed to bright sunlight and warming rays on a natural 12-hour cycle.
Therefore, to best recreate these conditions in an aquarium, you need to provide 12 hours of light per day, preferably with bright LEDs that penetrate the surface of the water, or use sunlight if the room in which the aquarium is placed is well lit.
Some species of tropical freshwater fish, such as tetras, may prefer low light. In this case, you need to leave enough hiding places in the aquarium so that these fish can escape there.
What happens if you don't turn off the lights
Some aquarists claim that the fish need light in the aquarium at night to search for food in the dark. In addition, night lighting allows you to easily see the inhabitants of the reservoir. Following these assurances, aquarists make a mistake, because fish have special organs to search for food, and besides, most pets sleep peacefully in the dark. But if an artificial reservoir is illuminated around the clock, this will cause the following problems:
- Deterioration in the health of fish, since pets are programmed at the level of instincts to change day and night. Fish need to rest at night, and the light in the aquarium will interfere with this.
- In nature, there is no round-the-clock lighting, and the closer the conditions in the tank are to natural, the better the pets and plants develop and live longer.
- Increased level of aggressiveness in pets: some phenotypes, in the absence of a day change, show increased anger towards their relatives.
- The main problem with 24/7 lighting is algae. The longer the daylight hours in an artificial reservoir, the faster the development of harmful tiny organisms in the reservoir, which can lead to the death of all living things.
Light for cold water fish
In general, cold-water fish do not need excessive lighting. Only if the owner wants to admire the aquarium. Therefore, only 8 hours of light is enough.
If the tank has enough hiding places for them, even 12 hours of daylight is fine, especially if there are also light-loving plants in the aquarium.
To create an optimal habitat for cold-water species, the owner should try to adjust the aquarium's lighting to seasonal daylight hours, as in the temperate climate zone where most cold-water species originate.
Choosing a location for installing lamps
Depending on the location of the aquarium lighting devices, they can be installed at the bottom, in the central part, on the side or on top. The most optimal option is the overhead installation of artificial lighting sources. If the type of lighting equipment does not provide for directional radiation of the flow, a reflector is placed around it.
Rice. 7: distribution of light flux throughout the aquarium
The choice of a specific location depends only on your personal preferences and the arrangement of interior items in the room.
If one lighting element is not enough, then combined options or several lamps are used to achieve the required lighting brightness. To do this, you can use two or even three types of lamps, which allow you to create interesting effects.
Light requirements of living aquatic plants
While light in aquariums is partly a pleasure for aquarists, plants rely heavily on daylight patterns and good quality light is paramount.
The light to be used in the aquarium and the duration of lighting will depend on the plants.
Some plants do well in low light, while others need bright light for longer. For plants that like low light, such as java moss, java fern and anubias, 8-10 hours of low light per day is fine. Plus, these plants are ideal for beginners.
On the other hand, light-loving species prefer:
- longer daylight hours, somewhere around 12 hours a day;
- adding CO2;
- feeding with fertilizers.
If the owner populates the tank with both plants and fish, experts recommend matching aquatic plants to the type of fish that are in the aquarium, for example, tropical plants with tropical fish.
Ideally, species such as platy, guppies, betta and catfish can be combined in aquariums planted with Java fern, Java moss, anubias, hornwort and cryptocoryne. Goldfish, minnows, orysia and zebrafish come from temperate climates where daylight fluctuates and pair best with various types of Anubias and Tiger Lotus.
Consequences of improper lighting
The natural alternation of light and dark times of the day allows plants to develop. Incorrectly calculated lighting power or duration for an aquarium can lead to serious consequences. The difficulty is that aquarium plants need bright light for photosynthesis, but fish do not need this, since they are accustomed to living in the shady thickets of a reservoir. Too much prolonged and bright lighting affects their color.
Problems with incorrect lighting intensity often arise in containers whose height exceeds 40 cm. In them, plants creeping along the bottom of the “jar” experience a lack of lighting. To solve this problem, increase the power of lamps and the duration of artificial illumination. The consequences of this wrong decision can be the appearance of various diseases in fish and water blooms.
Light and algae
1-Siamese seaweed 2-Amano shrimp 3-Neretina snail 4-Glass shrimpThe most noticeable disadvantage of using light for long periods of time is algae. Typically, if aquarists allow the light to run for more than 12 hours a day, blue-green algae will grow exponentially.
Although in this case you should worry not only about the lighting of the aquarium, but also about natural sunlight. If the aquarium is in a brightly lit room, it is not recommended to place it too close to the window.
However, algae will likely still grow in the aquarium whether there is too much light or not, so it is important to control their size.
In case algae thrives in the aquarium even in fairly low light, you should consider adding algae eaters: Siamese algae eaters, glass shrimp, Amano shrimp and neretina snails.
Without a doubt, light is critical for both plants and fish in warm or cold water aquariums.
The Best Full Spectrum Lamps for an Aquarium
Representatives of this group emit natural white light, which is similar to natural daylight. Thanks to it, the aquarium plants receive the necessary conditions for development and growth, and the color of the fish becomes incredibly bright.
Sylvania Aqua-Classic T5
5.0★★★★★editorial assessment
97% of buyers recommend this product
The fluorescent lamp of the German brand Sylvania is manufactured according to new standards using tri-phosphor technology and combines two functions at once. The balanced ratio of blue-red radiation promotes photosynthesis, and at the same time favorably illuminates all inhabitants of flora and fauna. With such a lamp your aquarium will take on a fabulous look.
Pros:
- Suitable for aquariums of different types and shapes;
- The spectrum corresponds to natural sunlight;
- Perfectly illuminates both plants and fish;
- Excellent quality (made in Germany).
Minuses:
- High price.
The lamp is designed for beginner aquarists. Its radiation will ensure the proper development of plants and will perfectly highlight the natural color of the fish.
JBL Solar Ultra Natur LT T5
5.0★★★★★editorial assessment
96% of buyers recommend this product
The unusually bright lamp can be used in tropical tanks, both with sea and fresh water. Excellent color rendering will provide bright and at the same time natural shades of all the inhabitants of the aquarium. Some components of the spectrum do not decrease to “0” and form a flux of light from sky blue to ruby.
Pros:
- Very bright glow;
- Ideal for tropical flora and fauna;
- Easy to find on sale.
Minuses:
- Expensive.
This versatile and very powerful device is suitable for any indoor pond.
Hagen Sun Glo
4.8★★★★★editorial assessment
87% of customers recommend this product
The glow emanating from this lamp is very soft, similar to daylight. Perfect for a fresh water aquarium with unassuming inhabitants with rich natural colors. For more demanding fish and plants, you will need to select an auxiliary light source.
Pros:
- Simulates daylight well;
- Slows down algae growth;
- Easy to find in stores;
- Budget cost.
Minuses:
- The color temperature is lower than that of daylight.
A lamp of medium brightness and a warm glow will create the most natural lighting for aquarium vegetation, and will also advantageously highlight the color of the fish. The manufacturer recommends combining it with the Aqua-Glo and Life-Glo models.
How long should I leave the light on?
Frankly speaking, there is no single answer to this question, since there are many factors to consider, and only this answer is true. On average, we can say that the owner will need 10 hours of light per day, again for an average aquarium.
However, tropical fish and plants do best with 12 hours of light per day, while cold-water fish and plants will only thrive with 8 hours of light per day.
Of course, if the aquarium contains only fish and no plants, less light will be needed. Conversely, only in a planted aquarium it is better to keep the light on for about 12 hours.
The timer is a good helper in maintaining the lighting regime
Aquarium lighting schedule
First, you need to create a lighting schedule for the aquarium so that the owner can monitor the lighting time.
Typically this plan should include:
- watch;
- the time of day at which you need to turn the lights on and off.
To relax and not be afraid of missing a deadline, it is better to simply set a timer so that you turn off the lights at the same time every evening and turn them on again the next morning.
How to choose the right lighting
When asked whether it is possible to turn off lighting devices, you must say with confidence that yes. However, some criteria should be taken into account:
- fish requirements. Some fish prefer a lot of light. Other inhabitants spend most of their time in the shade. Therefore, before moving in, you should clarify this information;
- presence of algae. Vegetation in a container requires lighting at least 14 hours a day. Otherwise, the plants become weak and grow slowly;
- device type. Some lighting devices tend to heat the liquid. This can negatively affect the condition of aquatic life. Therefore, it is necessary to switch off at night;
- capacity volume and lamp power. Powerful devices can illuminate the entire container. Therefore, it is recommended to reduce the period of use of lighting so that the fish do not lose their bright color. Medium-power lamps are left on for a longer period.
Often, experienced aquarists use lighting devices with a special timer. A time is set that will bring the artificial living conditions closer to natural ones, and the device independently determines the operating mode.
Should you leave the lights on in aquariums overnight?
Proper aquarium lighting is important for fish and plants, but they also need a period of darkness to allow them to rest and recuperate. Therefore, it is best to turn off your aquarium lights at night to mimic the natural light cycle of plants and fish.
Many newbies may not know, but fish do sleep, however most species do not have eyelids and are dependent on the owner to turn off the lights and provide them with enough hours of pure darkness for them to take a nap. Therefore, it is best to keep your aquarium lights on for the recommended 8 to 12 hours, then turn off the lights to mimic the natural day and night cycle.
If the fish becomes worried when the lights go out, it is worth turning off the overhead lights in the room an hour before the aquarium lights go out. This should give the fish eyes an hour to adjust to the lower light settings before total darkness.
For plants, you should also gradually reduce the light level before turning off the light completely.
When to turn off the heating of the aquarium.
Modern aquarium heaters are equipped with an automatic thermostat. You set the desired temperature, and the heater turns on automatically when the water temperature drops below the set temperature, and turns off when the temperature is normal. Turn it on and forget it, no need to monitor it further.
But to avoid getting an electric shock, always turn off the latter when you are going to put your hands into the water. And make sure that the heater is not turned on without water, for example, when you drain some of the water for a change.
How to choose light
The light must be chosen depending on the parameters of your aquarium and the desired result.
Intensity and spectrum
Not all the world is the same.
Intensity refers to how strong or “bright” the light is. A spectrum is a way of describing a mixture of different colors or wavelengths of light. The spectrum of light is often defined as color temperature. Light sources that emit a yellowish or warm tint have low values, while light sources that emit a crisp bluish-white or cool light have high values. Most freshwater aquarium lights range from 5,500 to 8,000 Kelvin.
Intensity and spectrum are less important in fish-only or artificially planted aquariums. Too much light can promote algae growth, especially in aquariums without plants.
With live plants, the right intensity and spectrum can make the difference between success and failure. Water depth also matters. Some wavelengths, especially blue ones, penetrate deeper into water than others, and this can be critical for living plants
Type of lighting equipment
There are several types of aquarium lights available, allowing aquarists to choose the one that best suits their needs and the needs of their aquarium occupants. Here are some common freshwater aquarium options.
Incandescent lamps
If the owner is using old-fashioned incandescent bulbs, the lighting power should be around 25 watts per square meter of aquarium water.
However, incandescent lamps are obsolete for several reasons:
- In most cases, they are ineffective in penetrating water below 12 inches and will provide uneven lighting to the aquarium.
- Causes excessive heating and can heat the water above the temperature that was set to maintain heat, and then allow the water to cool with the lights off.
- Incandescent light bulbs are very expensive to operate compared to fluorescent and LED lighting.
- They have a very short service life and may even break if water gets on them when turned on.
Standard fluorescent
For many years this was the most common form of aquarium lighting and continues to be popular today. Affordable prices and a wide selection of lamps for various applications make fluorescent lamps an excellent choice for many aquarists. You can find strip lights and hoods, as well as a wide selection of lamps for rectangular, hexagonal and curved aquariums.
Bulbs fade over time and should be replaced every 10 to 12 months.
LED
These energy efficient lights are quickly becoming the most popular type of aquarium lighting and offer features not found in other aquarium lights.
Their main advantages:
- LED lights can be found for aquariums of almost any size.
- They consume much less energy than other light sources.
- They don't heat the water.
- LEDs last for several years without loss of intensity.
- You can find options with higher intensity, programmable timers, power and spectrum controls, night moon lighting, adjustable sunrise/sunset and moonrise/moonset timers, and different color options.
Proper light in an aquarium is one of the main components of success. Therefore, this issue must be approached carefully and provide the inhabitants of the tank with comfortable conditions.
Types of lamps
The water column of artificial reservoirs is illuminated with different light sources. The following types of lamps are used for this purpose:
- luminescent, having a gas-discharge light source. The light they provide in the aquarium is closest to daylight, which allows you to create natural living conditions for fish and vegetation. Moreover, for this purpose, LLs that are less powerful than, for example, incandescent lamps are needed. Most often, 3 types of fluorescent lamps are used in aquariums: T5, T8 and compact (CFL).
- metal halide lamps are one of the types of high-pressure gas discharge lamps. They differ from other GRLs in that they have special emitting additives. The basis of the MGL is a burner made of quartz glass or special ceramics. The burner is placed in a flask made of borosilicate glass, which acts as a light filter that cuts off hard UV radiation. Metal halide lights produce pure white daylight.
- LED If the diodes are selected correctly, they are capable of generating scattered light with a yellow or reddish spectrum. This is exactly the spectral composition that fish and plants need. LED lamps have the advantage of economical energy consumption, which is important for large tanks. A significant disadvantage of LED lamps is their high cost.
- Not so long ago, incandescent lamps in aquariums were the only lighting devices. But due to the strong heating, they are now rarely used. Mainly for temporary lighting in table lamps or floor lamps above the aquarium, but not near the water.
Incandescent lamps
Despite the low efficiency, the release of a large amount of heat with minimal efficiency, and a short operating period, conventional incandescent lamps have such an emission spectrum. It almost completely coincides with the solar one, that is, the one that is necessary for plants and other aquatic inhabitants.
Fluorescent lamps
Fluorescent lamps are often chosen by aquarists for several reasons:
- due to the dimensions of the glow area;
- variety of model range;
- absence of thermal radiation;
- sufficiently long service life.
However, in general, these devices do not have a radiation spectrum sufficient for normal lighting of aquariums. However, the industry produces specialized lamps of a similar operating principle that are capable of providing good illumination in aquariums of certain sizes.
Metal halide lamps
Metal halide lamps, which are often used to organize effective lighting in an aquarium, have improved characteristics:
- high power and large range;
- light output exceeding that of many modern light sources;
- long service life;
- the ability to create a light regime that practically coincides with natural light in natural bodies of water, that is, light that needs to be maintained for a certain period for aquarium plants and other aquatic life forms.
In addition, metal halide elements help to equip a Dutch or marine aquarium with good light and create contrasting lighting that will help the artificial ecosystem become a bright accent of the interior.
However, the thermal radiation of such a lamp dictates special conditions for the placement of the panel or spotlight, namely: a special suspended structure, which requires more careful calculation for aquariums that are planned to be illuminated with these devices, since placing such light sources close to the surface of the water can be harmful to plants .
LED lamps
The complex production technology of metal halide lamps does not allow making such a light source yourself, unlike equipment equipped with LEDs, which many aquarists design and assemble with their own hands.
In addition, preference is given to LED lamps for a number of reasons:
- economical energy consumption;
- operation from low voltage in the network;
- long period of operation.
Mercury vapor lamps
Mercury vapor lamps (HQL) are more expensive than fluorescent lamps and are used for deep tanks. They are especially useful for large marine aquariums. Mercury lamps are very powerful and produce a lot of heat, so they must be placed at least 20 cm above the surface of the water. They are rare, since due to the combination of characteristics, most aquarists prefer metal halide lamps to them.
Aquarists, please advise!
Andrey Kovalenko
“Aeration is required and the aquarium must be cleaned once a month” is a typical answer from a newbie:) “You need 1 watt of light per liter. “-well, of course, this is not an overclocked herbalist: ) SMOK Bochkarevs with such light instead of plants will choke algae like mad :) )
“Is 50 watts of light sufficient for a 100 liter aquarium with average vegetation? “-enough for plants like Vallisneria, so it all depends on what kind of plants you have. “Is it possible to use ordinary fluorescent lamps (and not T5, T8, etc., otherwise they are expensive)? “Do you mean energy saving? If they are, then yes, you can (take them with a temperature range of 4200K). “Do fish need light at all, or is indoor light enough? “-if the room is bright, then this (room lighting) will be enough for them. » What will happen to plants without light? “-there won’t be any:) “And another question about water changes: what is the frequency of water changes in the aquarium? How much should I change if the volume of the water is 100 liters (please, not in % but in liters)? “-it all depends on what kind of filter you have (if you have one, of course), the amount of vegetation, the number and type of fish) “Do you need to take out the fish when changing the water? “-No way! » Should I pour water straight from the tap or let it settle beforehand? “-stand for 1 day (so that the chlorine disappears).
Alex
Plants without light will die; light needs 1 watt per liter. No less than 0.5 watt/liter. Fish don't need light. Replace depending on population density; the more animals there are, the more often the replacement is required. There is no need to get fish, it is better to add settled water. On average, 20-30% is recommended every two weeks. That is, 20 liters.
Natalya A.
50W per 100l is the minimum, that is, 0.5W per liter, ideally 1k1, but you can enhance the lighting by gluing, for example, foil under the lamp to the lid. We have already talked about replacements, but if the fish are tightly planted, then you can change 20 liters a couple of times a week, and 25-30 liters if the planting is loose can be done once every 7-10 days. Without lighting, the plants will definitely die, and the fish can easily get by, I have 2 120 liter jars, so I rarely set aside water for changes, I pour it through the shower at the required temperature from a distance of 1.5 meters into a bucket and change it, the fish feel great.
Yuri Balashov
Is it possible to use regular fluorescent lamps (not T5, T8, etc., otherwise they are expensive)? —-Luminescent (LB-moon-white) and energy-saving (warm or yellow) are also available. Is 50 watts of light sufficient for a 100 liter aquarium with average vegetation? —-Calculation based on water, you have 80-85 liters of water. This means 80 W incandescent lamps or 80:3 = 27 W lume (18 W LB + 9 W energy-saving) or three 9 W energy-saving lamps. Do fish need light at all, or is indoor light sufficient? --Yes. What happens to plants without light? - They will turn yellow and wither. What is the frequency of water changes in the aquarium? - Ideally once a week. You can do it less often, but this is bad for fish and plants. How much should I change if the volume of the aqua is 100 liters? -from 8 to 27 liters per week. Do I need to remove the fish when changing the water? - in no case, the water was siphoned off and carefully added, the fish were swimming in the aquarium. Should I pour water straight from the tap or let it settle beforehand? - I don’t defend it, I just pour it by pressing the tap with my finger or through the shower. In this case, all gases come out with bubbles. The main thing is to fill the water 1-2* higher than in the aquarium.
Vadim74
Here is Ramazanka here))))) Lighting is watts per liter, a spectrum specific to flora is also desirable, fluorescent is the optimal and convenient option! The light is parallel to Pisces! Plants will bend and not only light is important for them, but also the correct soil, feeding fish that do not eat them, water corresponding to the biotope of their growth, at least more or less approximately! If you start from the norm, then once a week 30 liters of your volume with a slight siphoning of the soil from excess nitrate masses! And the growth of plants is affected by the amount of nitrates; if they go off scale, then harmful algae will grow and the plants will die! Of course, you can’t get fish, this is stressful and generally not acceptable and incorrect, there are regions where you can immediately pour it from the tap (with us) and there are where this is absolutely not possible, it depends on the quality of tap water, namely nitrites, chlorine nitrates, chloramine compounds, heavy metal compounds, fluorine, etc. nasty things - and even settling does not always solve these problems; the only thing is that only chlorine evaporates and the rest remains, so I recommend a water conditioner, for example this one https://www.petsinform.com/aquariumpharm/conditioner/tap-water.html
Alexander Popov
Change the water 20 liters per week, be sure to let it sit for 3 days or more, you don’t need to take out the fish, clean the glass as needed, 50 watts of light is enough only if it’s of high quality and it’s better than 3 20s and the fish, by the way, also need light.
Common Mistakes
Beginning aquarists often choose the wrong time for lighting the aquarium, causing the inhabitants to experience an excess or lack of light. To avoid this, the main mistakes beginners make are described below:
- Choose white - it is more comfortable for fish and greenery than the blue and red spectrum. These colors are used as highlighting.
- When exposed to too much light, threadbare, beard algae, and other algae begin to multiply profusely.
- Choose metal halide lamps or combine different types of lamps.
Light in an aquarium is one of the first characteristics that should be taken into account when arranging a home for fish and vegetation. Choose it responsibly, choosing high quality equipment.
Previous
Aquarium Choosing an aquarium compressor and the 3 best aerators for an aquarium
Next
Aquarium Choosing glue for your aquarium
Light spectrum
Colorful temperature.
In a natural body of water, the sun's rays lose part of their spectrum when passing through the water column. The red and orange part is absorbed in the first five meters. After nine meters the yellow spectrum is lost. An aquarium of such depth can only be found in an aquarium. In most aquariums, the light reaches the bottom in the full spectrum.
Experts advise using lamps with a color temperature above 5000 K (blue-violet spectrum). This will create good color rendition in the water and allow plants to develop better.
Characteristics of aquarium lighting
From an electromechanical point of view, special technical requirements apply to aquarium lighting:
- The net volume of 1 liter of water should account for 0.1-0.3 W of power.
- For nocturnal, shade-loving fish, 0.2-0.4 W/l is sufficient. Shade-loving plants should also be planted in such light conditions, for example, cryptocoryne, vallinseria, Java moss.
- If there are not very many plants in an artificial pond, then a lighting power of 0.4-0.5 W/l is sufficient.
- Optimal illumination is considered to be 0.5-0.8 W/l. This is the norm for a beautiful aquarium with luxurious plants and fish.
- If the planting with aquatic plants is very dense or there are ground covers among them, then the illumination must be increased to 1 W/l. These are aquaspake or Dutch. They are also often called by the name of the famous Japanese aquarist Takashi Amano, creator of unique underwater gardens.
It must be remembered that the light intensity drops by 50% for every 10 cm of water of average transparency. But illumination depends not only on depth, but also on the surface area of the water, its condition (transparency) and the parameters of the tank itself.
It should also be remembered that the choice of plants for it depends on the lighting power of the aquarium, since neither fertilizing nor the forced supply of carbon dioxide will save them if the light intensity is insufficient.
Lighting options for your aquarium in the photo gallery:
This is explained by simple physical laws, because only light is a prerequisite for the process of photosynthesis - the conversion of water, carbon dioxide and fertilizers into plant tissue and oxygen.
A clear indication of this phenomenon can be the formation of oxygen bubbles on the leaves of aquatic plants a couple of hours after turning on the lighting in the aquarium. This is considered a sign of a healthy aquarium.