Quickly navigate to the article
- 1 Which live foods are suitable for freezing?
- 2 How to properly freeze live food
- 3 How to defrost food correctly
- 4 How to determine the quality of frozen live food 4.1 Other interesting articles
How to properly feed frozen fish food? Before answering this question, you need to know what frozen live food is? Which aquatic organisms are suitable for freezing and which are not? And when purchasing frozen food, be able to determine its freshness and suitability for feeding to fish. Why is this so important?
The fact is that pet store employees are, as a rule, not aquarists and they don’t really care whether you buy sick or healthy fish from them, as well as high-quality or low-quality food. Therefore, in order not to throw money away, and also not to spoil the water and undermine the health of your fish, you need to have some knowledge.
Why is live food frozen at all? Live food is frozen in order to preserve its nutritional value and essential amino acids, which are so important for the fish’s body. But that is not all!
When feeding frozen live food to fish, they instinctively feel that this food is intended for them by nature and eat it with pleasure. And the higher quality the frozen food, the more useful it will be and the fish will like it. Frozen live food is significantly inferior to non-frozen live food, but frozen food is always better than dry or artificial food.
What live foods are suitable for freezing?
In case of mass catching of live food, it can be stored for quite a long period of time using freezing. All food items are suitable for freezing, provided that they are suitable as food for aquarium fish.
Of the most well-known live foods that are suitable for freezing: the larva of the peristous mosquito - coretra, the larva of the bell mosquito - bloodworm, the larva of the mosquito - culex (“devil”), etc. Among the copepods is Cyclops, and among the cladocerans are Daphnia magna, moina, ceriodaphnia, etc.
The larva of the peristous mosquito - coretra
Bell mosquito larva - bloodworm
Mosquito larva - culex
The tubifex is a species of oligochaete worms in the family Tubificidae.
The tubifex (a type of oligochaete worm of the family Tubificidae) is less suitable for freezing. After freezing, tender tubifex worms significantly lose their original appearance and turn into a porridge-like mass.
Representative of copepods - Cyclops
Representative of the Cladocera Daphnia Magna
Ciliates and rotifers are very easy to breed at home, so there is no need to freeze such food items.
What to Avoid in Fish Food
Not all products are beneficial for aquarium fish.
They should not be given:
- wheat flour is not a healthy source of carbohydrates for fish;
- soy flour - there are more suitable sources of protein for fish;
- wheat gluten - used as a binding filler, not beneficial for fish;
- potato protein - too high carbohydrate content;
- sorbitol - too high carbohydrate content;
- inositol - too high carbohydrate content.
Important! Many aquarists give liver and beef heart to predatory aquarium fish. Since these foods are quite high in calories and can lead to fatty deposits in the liver and other tissues, they should only be given in very small quantities.
You should also avoid feeding your fish baked goods, including cookies, and cheese products, as they contain unhealthy saturated fats.
How to properly freeze live food
The easiest way is to freeze the coretra. For example, I do it this way: I keep the caught larvae in a net for 15 -20 minutes to allow the water to drain completely. When frozen, excess liquid will turn into ice and squeeze the contents of the larvae out, leaving only one shell of them. Such food is considered a waste and is eaten very poorly or not at all by the fish.
Next, I place the larvae in specially prepared plastic jars in a layer of 10-15 cm and place them in the freezer. You can make plastic jars from the cut off bottom of plastic bottles. It will be more difficult to freeze bloodworms, as well as copepods and cladocerans. For high-quality freezing, it is necessary that the water content in them is minimal.
For this purpose, the bloodworms and crustaceans must be dried well, kept for some time on any thick material and, in a semi-dry, dehydrated form, placed in plastic molds or jars and placed in the freezer. Before feeding the fish, frozen food must be thawed.
How long can you leave fish without food?
This depends on the activity and fatness of the aquarium inhabitants. The more active the fish and the less fat reserves it has, the sooner it will need food. For example, nimble barbs will get hungry much faster than leisurely catfish or cockerels.
In any case, leaving well-fed adult fish without food for 3-5 days does not have much to worry about. But the fry should not be fed for more than two days in a row. It should also be noted that after starvation, the amount of food must be increased gradually so that the fish do not overeat. And it is better to use live food rather than dry food.
If there is a need to leave for a week or longer, then it is better to ask someone to take care of the aquarium inhabitants.
How to defrost food correctly
Note: Remember that repeated freezing significantly reduces the quality of the feed! All prepared frozen food is never completely defrosted. When re-frozen, it not only loses its natural appearance, but also its nutritional value.
If you purchased a briquette of frozen food, you need to break off a small piece from it and place it in a net, hold it under the tap, washing it with cold running water until it is completely defrosted, and only then feed it to the fish.
If you have defrosted too much food, you need to place it in a separate container, store it in a cool place and feed it little by little to the fish. If the food is frozen in a plastic jar, you need to place the jar in a net and place it under a small stream of running water. As the required amount of defrosted food accumulates in the net, defrosting should be stopped and the jar of frozen food should be placed in the freezer.
This method of defrosting live food is good because it is thoroughly washed, and its defrosted amount can always be controlled. To ensure that the food is always eaten by the fish, it is necessary to add it in small portions using tweezers or a measuring spoon for hygienic reasons. Floating feeders for frozen food are not needed since the defrosted food does not spread over the surface, but falls to the bottom.
What can you feed fish if there is no food?
Aquarium fish need complete and balanced nutrition, therefore, even when making it yourself, we must not forget about variety.
Find out how to properly use cyclops, gammarus, and daphnia as fish food.
The following products will help you meet your protein needs:
- boiled chicken eggs;
- boiled meat: beef, beef heart and liver (in small quantities);
- shrimp and shellfish in any form;
- bloodworms, daphnia, tubifex.
Raw live food can be used fresh, but freezing and further thawing will destroy many pathogenic microorganisms. Bloodworms can be caught in muddy reservoirs by washing bottom sediments. The tubifex is also mined in the same way.
Daphnia is often found in small bodies of standing water and is easily caught with a net.
Self-caught food must be kept in clean, cool water for at least three days. During this time, the invertebrates' intestines will be empty, which will reduce the risk of infection spreading.
The plant part of the diet can be replenished with greens, salad, dandelion leaves and chopped vegetables, fresh or defrosted. For fish, fresh or frozen cucumbers, peas, spinach and lettuce are suitable.
Some vegetables must be pre-processed; for example, peas must be boiled and their hard skin removed. And lettuce and spinach must be doused with boiling water and chopped to destroy poorly digestible fiber.
Important! You should not give cabbage to aquarium fish, as it can lead to fermentation of the water and the rapid spread of pathogenic bacteria.
How to determine the quality of frozen live food
You can determine the quality of frozen food visually. If you have a briquette with frozen coretra or bloodworms in your hands, take a closer look: are the larvae themselves clearly visible, as well as their correct shape and shell structure? If everything is hard to distinguish, refuse to purchase such food.
When transporting frozen food, avoid defrosting it. To prevent this from happening, frozen food must be transported in a thermos specially designated for this purpose.
Other interesting articles
- Varieties of aquarium fish The number of varieties of aquarium fish is in the thousands, and each of them has its own characteristics. Agile and...
- Does loud music affect fish in an aquarium? Aquarium fish are rightfully considered one of the most delicate and vulnerable pets. Their calm...
- How to distinguish a female from a male fish in an aquarium Goldfish are recognized as traditional inhabitants of aquariums. Their aesthetics do not leave many aquarists indifferent. However, their...
Benefits of frozen food for aquarium fish
A varied and nutritious diet for fish is no less important than for other pets, because the health and life span of aquarium fish depends on it.
Frozen food has long taken a strong position in the range of ready-made food due to many advantages: high nutritional value, ease of storage and natural appearance.
In an aquarium, fish are limited in their movement, so the correct approach to their nutrition is of particular importance. The most natural and therefore healthy food for fish is live food. However, any type of it is seasonal, storing live food is difficult, it does not stay fresh for very long, and sometimes dangerous bacteria that cause fish diseases get into the aquarium with it.
In the production of high-quality frozen food, fresh raw materials of natural origin are used. Using special technologies, the feed is disinfected, and to preserve all the beneficial substances of live food, shock freezing and modern packaging methods are used.
Benefits of frozen food
• easily digestible by fish; • diverse in composition; • contains natural amounts and ratios of minerals and vitamins; • has a natural appearance.
Many fish refuse dry food due to differences in the appearance and smell of food in natural conditions. Frozen food best matches natural food and is therefore eaten by fish with pleasure.
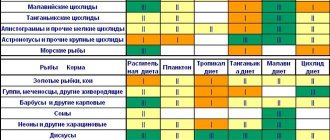
Typically, frozen food is divided into groups depending on the type of fish for which it is intended.
Table of approximate correspondence between different types of frozen food and different types of aquarium fish.
The frozen food includes: artemia, tubifex, gammarus, daphnia, bloodworms of various types, coretra, etc. Food can consist of one type of natural raw material or several in different combinations. Some foods are rich in vitamin complexes.