Very often in pet stores, aquarium fish sellers hear questions about how and what to feed them. However, the issue of feeding fish is not so simple at first glance, since it is necessary to know exactly the dosage of food per meal.
Proper feeding of the fish will be the key to their health and you will get great pleasure from watching them in the aquarium. Today we will try to outline in detail the basics of proper feeding of aquarium fish.
- Herbivores
Feeding aquarium fish: how many times a day
Beginning aquarists very often overfeed their pets, which has negative consequences. This most often leads to water contamination, which can cause the death of the inhabitants of the aquarium or cause them to become stressed. The harmful consequences that arise boil down to the following aspects:
- Leftover uneaten food decomposes quickly, which causes the release of ammonia.
- Excess food, especially protein ingested by fish, contributes to increased release of ammonia into the water space with waste products. The resulting ammonia in the water can deplete the biological filter. However, the biological filter can adapt and will cope with the increased level of the substance for some time, but the end result will be contamination of the aquarium and the development of various parasites.
So, how often should you feed your aquarium fish? At one meal, they need to be given as much food as they can eat in approximately five minutes. If excess food gets in, it must be removed before decomposition begins in the water space.
A very large number of fish and fry in nature feed continuously, for this reason it is recommended to feed them several times a day in small portions. Maintaining a large aquarium with a variety of aquatic inhabitants will require feeding them 2-3 times a day. An exception to such feeding will be representatives of predatory fish, for which 2-3 meals a day will be enough for one week. When predators are full, they may ignore new food.
When maintaining an aquarium, it is worth considering the fact that some species are nocturnal, as they may skip feeding. It is necessary to very carefully monitor the behavior of the fish when receiving food and promptly respond to loss of appetite.
From the video you will learn how to prepare semolina porridge for fish.
How to do it right
Before feeding, the aquarist should wash his hands thoroughly. Residues of soap or cream are destructive. Spices and spicy plant foods and sour vegetables should not be given. When selecting a diet, the characteristics of the fish are taken into account:
- size;
- age;
- food type;
- way of eating.
Herbivores with long digestive systems need to be fed small, frequent meals.
A proper diet contains:
- 5–10% fiber;
- 15–30% protein;
- up to 3% fat.
The lack of fiber is compensated by eating aquarium plants.
The basis of the diet of carnivores is live food. Predators eat rarely, but a lot.
- Proteins are required from 45%.
- Fat – 3–6%.
- Fiber is also important. Under natural conditions, they consume plant foods in an amount of 2–4%.
Most aquarium fish are omnivores; their diet should include:
- 30–40% protein;
- 2–5% fat;
- 3–8% fiber.
Eating methods
The fish are fed according to their feeding method. The position of the mouth plays a big role:
- Upper. For pets whose mouth is located on top, food in the form of chips or flakes floating on the surface is suitable.
- Average. Inhabitants of the middle layers of water eat the food that is located directly in front of them.
- Donny. Catfish that collect food from the bottom need heavy, sinking food.
What should you receive?
For good growth, normal development and strong immunity of a pet, the following nutrients and microelements are needed:
- choline;
- vitamins B and D3, A, E, C;
- folic acid;
- riboflavin;
- biotin;
- thiamine;
- cyanocobalamin.
How long can you not feed aquarium fish?
The need of aquarists for a summer vacation reflects a person’s natural desire to rest during the entire working year. However, during such periods the aquarium must be left unattended.
Note: A properly equipped aquarium can survive without human intervention for a certain period of time. Aquarium fish are very hardy creatures and can easily withstand a temporary lack of food.
Before leaving for a long period of time, you should not purchase new fish and plants (to avoid infection of the water area), fry and other small individuals. It is also worth reducing the dosage of food given and completely eliminating foods that pollute water from the diet. The fish will eat only the portion they need, and the remainder will begin to spoil the quality of the water. It is imperative to clean all aquarium equipment and refresh the water by replacing 1/3 of the total volume. It is not recommended to leave sick fish for a long time in a community aquarium.
Under such conditions, the fish can remain without feeding for 7-10 days, depending on the species.
How many days can fish live without food?
There are situations when you need to leave for several days, but there is no one to leave the fish with. This is where the question arises, how many days can the fish live without feeding?
Before leaving, thoroughly siphon the soil and replace 30% of the aquarium water with fresh water. A few weeks before departure, do not buy new fish, so as not to introduce an infection into the aquarium. Never leave healthy and sick fish together. Before leaving, you can feed your pets a little, but do not overfeed. If you do everything correctly, the fish will be able to live in the aquarium without human intervention for 7 to 10 days.
If you are leaving for a little longer, buy an automatic feeder. The principle of its operation is as follows: pour dry food into the drum (pellets, chips, tablets, the device instructions indicate which types of food are suitable), set an electronic or mechanical timer, with which you program the frequency of feeding and portion size, everything is ready. Then the drum rotates around its axis at a set time and food pours into the aquarium through the slots.
What to feed aquarium fish if there is no food
There are times in life when you suddenly run out of special food and you need to look for an urgent solution to the problem. However, there are ways to feed your pets by using the following tips (Figure 7):
- Earthworms: Large aquarium specimens are very willing to eat earthworms, but they must be thoroughly washed and crushed before dispensing. You should give the fish only the amount they need to completely satisfy their hunger.
- Raw meat without streaks of fat can be eaten in the absence of live food. Raw meat should be scraped off with a knife and given to aquarium pets only in this form.
- Cereals, especially buckwheat or semolina, as well as wheat porridge, are very readily eaten by all types of carp and labyrinth fish. However, such products should only be given as a last resort. The cereal must be boiled until it becomes a thick porridge, then rinsed under a stream of cold water and only after all the mucus has disappeared, strain through a sieve. You can store it in any cool place.
- Non-live food. This includes: dried daphnia, egg yolk, bloodworms (cut, dried and frozen), raw or dried meat, porridge, etc. Such feeds must be used with extreme caution, as they quickly decompose and begin to spoil the water.
Figure 7. Additional food for fish: 1 - earthworms, 2 - raw meat, 3 - semolina porridge, 4 - daphnia
Types of feed
Now let's talk a little about what types of food are
Artificial dry food
Currently, the choice of such feed is huge. Their quality is also at a fairly high level; Balanced in composition and containing many essential substances (some types of food combine 3-4 dozen plant and animal components), such food can satisfy the needs of almost all popular types of aquarium fish. When choosing food, pay attention to the manufacturer of the product, the shelf life of the food, its composition and what group of fish it is suitable for.
Please note that the information provided by artificial food manufacturers is not enough to evaluate and compare them. Until now, the main criteria when choosing food remain the authority of the manufacturer and application practice. The Aqua Logo company is the official supplier of the world leaders in the production of food for aquarium fish - Tetra, Sera and Hagen. In addition, from us you can purchase food from other brands popular in Russia (Aqua Medic, Dennerle, JBL, Tropic Marin). Feeds for different groups of fish differ in composition, size and shape of particles; they can sink (tablets and some granules) or float for a relatively long time in the aquarium (flakes and chips, floating sticks). Let's look at the feeding habits of some common groups of aquarium fish.
Let's start with goldfish, . Their diet (as well as the diet of other cold-water fish) should contain much less protein than food for tropical fish and more plant content. In addition, it is good if their food contains carotenoids - natural substances that increase the brightness of color. These requirements are best met by the brands Tetra Goldfish (the special formula of this food ensures health and increases the life expectancy of fish), Tetra Goldfish Color (balanced food Goldfish Color ensures the brightness of the color of goldfish, it contains an optimal set of vitamins and microelements for this type of fish, which improve health and give energy to pets), Tetra Goldfish Granules (food suitable for all types of cold-water fish, including
including gold ones, four different types of food are combined in one package: there are chips with high nutritional value and the required protein level, granules that provide bright coloring of fish, flakes that provide balanced nutrition), Tetra Goldfish Pro (about
The optimized protein to fat ratio of this food ensures better absorption of nutrients and guarantees an improved digestive process, used to reduce water pollution and therefore algae growth, the yellow center contains krill to enhance natural coloring and support muscle development, in red the rim contains nutritional elements, fatty
Omega-3 acids ensure healthy growth, the food contains shrimp to improve taste), there is a line of food for goldfish from Hagen Fluval and food from other manufacturers. For cold-water fish kept in ponds (koi carp, goldfish, sturgeon, etc.), special food is also produced, for example, the TetraPond .
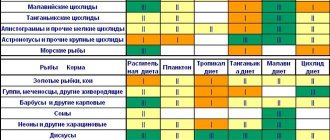
There are also separate types of food for fish such as cockerels (Tetra Betta, JBL Novo Betta, SERA BETTAGRAN, Dennerle Labyrinth, Dennerle Betta Booster), guppies (Tetra Guppy, Tetra Guppy Colour, JBL NovoBea), red parrots (Tetra RedParrot, Sera RED PARROT), Malawian cichlids (TetraCichlid Sticks, Fluval, JBL NovoMalawi, JBL NovoRift). The composition of these feeds is selected taking into account the food specialization of different fish species. Thus, food for red parrots contains special substances that keep the color of these fish bright and rich.
It is worth mentioning separately about fish, whose diet naturally contains many plant components, for example, mollies, swordtails, platies, labeos, and some cichlids. There are foods especially for them with a high content of plant fiber , for example, TetraPhyll, JBL GoldPearls, Sera FLORA, Fluval. Such foods may include spinach, as well as spirulina or other algae.
Picky and delicate discus need food that not only enhances color, but also contains easily digestible protein and many vitamins (for example, Tetra Discus Pro, JBL GranaDiscus Click, Sera).
For bottom-dwelling fish (various types of catfish, loachfish), shrimp and crayfish, there is food in the form of sinking tablets, which cannot be immediately chewed by the rest of the inhabitants of the aquarium. Often in such feeds the content of plant fibers and spirulina is increased, which corresponds to the tastes of benthic inhabitants (Sera Vipachips, Prodac ALGAE WAFER, Tetra TABLETS TABIMIN, Tetra WAFER MIX, Tetra PLECO TABLETS).
To enhance the brightness of the colors of red, orange and yellow fish (or those that have spots and stripes of such colors), for example, swordtails, platies, guppies, Sumatran and fire barbs, red neons, etc., we can recommend the following foods: like TetraRubin, TetraPro Color Crisps, JBL NovoGrano Color, Sera KOI ROYAL. They contain natural carotenoids, which affect the color.
For fry and growing juveniles, there are special foods that contain all the substances necessary for growth (for example, TetraMin Baby, TetraMin Mini, Tetra Tetramin Junior, Sera micron, JBL NovoBaby).
Many dry foods come in sinking kibble and floating flake forms. How to find out what suits your fish? - look at their mouth!
| Upper mouth fish prefer food floating on the surface. Above - Aplocheilus lineatus (lineatus, pike) Below - Altolamprologus compressiceps | It is more convenient for fish with a terminal mouth to collect food in the water column. Both floating flakes and sinking granules are suitable for them. Top - Apistogramma cacatuoides Bottom - Heros sp. | Fish with a lower mouth prefer to collect food from the bottom. Above - Corydoras adolfoi Below - Gyrinocheilus aymonieri |
When buying food, remember that an open can should be stored for no more than 2-6 months , otherwise the food will oxidize and some of the substances included in its composition, primarily vitamins, will be destroyed. So it’s better to buy a jar of a size that your fish will “eat” in the specified time. If you still feed the fish with food that has been open for a long time, add some vitamins to it: it won’t get any worse in any case.
Natural food
Live food should be used with caution . After all, it comes to pet stores, and therefore to our aquariums, from natural reservoirs. That is, there is a danger of bringing pathogens of fish diseases into the aquarium along with it; in addition, many bottom-dwelling invertebrates (for example, bloodworms and tubifex worms) can accumulate various harmful substances if they live in places where industrial waste flows. When buying such food, ask the seller where it comes from. And before feeding it, it must be washed more than once!!!
Some aquarists, when purchasing live food, freeze it in the freezer, thus killing possible pathogens. It is more convenient to purchase frozen food in the store. Our company offers Prime brand frozen food for any fish - predatory and herbivorous, marine and freshwater. The food is packaged in blisters - plastic containers with many small cells covered with foil. This food is easy to use and easy to store: it won’t spoil for months in the freezer!
Sometimes some particularly picky fish eat exclusively live food; they have to be gradually retrained to eat dry or frozen food. One of the most valuable and favorite types of live food for fish is bloodworms. Koretra is somewhat inferior to it in popularity; it is well suited for those fish that do not take food from the bottom. Cyclops is a very valuable type of food; it contains many vitamins, especially a lot of vitamin A and carotene, which make the color of the fish brighter. Tubifex is a very high-calorie and fatty food, often leads to obesity, and can accumulate large amounts of harmful substances, for example, heavy metals. Therefore, before feeding your pets a live tubifex, keep the worms for 4-7 days in a shallow tray with cool water with daily rinsing in cold running water (even better, of course, is to give the tubifex “constant” washing). Daphnia is rich in ballast substances that improve digestion; it is especially good to alternate it with protein-rich foods such as tubifex or bloodworms. Artemia larvae, ciliates and rotifers are often used in feeding fry.
Other types of aquarium fish are often used to feed predators: guppies, zebrafish, and young goldfish. You should not use fish caught independently in natural reservoirs; it may contain pathogens of dangerous diseases.
In addition to frozen food, you can please your pets with gelled food ( Tetra Freshdelica ), which preserves more vitamins and nutrients.
Food from your table and more
It turns out that fish are not at all against diversifying their diet with human food! For example, catfish, shrimp, ampularia snails will thank you for pieces of pumpkin and cucumber, carrots and apples, corn kernels (without juice, of course!) from a jar. They and many other fish will enjoy scalded leaves of lettuce, spinach, and nettle. Shrimp and squid meat, as well as mussel and oyster meat, will be enjoyed by many large cichlids and sea fish. Beef heart is not very suitable for feeding fish, the fact is that the protein contained in it is absorbed by fish only 3%, the rest decomposes and spoils the water! White bread is also not very suitable; in extreme cases, it is better to offer the fish some oatmeal or semolina. For fry, mashed boiled egg yolk is a very good food. But be careful: you need to feed it in very small portions, this food also pollutes the water a lot!
Vitamin supplements.
Here is a description of the most commonly found vitamin supplements for aquarium fish in stores. Sera Fishtamin is a multivitamin liquid preparation that is added both to fish food and directly to the salt or freshwater environment of an aquarium or garden pond. Application: 1. During illness and during the recovery period of fish. Add directly to the aquarium daily at the rate of 6-7 drops per 50 liters of water. Entered
before turning off the lights, since vitamins are destroyed in the light. 2. After possible stress (transportation, an overcrowded aquarium, or when incompatible fish species accidentally appear in the aquarium), as well as with each water change, it is necessary to add Fishtamin in a volume of 4-6 drops to the food. It absorbs the drug quite quickly, after which it can be fed to the fish. In case of stress, it is possible to add “Fishtamine” directly to the aquarium at the rate of 6-7 drops per 50 liters of water. 3. Adding new fish. After adding fish, you need to add Sera Fishtamin directly to the aquarium at the rate of 6-7 drops per 50 liters of water. 4. When breeding fish. Add “Fishtamin” before the start of the spawning process and within ten days from the start directly into the fish’s food at the rate of 4-6 drops per 50 liters of water. 5. To improve the growth of fry, once every two days, add “Fishtamin” directly to the food or brine shrimp solution, mix and give the enriched food to the fry. The daily dose of Fishtamine can vary from one to five drops and depends on the volume of food and the number of fry. 6. To enrich frozen live food with vitamins, immediately before feeding, add the vitamin at the rate of 3-4 drops per serving of food after thawing. Wait a while until the drug is absorbed into the food and then give it to the fish. 7. For pond fish, as well as for the prevention and treatment of fish from viral diseases, add Fishtamin 10-12 drops directly to their food every day for three weeks, wait until the drug is absorbed and then feed. Shake before use!
JBL Atvitol provides essential vitamins and amino acids to both fish and microorganisms living in the aquarium. Prevents symptoms of vitamin deficiency, increases color brightness, promotes fish growth, spawning, and increased appetite without the threat of obesity. Adding JBL Atvitol to aquarium water provides microorganisms with the vital active substances needed to combat biological pollutants, providing better conditions for biological filtration. Special emulsion treatment using lecithin prolongs the stability of vitamins in water. Application: Shake well before use. As a food supplement: 2-4 drops (per feed) daily per feeding. As an additive to aquarium water: 2 drops daily per 20 liters of water.
JBL Acclimol The vitamins and plant extracts in JBL Acclimol help acclimatize fish to their new aquarium environment without stress or other problems. Adds beneficial natural substances to aquarium water, reduces stress when introducing new fish into the aquarium, reduces the risk of disease and ensures stress-free transport of live fish. It is used when adding new fish to the aquarium, after working in the aquarium and during transportation of fish.
Dennerle S7 VitaMix is a complex of microelements and multivitamins necessary for fish and plants in the aquarium.
Supplies all necessary microelements and vitamins to the aquarium. Increases the color saturation of plants. Accelerates healthy growth of plants in the aquarium. Helps enhance the bright colors of fish. Application: 2 pumps of the measuring pump (approximately 3 ml) per 100 liters of aquarium water every week.
Tetra Vital
Tetra Vital contains a number of substances (vitamins, microelements, etc.) that have a positive effect on fish. The main features of vitamins: - improve vital energy, general condition and color - establish biological balance and contribute to the formation of a healthy biological environment in the aquarium - contain immunity-strengthening B vitamins and microelements - enhance the growth of aquatic plants and create a favorable environment for beneficial microorganisms - contribute to the creation of natural biological environment for fish in the aquarium, as they contain elements that are completely absent in tap water - the effect of the TetraVital conditioner is optimized using AquaSafe - suitable for all freshwater aquariums - used once a month (when using UV sterilizers - once a week).
Dennerle Elements+
contains a complex of vitamins that provides fish with all the necessary microelements. The complex includes minerals that are absent in tap water or consumed in the aquarium during life, such as iron, zinc, manganese, molybdenum and lithium. Ideal for adding trace elements to osmosis water. Does not increase overall or carbonate hardness. Dennerle Elements+ prevents micronutrient and vitamin deficiencies and diseases associated with these deficiencies. Suitable for all fish in a freshwater aquarium. Directions for use and dosage: 25 ml packaging per 800 liters of aquarium water. Usual dosage: for regular replenishment of spent microelements - once a week, 2 presses of the measuring pump-dispenser (3 ml) per 100 liters of aquarium water.
Is it possible to feed aquarium fish with bread?
All aquarists know that each type of fish needs special food. However, aquarium pets need carbohydrates and proteins. To correctly compile a feeding diet, consultations with experienced sellers in pet stores are necessary.
When it gets into water, the bread gets wet very quickly and begins to sour, which causes unpleasant smelling water. It will be possible to get rid of such a smell only after completely replacing the water space of the aquarium. For this reason, using bread as fish food is not recommended.
What happens if you underfeed?
The basic principle of feeding fish in an aquarium is: it is better to underfeed than to overfeed.
It is believed that a healthy adult fish can go without food for up to several weeks. However, you should not experiment, it can lead to unpleasant consequences. From rare and meager feeding, fish lose weight , their abdomens become sunken, and their backs dry out. It may all end with larger individuals starting to attack smaller ones and simply eating them.
The only exception to systematic feeding is the spawning period. The feeding pattern of the fish at this time should look like this: two weeks before spawning, they need to be well fed, especially with food of live origin, but during the spawning period the amount of food can be reduced. Experienced aquarists do not give them food at all for several days.
Features of feeding
When growing fish in a pond, the feed requirements are slightly lower, because in natural reservoirs there is natural food that needs a little supplementation. Typically, fish food is introduced in the form of granules, briquettes or dough-like mass. Pay attention only to granules or briquettes, as they have high moisture resistance, while the dough-like mass will soon lose half of its useful substances.
In early spring, when the fish wakes up, feed it more nutritiously than in summer. In hot weather, the fish do not eat as much, as they can find food in the pond itself. And in the fall, when the water temperature drops below 10 degrees, stop feeding the fish completely, since in winter most species go into a dormant state.
River fish hunters
Birds that feed on fish pose a great danger to them, regardless of their habitat. Winged enemies of river representatives are black-headed gulls, gray herons, cranes, ospreys and white-tailed eagles. These voracious birds can destroy huge quantities of fish. Let's find out more about them:
- The black-headed (river/black-headed gull) is an omnivorous, picky eating bird of small size. Thanks to the membranes on their feet, seagulls swim well, and catching fish from the surface of a reservoir is not difficult for them.
- Gray herons and cranes are fairly large birds that prefer only animal food. Fish makes up up to 80% of their diet, the remaining 20% are frogs and rodents.
- Ospreys are river eagles. They are listed in the Red Book. Osprey is a bird that feeds on fish and only fish! They hunt with the help of their clawed paws, capturing prey from the water. Osprey is the most terrible enemy of river inhabitants, regardless of species.
- The white-tailed eagle, like the osprey, is listed in the Red Book. It is a large bird of prey that feeds on fish and smaller birds. The white-tailed eagle's menu also includes hares, gophers, marmots and other rodents. They do not disdain carrion.
Winged sea hunters
Fish that live in the sea are also not immune to becoming food for birds. Their lives are actively encroached upon by such feathered gourmet lovers as cormorants, albatrosses, petrels, and gulls. In the northern seas and oceans, penguins hunt for fish.
- The cormorant is a fairly large bird that feeds not only on capelin, sardines and herring, but also on shellfish. The eyes of these winged hunters have a transparent nictitating membrane, which, when immersed under water, serves as a kind of underwater glasses. Thanks to this anatomical feature, cormorants can perfectly see their prey under the water.
- The albatross is a long-lived sea creature. During its 30-year life, one individual eats a huge amount of fish, as well as crustaceans, squid and mollusks. Albatrosses can dive 15 meters deep and also have an extremely accurate sense of smell.
- The petrel is similar in appearance to the pigeon, but, unlike the latter, it is much larger in size and has webbed feet. The life cycle of these birds is 20-26 years. Their diet is the same as that of albatrosses and cormorants. Petrels also often accompany ships, eating food waste.
- Seagulls are the only birds that have no natural enemies. Their main diet is primarily fish, but also shellfish, insects, small birds and their eggs, crustaceans, carrion and waste. These cunning creatures have become adept at getting mollusks out of even the most durable shells by throwing them from a height.
- Penguins are gourmet birds. They will never eat rotten or stale fish, as seagulls or petrels do. Their diet should be exclusively freshly caught, it consists of plankton, fish, krill, squid and cephalopods. Penguins obtain food by diving to a depth of 20-70 meters.
Aquarium migrants menu
Aquarists have a fashionable tendency to create imitation of the depths of the sea. To do this, the aquarium is decorated with corals, anemones and exotic fish from the seas and oceans are introduced there. An ignorant person is unlikely to be able to choose the right “company” - after all, many inhabitants of the pseudo-sea behind glass can destroy each other in accordance with their dietary characteristics. Aggressive fish-predators will always prey on peaceful phytophages - this should be taken into account when choosing multi-colored “residents” with fins. Particular attention should be paid to what fish eat in the sea. The most popular predatory aquarium “overseas guests” are discus, astronotus, piranha, lionfish, apistogramma, and yellow.
Among the peaceful inhabitants of the sea, clown fish, lalius, angel fish, neons, minors, and tetras can settle in the aquarium.
If you decide to create your own underwater world in your home, it is worth finding out what aquarium residents eat at home - in the sea or ocean. Predators like yellowfish dine on snails and small crustaceans, and are also not averse to hunting small fish. Other cichlids, as well as astronotuses and piranhas, are not far behind them.
But algae is what the clown fish eats. As well as most other peaceful aquarium inhabitants.
Food of marine predator fish
- Mackerel is one of the most beloved fish consumed by humans. This is a euryphage predator that feeds on both plankton and smaller ones of its own kind.
- Pink salmon is one of the most important commercial representatives of the Salmon family. In some countries this fish is called “Russian salmon”. Its diet consists of mollusks and smaller fish, crustaceans and fry.
- The catfish prefers cold water, so it lives at fairly great depths. Thanks to its well-developed jaws, its menu is very diverse. Catfish eat crabs, clams, sea urchins, lobsters, starfish and sometimes jellyfish. Catfish also do not disdain fish, which are significantly larger in size.
- Flounder is unique due to its unusual appearance. This flat creature leads a bottom-dwelling lifestyle and hunts crustaceans and small fish, attacking them from its sandy shelter.
- Halibut belongs to the Flounder family and eats the same food as flounder. Preference is given to capelin and pollock.
- Horse mackerel is a fast hunter. Its prey is such fish as anchovy, red mullet and mullet. It does not refuse its own young. In turn, horse mackerel is a favorite food for dolphins.
- Salmon is the most loved fish by people. It is widely used in cooking in all cuisines of the world. In the sea, salmon feed on herring, sprat, smelt, herring and crustaceans.
- Tuna belongs to the Mackerel family and is the most valuable commercial fish. It feeds on cephalopods and some species of small fish, as well as squid and shrimp.
- Cod and pike perch in their food preferences are no different from the above “brothers”.
Inhabitants of the salt sea
The depths of the sea are simply teeming with all kinds of fauna, and especially fish. Like river ones, they can be peaceful and predatory. What do fish eat in the sea? Due to the fact that it is more densely populated by different organisms, the menu of marine cold-blooded animals is more diverse than their river “relatives”.
The most common marine “brothers” of river fin fish, leading a relatively peaceful lifestyle, are pelengas, herring, mullet, red mullet and ram. Why "relatively"? Because these algae-eating fish can sometimes dine on their own kind.
The menu of aggressive fish, in contrast to the peaceful inhabitants of the deep sea, is more diverse. What do marine predator fish eat? It is interesting to know that a small predator with fins may well form the diet of a larger carnivorous fish. The most common commercial species are mackerel, pink salmon, catfish, flounder, halibut, horse mackerel, salmon, tuna, cod and pike perch.
Underwater vegetarians
The peaceful inhabitants of the river depths are harmless fish that feed on algae, phytoplankton, and detritus. Phytoplankton are tiny plant organisms that inhabit water bodies in large numbers and move due to currents.
Phytoplankton is often not visible to the naked eye, so people do not attach importance to it. Many of us are not even aware of these microscopic organisms, but they are the most important vegetarian component of what the fish in the river eat. This is especially true for species such as carp, silver carp and tench. Let's find out more about them:
- Cupid is a native of the Carp family. It feeds exclusively on plant foods: mud, various algae, reeds. It can also consume land plants that are flooded during river floods.
- Silver carp are in the same family as grass carp and prefer microscopic algae and detritus. The mouth of the silver carp is a kind of “filtering apparatus”, thanks to which this fish filters green water, being a kind of river orderly.
- Tench is a very sedentary fish that prefers to live near the bottom or in algae thickets. More than 60% of its diet consists of algae.
River settlers
Looking at the river, we can’t even imagine how many different living creatures live under the water surface. Each area has its own “sets” of river fish. For example, in rivers in Russia there are such representatives as bersh, cupid, dace, ruffe, sturgeon, char, whitefish, and grayling.
Also in Russian waters you can find smelt, pike, carp, bream, and asp. In addition, there are crucian carp, minnows, silver carp, roach, rudd, tench, catfish, burbot, and river perch so beloved by anglers. And this is not a complete list of all types.
What do fish eat?
The nutrition of fish, like any living creature on earth, ensures the flow of all energy (and other!) processes in their body.
Like many other inhabitants of the planet, fish in the first stages of their life provide it from the resources that were transferred from the mother’s body - we are talking about the yolk of caviar.
But due to this way of feeding, the fish cannot survive for a long time - only for a limited period of time. And after a period of mixed feeding, they usually completely switch to the appearance of the food.
What determines the effectiveness of feeding?
The conditions in which fish are grown have a direct impact on the growth rate and quality of fish meat. An important point is water temperature - a large number of species increases their growth rate when the water temperature in the reservoir rises. If the readings drop to 0 degrees, then food digestion first slows down, and a little later the process stops altogether.
The quality of food also matters (protein food accelerates the growth of fish) and the amount of oxygen in the water (a value of 1 mg/l is too low for fish, and it stops growing and eating). The big disadvantage of low oxygen levels is the increase in ammonia and nitrate concentrations, which also negatively affects growth.
Take care about the length of daylight hours. Since daylight hours tend to decrease with the approach of colder seasons, it makes sense to use artificial lighting to stimulate the production of growth hormone and improve food digestion.
Keep an eye on the salt level in the water because some fish species can only be kept in either fresh or salt water. The exception is tilapia, as it can grow in any type of reservoir.
To dispense food, use special feeders that you can make yourself. You will find detailed instructions on how to make such a feeder in this video:
To each their own menu
According to the nature of their behavior and food preferences, fish are divided mainly into predatory and peaceful. Predatory fish are fish that eat fish and only occasionally eat other foods. They pose a serious threat to vegetarian fish, especially if they are small in size.
Peaceful ones, in turn, are herbivores, benthophages and planktivores. Basically, these are fish that eat algae.
Herbivores consume exclusively phytoplankton, in other words, floating algae. Benthophages are fish that feed on algae that grow at depth (they are called phytobenthos) and organic particles. Planktivores prefer zooplankton and do not disdain single-celled organisms that inhabit the river.
In addition, there are omnivorous euryphages - fish that feed on fish, algae and small invertebrates. Their menu is the most diverse.
What do different types of fish eat?
Absolutely all fish differ from each other in the food they eat and their behavior during feeding. Predatory fish species can set up some kind of ambush when hunting their prey or freeze in anticipation of approaching prey. However, other predators may pursue their prey in the desire to overtake and capture the prey.
Herbivorous species primarily feed on living or decaying plant tissue. Aquarium fish get food by biting off parts of plants or can swallow them whole. However, among herbivorous fish there are species that eat only algae.
Herbivores
Herbivorous or herbivorous fish
They have a small stomach and long intestines, so one meal is not enough for them. Some herbivores, such as cleaner fish, spend the entire day “grazing” on aquarium plants and eating small algae. The protein content in the diet of herbivorous fish is 15-30%.
The diet of herbivorous fish can be made up of specialized food and scalded vegetables, for example, zucchini, cucumber or lettuce.
Carnivores
Carnivorous or predatory fish
feed mainly on protein foods. Protein in the diet of such fish is more than 45%. Predatory fish have a large stomach. Typically, they are fed once a day. There are species of fish that swallow food fish whole and then digest it for several days.
The diet of predatory fish can be made up of specialized dry food and live or frozen food.
Omnivores
Omnivorous fish
the most common inhabitants of aquariums. Protein in the diet of omnivores is about 40%. These fish are the easiest to feed; you can offer them any type of food, just don’t forget to vary their diet.