This species is an artificially bred form of the Blue Gourami. Breeders selectively bred the desired traits and reinforced them over several generations, resulting in new color variations, including Gold and Platinum Gourami.
Requirements and conditions:
- Aquarium volume - from 130 liters.
- Temperature - 22–28°C
- pH value – 6.0–8.0
- Water hardness - soft to medium hard (5–19 dH)
- Substrate type - any dark
- Lighting - moderate
- Brackish water - no
- Water movement - weak or standing
Fish parameters:
- Size - about 13 cm.
- Food - any
- Life expectancy - from 4 to 6 years
Description
The fish is medium in size, has an elongated, somewhat oval body, laterally compressed. The fins are large in comparison with the body, round in shape. In the process of evolution, the pelvic fins have changed to thread-like sensitive processes, with the help of which Gourami studies the world around it. Like other representatives of Labyrinths, it has a special organ that allows it to absorb atmospheric air, swallowing bubbles from the surface of the water. The color is pale blue with dark spots of irregular shape, reminiscent of a marble pattern. Small light specks are noticeable throughout the body, which together give a unique ornament.
What are antibodies to coronavirus?
Antibodies (also known as immunoglobulins) are special proteins that are produced and/or produced by plasma cells.
What do immunoglobulins do?
Immunoglobulins are formed in response to foreign bacteria or viruses entering the body. They interact with the antigen (specific site of the pest) and neutralize it.
Thus, our immunity guards our health.
What classes of immunoglobulins are there?
There are 5 classes of immunoglobulins
, some of which contain subclasses.
IgA - secreted on the surface of the epithelium and present in saliva, tears, and on the surface of mucous membranes.
IgM - detected upon initial exposure to antigen.
Indicates an acute infectious process in humans.
IgG is the main class of immunoglobulins that protects against viruses, bacteria, and toxins.
IgD is found on the surface of developing B lymphocytes. The function is not installed.
IgE - secreted during an immediate allergic reaction.
Maintenance and care
A group of fish will require a spacious tank of about 150 liters, although for one fish a volume of 40–50 is quite sufficient. The design of the aquarium should include a tight-fitting lid, under which an air layer with increased temperature and humidity is formed, which minimizes the risk of damage to the labyrinth organ of the fish when swallowing atmospheric air. The recommended equipment is as follows: filter, aerator, heater, lighting system. There are combination filters that spray air bubbles instead of an aerator, so the latter may not be necessary. It should be borne in mind that the fish prefers very weak water movement; a strong current will lead to stress and unnecessary physical exertion in an attempt to cope with it. When choosing a filter, choose a productive model, but it should create a weak water flow. The design must include shelters in the form of grottoes, rocks, snags and loose vegetation cover. The optimal location of plants is along the side and back walls of the aquarium. Floating plants are welcome. The substrate is preferably dark, it will highlight the color of the fish.
How to distinguish a female from a male
An important factor when breeding Gourami is sex determination.
The main most informative feature by which sex can be determined is the dorsal fin. Males have a longer and pointed dorsal fin. In females it is much shorter and has a rounded shape.
Another sign is the brightness of the color. Males have brighter, more striking colors, while females look noticeably simpler. But when determining sex by this characteristic, it is easy to make a mistake, since with the disease the color can become noticeably duller.
Social behavior
Adults exhibit individual behavioral traits ranging from shyness to aggression, which can create problems in the future, especially if a very temperamental fish is encountered. However, hostility is directed primarily towards newcomers, and to a lesser extent towards those with whom Gourami grew up. There is a clear intraspecific hierarchy, the stronger male becomes the dominant individual and can attack his weak relatives. Single, pair or harem housing seems optimal. You can choose from large and calm fish as neighbors, such as some catfish. Active individuals provoke aggression, and very small fish can be perceived as food/prey.
BAU/ml - new interpretation of the test for antibodies to coronavirus
The World Health Organization has approved a new international standard for the determination of immunoglobulins for coronavirus, with the unit of measurement BAU (translated as “binding antibody coefficient”).
Interpretation of quantitative analysis for antibodies to coronavirus
Laboratory diagnostics
the level of immunity protection against coronavirus is carried out by studying immunoglobulins to the S-protein of the virus. To facilitate the interpretation of the study results, it was proposed to use a universal measurement system.
Conversion table for antibody test results from different manufacturers in BAU/ml
| Manufacturer | Conversion factor to BAU/ml |
| Abbott ARCHITECT | 0,142 |
| Roche | 1 |
Breeding/reproduction
Breeding is quite simple. If you keep only two fish, then spawning can be carried out in the main aquarium; otherwise, it is recommended to use a spawning tank, where the pair will be temporarily located, and then their offspring. Spawning is stimulated by the inclusion of meat products in the diet and an increase in water temperature to 26°C. If there are few plants in the aquarium, including floating ones, the fish may not begin to spawn. Over time, the female becomes filled with eggs, and the male begins to build a nest from bubbles and pieces of plants, usually in the corner of the tank. After the completion of construction, the courtship period begins, the male presses against the female, touches her, inviting her to the nest. An adult is capable of releasing up to 700 eggs, which are immediately fertilized, the male collects them and transfers them to the nest, the female should be immediately removed from the aquarium. The male stands guard over the clutch and attacks anyone who gets too close; his attacks can be fatal to those attacked. When the fry are born, it is time for the male to leave his offspring and join the female, otherwise they will become his prey. Feed the fry with microfeed, artemia, ciliates.
Frequent symptoms
Most gourami diseases are accompanied by characteristic symptoms. For gourami gastrointestinal problems, these include lack of appetite and unhealthy excrement. Lack of mobility usually means internal illness, such as infection or viruses. Photophobia accompanies eye problems. But some symptoms correspond not to one disease, but to dozens, so you cannot stop at one variant of the disease and immediately begin treatment.
Lies or sits on the bottom
This problem is usually encountered by aquarists who have just recently bought gouramis and placed them in a community aquarium. At first, the new inhabitants behave like healthy gourami, but then they begin to swim less, move only when feeding, and then do not float up from the bottom. Usually, if a gourami lies on the bottom with a large slope towards the substrate, then it is difficult to save it, because this is the end of the development of diseases.
This condition develops when gourami are not properly cared for: in conditions of lack of filtration, overcrowding.
What to do if the fish is lying on the bottom:
- Remove the sick gourami from the general aquarium and place it in a separate container.
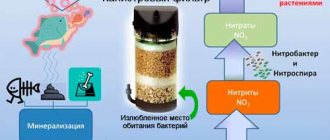
- Before treatment, check the water parameters for nitrates, nitrites and other poisons using tests.
- Replace some of the water in the community aquarium with clean water.
- Check other residents for similar symptoms of the disease.
- In a patient with gourami, based on other accompanying symptoms, determine the approximate source of the disease and apply treatment in accordance with it.
- If the treatment helped, then apply the medicine in a weak concentration to the rest of the aquarium for prevention. Provided that it is not physical damage.
Gourami lies on the bottom usually due to several possible diseases:
- Ecto- and endoparasites manifest themselves by forming abscesses, holes, and rashes in the body and fins.
- Fungal diseases - a coating similar to cotton wool or white fluff forms on the pet’s body.
- Bacteria cause disorder of internal organs, so the disease is manifested by changes in excrement, mucus discharge from the mouth and gills, and swelling of the insides.
Has turned black or darkened
Changes in color by several tones are typical for gourami fish at different periods of life. A pet can lighten or darken a little due to changes in the composition of the water and food diet. The coloring appears brighter before the spawning period to attract females. Therefore, the aquarist should not worry.
It is normal for some gourami species to darken before spawning. This is especially true for the marbled gourami, which turns into almost a black gourami to attract a female. But the pearl gourami, which is usually distinguished by its silver color, becomes purple in color before spawning. Before breeding, the spotted gourami changes its color from light olive to several darker tones, the spots and stripes take on a dark color. In honey gourami, a change in color causes not only procreation, but also fright, in which they turn into honey-brown and dark orange fish.
But the reasons for the darkening of the color of gourami also depend on changes in the composition of the water, not always in a positive direction. Therefore, check the water for nitrates and nitrites, replace some of the water.
Diseases
A very hardy species, able to adapt to various conditions and survive short-term deterioration in water quality. In a balanced aquarium, health problems, as a rule, do not arise. Systematic disruption of the diet, long breaks in food supply, and significant deterioration of living conditions will inevitably lead to outbreaks of diseases. Read more about symptoms and treatment methods in the section “Diseases of aquarium fish”.
Peculiarities
- Adults can be aggressive
- They do not tolerate water movement in the aquarium well
What to feed Gourami in an aquarium at home
Under natural conditions, the food consists of malaria mosquito larvae and small aquatic invertebrates. They can also feed on tender parts of plants. They are unpretentious when it comes to food, but it is still advisable to provide them with not only a varied, but also a balanced diet.
There is a large selection of different dry, live and frozen food available for sale. When choosing food, you should take into account the types of fish living in the aquarium. And it must be remembered that Gouramis have a small mouth and the size of the food should correspond to the capabilities.
Feeding should be done several times a day. In this case, the food should be eaten within a few minutes. When an excessive amount of food enters the aquarium, some of it does not have time to be eaten by the inhabitants, and it settles to the bottom, which leads to the avalanche-like development of a large number of harmful bacteria. Thus, uneaten food residues not only worsen the quality of water, but also create unfavorable bacterial conditions for normal development and life. Very abundant feeding also leads to obesity, which leads to a short life. It is better to underfeed a little than to overfeed, especially since the lack of food for 2-5 days will not have a negative impact on health.
Aggressive neighbors
Before you go to the store for pets, think through to the smallest detail: will several species be able to get along in one fish house? You should not count on the seller’s competence, since his main goal is to sell as much product as possible.
A few fundamental rules:
Unfortunately, it is impossible to determine why the fish are dying. The death of a pet can happen even among experienced breeders. Treat your fish carefully, and you will definitely notice a change in behavior and eliminate the cause of concern in time. More often than not, fish die in an aquarium due to oversight, and not due to other criteria.
Hello, dear friends!
3) The third mistake is neglecting the aquarium lighting. The fact is, friends, that for most tropical fish the daylight hours last 10 - 12 hours. Our daylight hours are somewhat shorter, especially in winter. And if the fish does not receive enough light, then its biological clock will simply break. And since a fish is a fragile creature, death follows such a breakdown. Keep this in mind for the future!
4) Another reason for the frequent death of fish is the incompatibility of species. And this applies not only to carnivorous and herbivorous fish. There is also the factor of nitrogen tolerance. For example, if some fish do not react in any way to an increase in nitrogen concentration, then others die from acute nitrogen poisoning! There is only one piece of advice in this case: study the characteristics of each species before combining them in one aquarium!
6) Improper feeding is also a common cause of mass death of fish. For some reason, beginners think that all they have to do is throw a pinch of dry food into the aquarium and that’s it! This is absolutely wrong! Fish should eat a varied diet! And if they eat only dry food, they will very soon die from inflammation of the stomach and intestines: dry food is very difficult to digest! Diversify your fish's menu: give them dry food, live food, and plant food! For example, many fish love lettuce leaves, which need to be chopped.
That's all, dear friends. I really want you to draw the right conclusion from everything you read in this article. And remember: if you are too lazy to care for fish, then you shouldn’t have an aquarium!
All the best to you and see you in the next articles!
Have you ever looked into an aquarium trying to figure out whether your fish is alive or not? Read this article to see if it's her time to die.
Prevention
Many diseases of gourami are directly related to poor quality care and maintenance:
If all these facts are eliminated in a timely manner and the conditions are made suitable for maintenance, then many diseases can be prevented. To do this, you need to quarantine new plants and fish, change water weekly - 30% of the total volume, siphon the soil, wash the filter, remove rotten parts of plants, dead fish and snails. Caring for an aquarium with gourami is the key to fish health!
Undoubtedly, there are many medicines that can be used to cure gourami. However, it is easier to prevent this from happening by sticking to prevention. Good and high-quality care is the key to healthy fish, which will delight you with their beauty.
Source
Prevention
Many diseases of gourami are directly related to poor quality care and maintenance:
If all these facts are eliminated in a timely manner and the conditions are made suitable for maintenance, then many diseases can be prevented. To do this, you need to quarantine new plants and fish, change water weekly - 30% of the total volume, siphon the soil, wash the filter, remove rotten parts of plants, dead fish and snails. Caring for an aquarium with gourami is the key to fish health!
Undoubtedly, there are many medicines that can be used to cure gourami. However, it is easier to prevent this from happening by sticking to prevention. Good and high-quality care is the key to healthy fish, which will delight you with their beauty.
The kissing gourami wishes health to you and your pets!