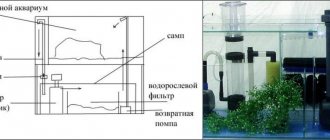
Advice
Peroxide is a cheap and quite effective remedy. When it gets into the aquarium, an active reaction begins to occur. In this case, the substance decomposes into two harmless components - oxygen and water. But despite this, peroxide should only be used if severe rot of the fins of veiltails, barbs, livebearers, etc. is detected. At the initial stage, it is better to treat the fish with some more gentle commercial product. In any case, you need to add peroxide to the aquarium in an amount of no more than 2.5 ml per 10 liters of water. Otherwise, aquatic plants will be damaged. In particular, they do not like vallisneria peroxide, various types of mosses, camboba and hornwort. Adding 4 ml of this substance per 10 liters to an aquarium will pose a danger to the fish themselves. Fortunately, peroxide does not have any special effect on the biofilter bacteria.
Is it true that anal sex leads to hemorrhoids?
There is no data that would reliably confirm the correlation between anal sex and, for example, hemorrhoids. The main danger of anal sex is, of course, the transmission of infections, for example, the human papillomavirus, which causes cancer. human papillomas. Even Koch bacilli - the culprit of tuberculosis - in 5% of cases live in the rectum, and not just in the lungs.
“Non-standard” sex can lead to anal fissures, damage to the mucous membrane, and bleeding. Insufficiency of the anal sphincter also develops, which can lead to fecal incontinence. And weakening of the ligaments leads to prolapse of hemorrhoids.
Evidence-based medicine does not answer this question, but it’s better to be careful.
Treatment
The initial stage of therapy consists of examining and changing for the better the microclimate of the aquarium.
First you need:
- clean the filters;
- remove rotten aquatic plants from the aquarium;
- Boil the soil, decorations, and net for 15-20 minutes before putting them back.
Next you need to replace the water. It is better to increase the water temperature to the maximum tolerated by this type of fish.
The main thing to remember is all aquarium inhabitants. It may happen that others will not tolerate the change in temperature. In such a situation, the sick fish can be moved to another place, or wait a couple of days without changing the temperature.
If her condition begins to improve, then there is no need to take any further actions.
If increasing the water temperature does not produce results, then drug therapy must be used. Basically, for a mild stage of the disease, treatment will consist of adding a mixture of a specific element to the general aquarium in an appropriate dose, or taking separate treatment baths for the fish.
Prevention
It should be remembered that the causes of outbreaks of fin rot are often violations of the basic rules of maintaining an aquarium. To avoid this unpleasant disease, you need to be careful when selecting fish for your home pond: choose healthy, active specimens, without the slightest sign of infection. Be sure to withstand quarantine for newcomers.
The maintenance of the community aquarium should also be at a high level. Good aeration, filtration and regular water changes, control of its quality, correct temperature - these are the necessary conditions that prevent the growth of bacteria. It is also worth avoiding changes in temperature - it has been noticed that fish that for some reason find themselves in water that is too cold for them often get sick with fin rot. This happens especially often with guppies, which are generally very hardy, and various types of angelfish, which are generally very thermophilic. And even seemingly cold-resistant species of goldfish are sensitive to sudden temperature changes.
Healthy fish, living in good and calm conditions, consuming high-quality and varied food, have strong immunity and are less susceptible to any diseases.
Fin rot: treatment in a community aquarium with hydrogen peroxide
Of course, H2O2 should be used correctly. To treat fish from fin rot, a 3% solution of this substance is used. It is this peroxide that is sold in pharmacies in liquid form. If necessary, you can make a 3% solution from tablets. You will need 6 pieces for a glass of water. To treat fin rot, you need 2-2.5 ml of the product per 10 liters of water.
Of course, you cannot pour a pharmaceutical solution or a solution prepared from tablets directly from a glass or bottle into an aquarium. After all, in this case, you can accidentally hit some fish with the jet and burn it. The same goes for plants. It is better to dilute the required amount of peroxide with water in a half-liter jar and carefully pour everything into the filter stream. When treating a disease such as fin rot, H2O2 should be added to the aquarium 1-2 times a day until the fish recovers (7-14 days).
Since after using this product a lot of dead organic matter appears in the aquarium, at least 30% of the water should be changed daily during the treatment process. Otherwise, rotting residues can cause poisoning in the fish.
Non-infectious
This type includes diseases that appear due to irrational maintenance or the influence of large parasites.
Chlorine poisoning
Caused by exposure to a chemical element.
Symptoms:
- difficulty breathing;
- mucus on gills;
- lightening of the color of the gills;
- restless behavior of pets: they rush around and try to jump out of the container;
- apathy.
At the first manifestations, the pets are immediately transplanted into another container.
Lack of oxygen
The disease occurs in an overcrowded vessel with oxygen deficiency, due to rotting feed residues and dead individuals, at elevated temperatures.
Symptoms:
- restless behavior;
- swimming near the surface;
- gasping for air;
- weakening of the immune system;
- suffocation;
- infertility;
- lack of appetite.
First you need to eliminate the cause of oxygen deficiency, then change some of the water and carry out aeration.
Failure to comply with temperature conditions
The disease is caused by increased or, conversely, decreased temperature of the water in the vessel.
Symptoms of high fever:
- excessively energetic behavior;
- fish rise to the surface due to lack of oxygen.
Symptoms at low temperature:
- lethargy;
- motionless presence at the bottom;
- cold symptoms, often leading to death.
To avoid the occurrence of such diseases, you need to constantly check the water temperature.
Alkali disease
Caused by increased (alkalosis) or decreased (acidosis) pH levels in water.
Symptoms of alkalosis:
- excessive activity;
- spreading of gills and fins;
- lightening of color;
- covering the gills with mucus.
Symptoms of acidosis:
- excessive fearfulness;
- decreased energy;
- fish can swim sideways or belly up.
As a therapeutic measure, you need to gradually change the acid-base balance in the container to normal.
Obesity fish
The reason is an increase in the fat content of food by 3% in herbivorous individuals and 5% in carnivorous individuals. If fish are overfed, provided with a poor or irrational diet, they may also develop signs of obesity. As a result, internal organs are damaged, leading to death.
Symptoms:
- apathy;
- rounding of sides;
- infertility.
From the editor: Sanguinecolosis
To prevent obesity, you need to provide the fish with a varied diet, give them fatty food, and also, for preventive purposes, do not feed them for 2 days. Pets need to swim freely, so you should worry about choosing a container of the appropriate size.
Gas embolism
Appears when the volume of oxygen is exceeded, as a result of which the fish’s blood vessels become clogged and blood supply is disrupted.
Symptoms:
- anxiety;
- sidestroke;
- immobility of gill covers;
- bubbles on individuals.
It is necessary to check air circulation and avoid excess plants, which contribute to the release of increased oxygen and soiling of the soil.
Tumors
As a rule, tumors are caused by physicochemical factors, ionizing radiation, and oncogenic viruses. In some situations, parasites and genetic code become the causes.
Symptoms of melanosarcoma:
- neoplasm;
- black body color.
Other types of tumors can be recognized by their characteristic shape and color. Sometimes they are so large that they swell the pet’s body. Small internal neoplasms are revealed only at autopsy.
Therapeutic measures are powerless. Tumors are quite rare. The affected individual is killed.
Improper feeding
Frequent and abundant feeding of fish, especially monotonous feeding, can cause a number of diseases, including fatal ones. This, as a rule, leads to obesity of internal organs and liver degeneration, as a result of which the fish dies.
Symptoms:
- colorless or bloody thread-like feces;
- hydrocele of the abdomen.
- Dropsy cannot be treated, so the sick fish is removed from the container.
Feeding a monotonous diet poor in vitamins causes vitamin deficiencies, which in turn can lead to metabolic disorders, weakening of the pet’s immune system, and deterioration in its health and appearance.
Therefore, it is necessary to provide your pets with a varied, balanced diet and follow the golden rule of aquarium keeping: “It is better to underfeed than to overfeed.”
Why does the disease appear?
Rotting of fins in fish develops only in conditions favorable to it: where there is no biological balance, feeding is not carried out according to the rules. That is, they do not receive enough necessary microelements and vitamins, as a result of which immunity decreases, and it is easier for any viruses to penetrate into a weakened body.
The cause of the disease is the bacteria Vibrio, Pseudomonas and Aeromonas; they can be introduced into the home pond in various ways. Most often, the source of infection is a sick fish released into a community aquarium.
The disease has another name; in scientific circles it is usually called pseudomonosis.
Symptoms
Characteristic signs of the disease are:
- fin rot at the edges;
- partial splitting;
- the occurrence of ruptures;
- pale blue coating.
Adult fish rarely die from it; young fish are more often affected.
Pseudomonosis in a cockerel
If the symptoms of fish pseudomonosis are ignored, the disease completely destroys the caudal fin. Fin rot is easily detected and treated in the early stages. A timely diagnosis will prevent the development of the disease.
What species of fish are at risk?
This disease is often considered characteristic only of veiled forms, but this is not entirely true. Indeed, fin rot is more common in fish, but representatives with shorter fins can also suffer from it. Even commercial species are susceptible to this.
Risk groups include:
- veil forms (cockerels, angelfish and others);
- swordtails;
- platies;
- neons;
- barbs (especially cherry ones);
- viviparous fish;
- gold;
- labyrinthine (gourami, macropods, etc.);
- characins.
How to prevent fin rot
Fin rot is a disease that often worries aquarium fish and makes aquarists nervous. However, it is possible to avoid the development of the disease if you follow the recommendations for the care and maintenance of pets:
- Phenotypes should not be fed live food that the owner is not sure is safe. This is especially true for food that is caught independently in reservoirs and rivers - with such food there is a high chance of introducing bacteria into the tank that causes fin rot.
- After purchasing a new fish, you should carefully examine your pet for symptoms of the disease. If the fish is suspicious, the underwater inhabitant is placed in a quarantine tank, where they are kept for twenty days.
- The aquarium with fish is regularly cleaned, cleaning equipment and siphoning the substrate. If the owner has several tanks, separate care tools are used for each and disinfected.
The best treatment for fin rot in fish is considered to be taking preventive measures in the aquarium. You should take care of the life and health of pets, which are completely dependent on the aquarist: clean the tank, monitor the quality of food and water parameters. If the disease does attack, you should not despair, but use one of the methods for treating fin rot, following the advice and instructions.
Is it possible to cure hemorrhoids using traditional methods?
Herbal baths, decoctions and compresses are appropriate only as part of combined conservative therapy for uncomplicated hemorrhoids. We are not aware of cases in which these isolated measures would be truly effective. Traditional methods of treating hemorrhoids should be treated especially carefully and from a critical point of view. Still, we are talking about a serious pathology of the rectum, often with cracks, prolapse of nodes and even thrombosis. Self-medication can be dangerous.
A separate group of proctologist patients are those whom doctors treat for complications after treatment with traditional methods.
They will definitely not help with hemorrhoids:
- ice candles
- fresh potato paste
- aloe leaf
- cucumbers from the garden
- steam baths
- leeches
Causes of rot
Individually pathogenic bacteria are constantly present in aquarium water, which is considered normal. They are not dangerous for aquarium fish, whose immunity resists them. The situation changes at the moment when, due to unfavorable conditions, a sharp drop in the natural protective forces of the fish occurs, or bacteria begin to actively multiply. If the number of pathogens increases rapidly and significantly, the fish cannot protect themselves from them. Fin rot is caused by the following factors:
- severe stress in fish;
- rotting plants in a pond;
- low water temperature;
- high water temperature;
- insufficient cleanliness in the aquarium;
- incorrect selection of fish in the vicinity - if some of the inhabitants of the aquarium are aggressive and damage the fins of the others, then bacteria can easily enter their body through the wounds;
- improper feeding of pets - a lack of necessary substances in the body leads to a weakening of the fish and a decline in its immunity.
When buying fish, they are examined to identify pathologies, including destruction of fins. If there are defects, you cannot buy a fish, because even if it is not sick yet, pathological pathogens will penetrate through the wounds on the fins after stress due to the move and fin rot will develop, the treatment of which is not always successful.
How to prevent the disease
- Do not use live food caught in waters where fish live. With it you will most likely introduce bacteria, which will cause fin rot. It is better to use frozen food to diversify your diet.
- Carefully evaluate the fish you buy. If you have any doubts about her health, it is better to refuse the purchase.
- Newly acquired fish should always be kept in quarantine for 2-3 weeks (separate from the rest).
- For each aquarium, use different nets and other fish care tools. This will eliminate the possibility of transmission of infection.
Treatment of columnaria
Typically, chloramphenicol is used to treat columnaria, a highly water-soluble antibacterial drug in tablet form sold in pharmacies.
It is better to treat fish in a community aquarium in order not only to cure the fish themselves, but also to kill pathogenic bacteria present in the aquarium environment.
From the editor: Planaria in an aquarium, how to get rid of it?
Levomycetin is added to the general aquarium at the rate of 3.5-4 g of the medicinal substance per 100 liters of water. The temperature during treatment is maintained at 26-27 0C.
After 4-5 days, you need to reduce the concentration of the drug in the aquarium with partial daily water changes.
If the next day after the start of treatment of fish with chloramphenicol, the water in the aquarium becomes cloudy, then 1/4-1/3 of the water is replaced with fresh, settled water to reduce the concentration of the drug.
To increase the therapeutic effect, you can add table salt to the water at the rate of 4-5 tablespoons per 100 liters of water.
What foods are good for preventing intestinal diseases?
In order not to risk your health and not be a victim of hemorrhoids, it is recommended to include more vegetables, fruits and fiber in your daily diet.
For the prevention of hemorrhoids it is useful:
- Fiber-rich fruits and vegetables (apples, avocado, pumpkin, broccoli)
- Beetroot and beet salad
- Freshly squeezed juice, especially pumpkin juice
- Prunes
- Chew food thoroughly
Harmful:
- Hot, spicy, fried, smoked
- Marinades
- Eat dry
- Soda
- Whole milk
- Baking and flour
- Lots of sweets
- Pasta, white rice and bread
- Canned food
If microflora disorders are detected, it is better to cure them. Sometimes it is necessary to prescribe probiotics that restore the intestinal microbiome, and enzymes that help digest food.
*For patients with diagnosed intestinal disease, the diet is individually prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment of fin rot
The initial stage of treatment is to check and improve the internal environment of the aquarium. This includes a whole range of activities and is carried out consistently and entirely.
First of all you need
- clean the filters,
- Remove rotten plants, if any, from the aquarium.
- Boil the soil, net, decor for 15-20 minutes before returning it back.
The next step is changing the water. The volume of new fluid should be approximately 30%.
Since the disease has a bacterial etiology, it must be remembered that too high a water temperature can promote the development of bacteria, thereby aggravating the course of the disease. The optimal temperature for treating fin rot is 24-25ºC.
Let's take a closer look at what medications should be used to carry out the procedures and how long to treat the fish.
- Adding Levomycetin to the general aquarium. It is necessary to dissolve 1 tablet in 20 liters of water and change 30% of the total volume of water to the medicinal solution every 3 days until complete recovery.
- Salt baths (not suitable for cockroaches and some other species; prior consultation with a specialist is required). Dissolve 1 tablespoon of salt in 10 liters of water and place the sick fish in the solution for 30 minutes. If the causative agent of the disease is the bacteria Aeromonas hydrophila and Pseudomonas fluorescens, then treatment with salt will not bring any results, since these species are resistant to high salt content in water.
- Treatment with Biomycin. 1.5 g per 100 liters of water. The drug is added to the general aquarium once a week. The course of treatment is long - 2-3 months.
Baths with potassium permanganate. 1 g per 20 liters of water. In this case, you should first dilute the potassium permanganate in a separate container, then pour half of it into the total volume of water, add the fish, wait 5 minutes and add the remaining liquid. Application time: no more than 10 minutes, morning and evening.
There are a number of special antibacterial drugs that can be purchased at a veterinary pharmacy in consultation with a pharmacist or veterinarian.
Treatment with streptocide. 1.5 g per 10 liters of water. First dissolve, then add to the aquarium. Or use in the form of baths in a dosage of 1 tablet per 6 liters of water. It is worth placing sick fish in them for 30 minutes.
Formaldehyde baths. 1 ml per 6 liters of water. Acceptance time: 15 minutes. To check tolerance, you should first place the fish in the solution for a shorter time, and if it becomes ill, stop the procedure and transfer the patient to clean water.
Upon completion of treatment, the process of fin regeneration will gradually begin, which will mean the success of the procedures performed. If this does not happen, another treatment method should be used.
Also, after final recovery, you need to disinfect the general aquarium with a chloramine solution, and boil all equipment and soil again.
If treatment is started in a timely manner, then all the inhabitants of the aquarium will be saved without high costs and complex manipulations.
Is it true that hemorrhoid surgery is painful?
Any surgical intervention is associated with some discomfort during the rehabilitation period. However, our clinic performs minimally traumatic operations using a laser or ultrasonic scalpel, as well as using the improved technique of Milligan-Morgan, Longo, etc. Thanks to modern technology and the experience of our surgeons, patients recover after surgery without prolonged bed rest.
Read more about the treatment of hemorrhoids at the Pirogov Clinic (St. Petersburg)
9. What methods of intestinal examination exist?
This or an X-ray examination - irrigoscopy
,
passage of barium through the intestines;
or endoscopic: sigmoidoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy. Capsule endoscopy also allows complete visualization of the small intestinal cavity.
For other methods there are separate, strictly limited indications.
Causes and symptoms
The causative agent of fin rot disease is the bacteria Aeromonas, Vibrio, Pseudomonas. Usually, the immune system of healthy fish resists them well, but if the inhabitants of the aquarium are weakened, have experienced stress, or live in insufficiently favorable conditions, they can easily become victims of bacteria.
A sick fish develops a white coating on the edges of its fins, their edges become uneven, rotting, and their color fades. The behavior of the fish also changes: it becomes lethargic and does not show normal appetite. In the later stages of the disease, the surface area of the fins is significantly reduced and they turn into rags. In fry, especially viviparous fish such as guppies or mollies, the caudal fin is often completely destroyed. In adult fish, rotting reaches the base of the fin, and when they are completely destroyed, ulcers with a whitish edge form at this place, and the fish dies.
As long as the muscles and blood vessels are not affected, treatment is still possible. Unfortunately, fish with a destroyed anal, dorsal or pectoral fin no longer have a chance.
Fin rot can affect any fish, but species with long and veiled fins are especially susceptible to it - cockerels, all types of angelfish, veiled forms of goldfish, guppies. The surface of their fins is larger and thinner (remember the delicate veils of guppies and goldfish), and is more vulnerable to bacteria. Unfortunately, it is also difficult for these species to return to their previous shape after recovery - the fins may lose their former even shape during recovery. For example, in angelfish that have suffered from disease, the rotted edges of the “feather” are thinner than the fin that was not affected by the disease. The growing rays of the fins may have knots or an irregular bend, similar to a break.
Symptoms of fin rot
Fin rot is a rapidly progressive disease that causes rapid erosion and subsequent disintegration of the fins. The course of the disease in young fish begins with the disintegration of the fins on the belly and tail; in adult fish this sequence is not observed. First, pathology of the fins occurs at their edges, gradually moving towards its base.
The very first sign of fin rot is a blue-white clouding of the fins that forms at their edges. The blue-white border on the fin subsequently expands and soon covers the entire fin. This is more noticeable in young fish, since their fins are almost transparent.
Another symptom of rot is spots and red stripes on fish fins. They are thought to be caused by a blockage in the blood vessels, also called fin blockage.
From the editor: Sulfadimethoxine for the treatment of aquarium fish
Rotting fins can become inflamed at the edges, and if this infection is not eliminated for a long time, it will soon be transmitted to the fin base. The fins will gradually become smaller due to the falling off of the ends of their rays. But still the split is not very deep. In young fish, the fin tissue dissolves completely.
As the disease progresses, small ulcers begin to appear at the bases of the fins. They are white in color due to the liquid that covers the base with a thin light layer. If you do not take immediate measures to treat your aquarium fish, the infection will spread to the entire body of the fish. The tissues are gradually destroyed and after some time the fish dies. Often with fin rot, clouding of the surface of the eyes is also observed.
Description of the disease
Fin rot is a common fish disease among aquarium fish. It is bacterial in nature and may be a secondary infection accompanied by other symptoms. Rot destroys the animals' fins, which take on a torn and worn-out appearance.
Pathogen
The causative agent is bacteria:
- Pseudomonas;
- Aeromonas;
- Vibrio.
They develop only in natural bodies of water, so they cannot appear on their own in an aquarium. Infection can be acquired through:
- Water;
- Feed;
- Priming;
- Decor;
- Sick fish that have not undergone quarantine.
Symptoms
You should pay attention if you have the following symptoms:
- Changes in color on the fins and tail of the animal;
- Blockage of blood vessels;
- White and gray coating on the fins of aquarium fish;
- Cloudy eyes;
- Ulcers on the body;
- Broken and mechanical damage to fins;
- White color of the cornea.
Note! These symptoms cannot be ignored, as lack of treatment can lead to the death of the animal.
initial stage
At the initial stage of development, the infection can be difficult to notice. The first signs are similar to ordinary mechanical damage. The fins slowly lose color and become cloudy at the edges, acquiring red stripes and spots due to clogged blood vessels. Gradually, defeat covers them completely. The cloudiness is easier to notice in young individuals, as they are mostly transparent at this stage of development.
Severe stage
In the advanced stage, the disease completely affects the fins by erosion, which leads to their destruction and rotting. In some fish species, clouding of the cornea is noticeable at an advanced stage. Pus from the fins spreads to the body, forming ulcers. At this stage, animals are in mortal danger. This is especially true for young fish and fry.
Why is it dangerous?
The danger of infection lies in its rapid development and short amount of time for treatment. For this reason, it is important to carefully monitor the condition of the animals in the aquarium. With timely assistance and the right conditions of detention, adult individuals are able to independently restore fin tissue. For fry, the damage can become irreversible.
How to treat fin rot
Every aquarium owner should know how to treat fin rot and how. In the first stages of development of fin rot, it will be enough to replace 30% every day for 5 days. If during this time there is no improvement, and the disease begins to progress, then medications are used. It is best to treat fish together, rather than transplanting sick fish into another aquarium. Since a sick fish could infect a healthy one. But in this case, the biobalance in the aquarium may be disrupted due to medications.
Treatment of fin rot with chloramphenicol
Fin rot should be treated with chloramphenicol until the fins begin to recover. 1 tablet of chloramphenicol per 20 liters of water. First, the tablet must be ground into powder and dissolved in a glass of water and poured into the aquarium. Every 3 days you should do a 30% water change and add a new portion of the drug. The visible result will be in 4-6 days.
Treatment of fin rot with streptocide
Fin rot can be cured with streptocide. If streptocide is in tablets, then it must be crushed and then dissolved in water. Dissolve the medicine at the rate of 1.5 g/10 l. The solution is then poured into the aquarium. You can also make baths for individual fish. To do this, one tablet is dissolved in 6 liters of water at a temperature of 28 degrees. Sick fish are placed in the solution for 30 minutes. This procedure can be repeated after 2 days.
Treatment of fin rot with salt
In the early stages, fin rot can be cured with table salt. For this, baths are made, 3 level teaspoons are dissolved in 5 liters of water. Sick fish are placed in such a bath for 15 minutes. This procedure can be repeated every other day until recovery. If such a procedure occurs with corydoras, teracatum or callichthid catfishes, the solution is made a little weaker. 2 g salt/1 l. The rest of the procedure is the same.
Fin rot treatment with hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a good remedy that has a detrimental effect on parasites that cause fin rot. For treatment, 2.5 ml/10 l of the drug is added to the aquarium in the morning and evening for two weeks, after diluting it in water so as not to burn passing fish. For the bath, the proportions are slightly different. Peroxide is dissolved in a dosage of 10 ml/10 l. Baths can be used only in the most difficult cases. Such baths are repeated every other day for 10 days. Improvements are already noticeable on the second day.
Potassium permangantsovka
The proportions of potassium permanganate are 1 g/20 l of water. First, potassium permanganate is dissolved in a glass of water, half is poured into the bath and the fish is introduced. After 5 minutes, pour out the remaining solution. The fish are left in the bath for another 5 minutes and then returned to the main aquarium. This procedure is performed morning and evening until there is improvement.
Formalin
You can also try formaldehyde to treat fin rot. Formalin is dissolved in the following proportions: 1 ml/6 l of water. Such baths are used once every 2 days. During this procedure, you need to diligently monitor the fish; if the fish becomes ill, then the fish urgently needs to be moved to a common aquarium. These baths last 15 minutes. But the very first procedure takes 5 minutes.
Causes of the disease
Before moving on to the question of how to cure aquarium fish, it is necessary to understand the causes of ichthyophthyriosis. The most common provoking factors include:
- Finding fish in a common aquarium with a sick individual. Beginning aquarists often make a common mistake - they immediately place the acquired fish with the others. If the new inhabitant is sick, infection occurs. To avoid this, you need to place the “newbies” in a quarantine aquarium for 3-4 weeks. It is not necessary to purchase a separate container; a regular jar will do for these purposes. If no alarming signs are found during this time, you can add the fish to the others. If there are any diseases, it is necessary to first carry out treatment, and only then place the new inhabitants in a common aquarium.
- Frequent aquarium treatment. It is necessary to clean an artificial reservoir as it becomes dirty, without overusing mechanical cleaning. It is important to realize that any third-party invasion is stressful for its inhabitants, which is why the fish’s immunity can be significantly reduced.
- Infection through food, soil, vegetation and decorative elements. Before placing any objects in the aquarium, they must be subjected to antiseptic treatment.
- Frequent temperature changes. Unstable water temperature and sudden transitions from excessive heat to cold can provoke various fish diseases.
- Aquarium pollution. In order for the fish to feel comfortable, it is necessary to promptly clean the filters and soil, as well as remove plaque that appears on the internal surfaces.
By following these precautions, you can significantly reduce the risk of contracting ichthyophthyriasis.
Medicines
- Adding Levomycetin to the general aquarium. You need to dissolve 1 tablet in 20 liters of water and replace 30% of the total volume of water with the medicinal mixture every 3 days until the final correction.
- Salt baths (not suitable for cockroaches and some other species, so you can’t do without consulting a specialist). Dilute 1 tbsp. spoon of salt in 10 liters of water and let the sick fish into the solution for half an hour.
- Biomycin - 1.5 g per 100 liters of water. The product is added to the general aquarium once every seven days. The course of treatment is several months (2-3).
- Potassium parchment baths - 1 g per 20 liters of water. You need to dilute potassium permanganate separately, then pour half of it into the total volume of water, let the fish in, wait a few minutes and only then pour in the rest of the solution. Use no more than 10 minutes, 2 times a day.
- There are several specialized antibacterial drugs that can be purchased at a veterinary pharmacy in consultation with a pharmacist or veterinarian.
- Streptocide – 1.5 g per 10 liters of water. First dilute it, then pour it into the aquarium.
- Formaldehyde baths - 1 ml per 6 liters of water. The fish should be allowed in for 15 minutes. To determine tolerance, it is necessary to release the fish into the solution for a minimum period of time; if it becomes unwell, then end the session and send the sick one back.
Upon completion of the procedures, the fins will begin to regenerate over time, which will confirm the success of the treatment. If this does not happen, then it is necessary to use a different method of treatment.
After curing the inhabitants of the aquarium, it is necessary to disinfect the general aquarium with a chloramine solution, and boil all the equipment and soil again.
If you start treatment in time, then all the aquarium inhabitants will be saved without major expenses and difficult manipulations.