Characteristics of the crustacean
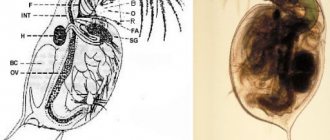
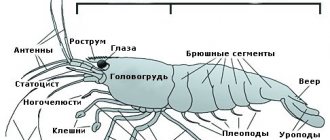
Artemia is a branchiopod crustacean that belongs to the subphylum of crustaceans. Males are distinguished from females by their claws located in the head area. Females have a sac for laying eggs located on the abdomen.
Habitat
Crustaceans are heat-loving mollusks, so in nature they live in tropical, subtropical and temperate climatic zones. Salty reservoirs with a chloride, sulfate and carbonate composition are a natural environment for artemia.
Description and life cycle
An adult crustacean has 11 paired legs and three eyes. Bisexual individuals reach a length of up to 15 mm. The color of the body may differ depending on the concentration of oxygen dissolved in the water and the food consumed by the mollusk - from a greenish tint to bright red.
Young nauplii have only one eye. They see light well and swim toward it, unlike adults, who avoid direct light.
Artemia salina reproduces in two ways:
- dioecious;
- parthenogenetic, i.e. without the participation of a male.
After mating with the male, the female lays eggs in a special egg sac located on the abdomen. Under favorable conditions, the maximum quantity that is included in it is up to 200 eggs. However, the average number does not exceed 50-60 pieces. Embryonic development of the egg begins as soon as it enters the brood sac. Nauplii hatch from them.
The size of one nauplius is so small that it is impossible to see it with the naked eye. The length of the body is 0.45 mm, the mass is less than one gram - 0.01 mg. Color varies from pale pink to bright red. Newborn nauplii actively move in the water and begin to feed 10-12 hours after birth. During this period, the first molt occurs.
During the period of maturation, the future crustacean goes through 15 stages of molting during the first eight days. Full maturity occurs at 18-30 days.
On a note! The average lifespan of Artemia salina is up to 6 months. However, in the absence of oxygen entering the water, the adult dies within two hours.
Application
Artemia crustaceans are of great importance in fishing, pharmaceuticals and cosmetology.
Where crustaceans are used:
- For feeding aquarium fish. Nauplii serve as a nutritious starter food for young fish and fry; adult crustaceans are provided for older fish. Used for food in dry, fresh, frozen, freeze-dried or liquid form.
- Mud therapy. Dead crustaceans form layers and accumulate at the bottom of reservoirs. During the process of decay, they are mixed with silt and salt. As a result, mud is formed that has healing properties. People who have visited mud resorts successfully treat diseases of the musculoskeletal system, joints, and urinary system.
- In cosmetology. For the prevention and treatment of skin diseases, products with a rejuvenating effect are produced, for example, “Diamond” (Italy).
- In medicine. Artemia is used as a dietary supplement (for example, “Kavesan”), and preparations are made that normalize metabolism in the body.
Description
Artemia crustaceans (lat. Artemia salina) grow up to 12–18 mm. Average life expectancy is 4–6 months. These are heterosexual creatures, but in the absence of males, female Artemia are capable of parthenogenetic reproduction. Externally, a male can be distinguished from a female by the “claws” near the head in males, and the egg sac in females. Claws help in feeding on phytoplankton, the main diet, and in mating.
What types of eggs are there?
Artemia eggs are used as food for fish fry. From them, larvae (nauplii) are obtained, and with the help of special feeds, they are grown to adult individuals. There are regular eggs with and without shell (decapsulated). They are more sensitive to environmental conditions. For cultivation, cysts are used for 2–3 years.
Breeding methods at home
If you follow all the necessary recommendations, growing Artemia salina at home will not be difficult, even for beginners.
Eggs of future crustaceans are purchased at a pet store. They can be decapsulated (the crustaceans hatch within a few minutes) or regular, from which the crustaceans hatch in 7-10 days. One gram of eggs produces 160 thousand individuals. Most of them die in the first few days of life.
Important! Eggs that have been stored for more than one year have a low rate of nauplii hatching.
Crawfish eggs must be prepared for hatching. To do this, they are poured into a 0.5-1 liter container, filled with settled water and left for 10-20 minutes. After time, the husks that have accumulated on the surface are drained. Then fill them with a salt solution (35 g/liter) and place them in the freezer for a period of 1 day to two months. This activates the eggs for further hatching.
Simple option
There is the easiest way to grow brine shrimp at home to feed aquarium fish. For breeding, a small container (biotope) with a volume of 2-3 liters is used. These can be tall glass vases or micro-aquariums. A place for it is chosen on a windowsill that is well lit and warmed by the sun. Several pebbles and clay shards from flower pots are laid out at the bottom. Over time, green algae will form on their surface, which will serve as natural food for artemia.
On a note! Algae not only serve as food, but also participate in the natural process of gas exchange. Therefore, their presence is mandatory.
Pour salted water into the container and add the prepared Artemia eggs using a spoon. Cover with a lid to prevent dust from entering from the environment.
In the incubator
Hatching and reproduction of crustaceans is carried out in special incubators, for example, JBL Artemio set. It has a rectangular shape, with an inverted conical bulb built inside and a beveled end.
On an industrial scale, complex incubators are used that are connected to aquariums and feed hatched brine shrimp automatically (for example, TOM Aquarium Hatch N' Feeder Brine Shrimp Hatchery).
At home, you can make a homemade incubator for breeding and propagating crustaceans. For this you will need:
- 2 plastic bottles with a capacity of 2 l;
- a compressor for the aquarium and a tube for connecting it to the incubator;
- tube with spray;
- a flashlight or table lamp for lighting and heating the incubator;
- sea salt and brine shrimp eggs.
The process of making a home incubator:
- Cut off the upper part with the neck of the first bottle, and the lower part with the bottom of the second bottle so that they can then be inserted into each other, with the closed neck down.
- A tube with a sprayer connected to a compressor is inserted into the resulting container.
- Pour in salted water (at the rate of 2 tablespoons per 3 liters) and turn on the compressor.
Then the eggs of future crustaceans are poured in and a lamp is installed nearby to illuminate and heat the incubator.
Important! During the incubation period, the water temperature should be at least +27…+30°C. In this case, the first crustaceans will appear within 48 hours. If the temperature is increased to +29…+35°C, the elimination period will be reduced to 36 hours.
In aquarium
To grow, you need to prepare in advance:
- an aquarium made of ordinary or organic (plexiglass) glass, with a volume of at least 10-15 liters;
- thermometer for measuring temperature;
- refractometer for measuring salt in water;
- heater with regulator;
- sea salt – 350-500 g;
- water filter and flashlight;
- Buy brine shrimp eggs at a pet store.
The aquarium is doused with boiling water and dried, then placed near an electrical outlet. Pour sea salt into the settled water in a ratio of 35 g per liter of liquid, then pour the solution into the container. Install electrical equipment: filter, heating element, thermometer. Add Artemia eggs to the saline solution.
Important! Every 24 hours it is necessary to check the salinity of the water and its temperature.
Adviсe
- To raise the brine shrimp to adulthood after the nauplii hatch, transfer them to a separate aquarium with salty, warm (25°C) dechlorinated water.
- Use an airlift filter in the incubator. It does not attract crustaceans.
- You can get larvae (nauplii) at any time of the year. It is enough to place the cyst in the necessary conditions.
- Use yeast to feed crustaceans.
- If spawning is planned in 3-4 weeks, then let the brine shrimp eggs spend the entire period in the freezer. Before incubation, keep them at room temperature for 2-3 days. This is to multiply the germination results.
- Just do not give the emerging fry too many nauplii, otherwise the ones that are not eaten will grow and eat the fry themselves.
- Once decapsulated, the eggs will keep for 14 days in an airtight container in the refrigerator. They can be frozen and used for feeding as needed. They will no longer be able to reproduce.
(Visited 3,280 times, 1 visits today)
Favorable conditions for growth
Conditions for withdrawal:
- Suitable water for breeding crustaceans with a neutral reaction is distilled or boiled.
- The salt concentrate in water should be at least 25-35%. To obtain this indicator, add 4 tbsp to the liquid. l. salt (sea or table salt without added iodine) with a small pile per one liter of water.
- An aquarium pump is used to saturate the water with oxygen and circulate it. Oxygen pumping in the biotope is carried out 2-3 times a day. If it is not possible to purchase it, then stir the water several times a day using a plastic stick.
- They maintain the optimal temperature for reproduction +22…+25°C.
- The density of eggs is 2.5 g per liter of water.
- Illumination with a lamp until the larvae appear - 24 hours.
Feeding - speeding up and increasing the yield of crustaceans
Food for adult artemia at home is: fish food ground into fine dust, fresh yeast, detritus, egg powder, dry mixtures based on plant components, milk powder, and green microalgae. They can be purchased at a specialty store or grown yourself.
Feed is given in small portions 2-3 times a day. If you add too much, the water will become cloudy and food debris will begin to rot and spoil. Therefore, they feed again only after the first portion has been eaten.
About Artemia
Artemia lives for about 4-6 months. The crustaceans are heterosexual; males are distinguished by an enlarged pair of antennae, with which they capture the female during fertilization. Linked together, a pair can swim for several days. Adult brine shrimp can lay eggs every 4 days.
In the absence of a male individual, females are able to reproduce through parthenogenesis - larvae. Then young crustaceans emerge from the mother’s unfertilized egg.
Artemia have acquired particular value in the aquarium industry as live food for fish. During all life cycles, Artemia is suitable for food. Almost all aquarium fish fry are fed nauplii (artemia larvae), and medium-sized fish are fed with mature crustaceans.
Life cycle of Artemia: cysts - hatching process - young crustaceans - nauplii - juvenile stage - adults.
Capture and storage
To feed fish and fry, it is necessary to properly remove hatched brine shrimp or decapsulated eggs.
Crustaceans and hatched nauplii
To catch adult individuals, first disconnect the compressor from the power supply. Then, with the help of light (lamp or lantern), Artemia are lured in one place. After this, large crustaceans are caught using a strainer with large holes, then the remaining nauplii are collected using a sieve with small holes. Before feeding them to fish, adult brine shrimp are washed with fresh water.
On a note! To preserve the excess amount of caught crustaceans for future use, they are frozen in the freezer.
Decapsulated eggs
After turning off the compressor and light, after a few minutes the decapsulated eggs will fall to the bottom of the aquarium. To catch them, use a thin hose. It is lowered to the bottom, then the salt water is filtered through a dense fabric that allows water to pass through.
When stopping the breeding of artemia in a biotope, it is necessary to allow the water to evaporate naturally. The crustaceans will lay eggs that will fall to the bottom. To revive them, it will be enough to pour salt water into the container again.
On a note! Cysts are stored in the refrigerator. To do this, they are placed in a dry, sealed container or bag.
Mr. Tail recommends: how to feed your underwater pets Artemia nauplii
Nauplii are given to the fry of spawning fish. A menu of Artemia alone is not recommended; it is better to use it for complex feeding in combination with plant foods.
Overfeeding fish can lead to illness, death, and inflammation of the stomach. The crustaceans are fed in small doses. All the food must be eaten, otherwise the aquarium will turn sour, the ammonia level will increase, and harm its inhabitants.
The fry require daily food; they are given eggs in the first days of emergence, but only decapsulated (outside the capsules). Before use, the cysts are filled with water for 20 minutes and washed well.
Pros and cons of growing Artemia salina
Growing Artemia salina at home as live food for aquarium fish has its advantages:
- nutritious food accelerates the growth of fish fry;
- increases the survival rate of fry;
- the process of growing artemia can be made endless if salt water is added to the container as it evaporates.
Minuses:
- breeding crustaceans requires time and special equipment;
- if you give fish fry too much food, then the remaining brine shrimp larvae, which quickly mature, will eat the fry themselves;
- If the cultivation technology is violated, bacteria, parasites, and infections form in the water, which can subsequently enter the aquarium.
Advantages and disadvantages
One of the main advantages of using brine shrimp as feed is their nutritional value.
Due to their high-quality composition (about 20% fat), crustaceans provide fry and medium-sized fish with all the necessary substances. The result of feeding young animals with Artemia is high survival rate and rapid growth. For larger fish, adult crustaceans can be given as a delicacy.
But this is not the only advantage of Artemia:
- cysts are inexpensive and are sold in many pet stores;
- Artemia eggs are stored in the freezer for a long time without losing their ability to develop;
- incubation of nauplii takes about two days, so even if there is an unexpected addition to the aquarium, there will be something to feed them;
- minimizes contamination of the fish aquarium;
- Even a beginner can cope with the removal of Artemia.
With all the advantages, there is also a disadvantage. Breeding brine shrimp takes time and effort. It is necessary to follow all the recommendations so that the crustaceans hatch, do not get sick in the future and do not infect all the inhabitants of the aquarium.
Interesting Facts
Interesting facts about crustaceans:
- brine shrimp salina never sleep;
- considered the most ancient creatures on Earth;
- when diluted, you can feed regular baker's yeast;
- The female's egg sac can hold up to 200 eggs.
Artemia salina is not only a unique, nutritious, live food for aquarium fish, but also a valuable mollusk used in cosmetology and mud therapy. Growing at home is carried out in compliance with special conditions and is accessible even to beginners.