Attention! The calculator calculates the most optimal conditions for keeping fish in the most comfortable conditions for them. You can slightly increase the number of fish, provided that you either have excellent water filtration, or regularly change it with a soil siphon, or have a lot of fast-growing plants that absorb trace elements and nitrates from the water, or a combination of these factors.
Beginner aquarists complain that the calculator has too large volumes, but understand one thing, if you do not trust the calculation result, then in the future you will have to deal with algae (beard, flip flop, filament, xenococus), fish diseases (semolina, bloating, ruffled scales , various infections and fungi) and other troubles (white worms).
When calculating the quantity, be sure to take into account the size of adults, and not young animals or fry, and the characteristics of their behavior, fast or slow, love shelters and thickets or open space, etc. And only based on this, calculate the number of fish you like. How to do this correctly? Let's find out below.
How many fish can you put in an aquarium?
The first thing you should pay attention to when calculating the number of fish is the volume of the aquarium and its geometric dimensions. In the literature, one often comes across a rather primitive calculation - 1-2 liters of water are needed per 1 cm of fish length . This method can only be used with reservations:
- When calculating, the size of adult individuals is taken into account, and not the purchased young animals;
- the aquarium must be equipped with a water treatment system and an aerator;
- it is necessary to take into account the layer-by-layer filling of the aquarium, especially when filling aquariums from 30 liters - so that in the end it does not turn out that most fish prefer to spend time in the middle layers, and the bottom and surface layers are empty;
- do not forget that large fish produce a lot of waste, which in small aquariums can quickly render the water unusable;
- From the nominal volume of the aquarium, the volume of soil and decorations, if any, should be subtracted - approximately 15%.
You should also take into account the geometric dimensions of the aquarium - the ratio of width, length and height. For the most part, this indicator will affect the overall aesthetic perception of the filled aquarium, for example, fish with a tall, laterally compressed body (gourami, angelfish, Sumatran barb) look more advantageous in aquariums where the height exceeds or is equal to the length, and the width is small (screen aquarium) . Elongated fish (zebrafish, swordtails) look advantageous in low, long aquariums. For a round aquarium, it is worth giving preference to fish with a voluminous body - varieties of goldfish - telescopes, vole tails.
The disadvantage of this approach to calculating the number of fish in an aquarium is that it does not take into account the characteristics of different breeds , providing only the minimum space for physiological health. This often leads to the fact that some specimens can show aggression towards their neighbors (for example, betta fish); less energetic fish will hide in corners and in algae bushes.
Basic sizes of the most common fish and the number of liters of water required for keeping.
| Size and type of fish | Water volume, l |
| Small - up to 6 cm in length: neons, guppies, platies, some types of barbs, zebrafish, cardinal. | 5-7 liters per couple. |
| Medium - from 7 to 12 cm in length: swordtail, black molynesia, Sumatran barb, rasbora, cockerel, speckled catfish, macropod, gourami. | 30 liters per couple. |
| Large – 15-20 cm in length: goldfish and their varieties, pearl gourami. | 40-45 liters per couple. |
| Very large - over 20 cm in length: discus fish, African and American cichlids, Indian knives, Botia modesta. | From 150 liters per couple and above. |
This table is compiled from various sources on the Internet. Compiled by: Lapa, EugenyCh, gannush, wayward2004, Diesel, Jararaka. (Table in the process of replenishment)
Table of basic parameters for keeping aquarium fish
| Name of the fish | Max fish size | Min number of liters | T°C water | pH of water | dH° water |
| Viviparous | |||||
| Guppy | 6 cm | 5 for a couple | 24-26 | 7.0-8.5 | 10-25 |
| sword bearer | 10 cm | 30 per couple | 20-26 | 7-8 | 10-25 |
| Mollies "red leopard" | 12 cm | 50 per couple | 22-28 | 7-8,5 | 10-25 |
| Velifera molly | 15 cm | 60 per couple | 22-28 | 7-8,5 | 8-25 |
| Silver molly (Snowflake) | 14 cm | 60 per couple | 22-28 | 7-8,5 | 8-25 |
| Mollienesia sphenops | 10 cm | from 50 per couple | 23-28 | 7-8 | 10-30 |
| Black mollies | 12 cm | 50 per couple | 23-28 | 7-8,5 | 10-30 |
| Nomoramphus Lima | 10 cm | 20 per couple | 22-28 | 7-8,5 | 5-25 |
| Pecilia | 6 cm | 15 per couple | 20-26 | 7-8 | 10-25 |
| Cyprinids and carp-toothed | |||||
| Afiosemion ayseri | 7 cm | 20 per couple | 22-26 | 6-7 | 8-12 |
| Afiosemion gabon fringe | 7 cm | 15 per couple | 20-22 | 6-7 | 10-12 |
| Afiosemion Gardner "Macurdi" | 8 cm | 15 per couple | 22-24 | 6-7 | 8-12 |
| Afiosemion gresensi (azure) | 7 cm | 15 per couple | 20-22 | 6-6,5 | up to 12 |
| Afiosemion primigenium | 4 cm | 15 per couple | 20-22 | 6-7 | 10-12 |
| Afiosemion striatum | 6 cm | 2 | 20-22 | 6-6,5 | up to 20 |
| Afiosemion sjöstedti (Blue Pheasant) | 12 cm | 20 per couple | 20-25 | 6-7 | 8-12 |
| Afiosemion southern | 6 cm | 5 for a couple | 20-25 | 5,5-7 | 8-12 |
| Aplocheilichthys Normana | 4 cm | 10 | 22-26 | 6-7 | up to 20 |
| Aplocheilus aureus | 12 cm | 50 per couple | 22-25 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Aplocheilus lineatus | 10 cm | 60 | 22-26 | 6-7 | up to 20 |
| Aplocheilus torch | 4 cm | 10 per couple | 22-26 | 6-7 | to 10 |
| Shark Bala | 10 cm | 30 per couple | 22-28 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Barbus shark | 35 cm | 100 | 22-26 | 6.5-7.5 | 5-7 |
| Scarlet Barbus (Odessa) | 10 cm | 20 per couple | 15-23 | 6.5-7.0 | Up to 20 |
| Barbus apogon | 50 cm | 200 | 22-26 | 6,4-7,2 | up to 25 |
| Barbus arulius | 12 cm | 80 | 20-26 | 6-7 | 4-15 |
| Barbus cherry | 5 cm | 15 per couple | 23-26 | 6.0-7.0 | 6-18 |
| Eight-bar barb | 5 cm | 15 per couple | 24-26 | 6-7 | 6-15 |
| Denison Barbus | 20 cm | 150 per flock | 15-27 | 6-8 | 5-25 |
| Barbus long-striped | 10 cm | 20 per couple | 24-28 | 6.0-7.0 | 3-12 |
| Barbus green | 7 cm | 30 per couple | 20-26 | 6.0-7.0 | 4-15 |
| Indian striped barb | 6 cm | 50 | 22-27 | 6-8 | 5-18 |
| Barbus cross | 18 cm | 150 per couple | 22-28 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Barbus linear | 12 cm | 100 per couple | 22-28 | 6-8 | up to 15 |
| Barbus brevis (Schwanifeld barb) | 35 cm | 250 | 22-25 | ~ 7.0 | before 18 |
| Golden bream barb | 35 cm | 70 | 22-25 | ~ 7.0 | before 18 |
| Fire barb | 10 cm | 30 per couple | 18-23 | 6.5-7.0 | Up to 20 |
| Barbus oligolepis | 15 cm | 30 per couple | 22-25 | ~ 7.0 | before 18 |
| Barbus panda | 15 cm | 80 | 22-26 | ~ 7.0 | up to 20 |
| Barbus five-striped | 5 cm | 20 per couple | 20-26 | 6.0-7.0 | 4-15 |
| Barbus blue-hatched | 6 cm | 40 per couple | 20-25 | 6-8 | up to 20 |
| Barbus solar | 5 cm | 40 per flock | 18-20 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Barbus Sumatran | 7 cm | 20 per couple | 20-26 | 6.5-7.0 | Up to 15 |
| Barbus black | 6 cm | 30 per couple | 22-26 | 6.5-7.0 | Before 18 |
| Schubert Barbus | 10 cm | 20 per couple | 18-24 | 6.5-7.0 | Up to 16 |
| Danio leopard | 6 cm | 30 per flock | 18-25 | 6-8 | up to 20 |
| Danio pink | 6 cm | 30 per flock | 20-25 | 6-7 | before 18 |
| Danio rerio | 6 cm | 30 per flock | 18-25 | 6.0-7.0 | Before 18 |
| Jordanella florida (Florida) | 6 cm | 10 per couple | 18-22 | 7-7,5 | up to 20 |
| Cardinal | 4 cm | 30 per flock | 18-25 | 6-7 | before 18 |
| Labeo two-color (bicolor) | 12 cm | 60 | 22-26 | 6-7 | before 18 |
| Labeo green | 12 cm | from 30 | 22-24 | ~ 7.0 | up to 20 |
| Labeo thailandis (phrenatus) | 15 cm | 60 | 22-26 | 6-7 | before 18 |
| Leptobarbus jovena | 30 cm | 200 per flock | 22-28 | 6-8 | up to 20 |
| Notobranchius Cafuensis "Mambova" | 5 cm | 5 for a couple | 24-28 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Nothobranchius Courthaus | 6 cm | 5 for a couple | 22-26 | 6-7 | 10-12 |
| Nothobranchius redfin | 5 cm | 5 for a couple | 24-28 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Nothobranchius patrici | 5 cm | 5 for a couple | 22-28 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Rasbora heteromorph (wedge-shaped) | 5 cm | 15 per flock | 22-25 | ~ 7.0 | before 18 |
| Rasbora red-lined | 7 cm | 50 per couple | 22-28 | 6-7 | up to 12 |
| Rasbora trilinear | 15 cm | 150 | 23-25 | 6-7,5 | 5-15 |
| Rasbora Henkel (Rasbora Espei) | 4.5 cm | 10 per couple | 23-28 | 6-6,5 | up to 12 |
| Savbva | 5 cm | 20 per couple | 21-25 | ~ 7.0 | up to 15 |
| Goldfish (all varieties) | 20 cm | 100 per couple | 14-30 | 6-8 | up to 20 |
| Wakin | 30cm | 100 per couple | 14-30 | 6-8 | up to 20 |
| Water eyes | 20 cm | 100 per couple | 14-30 | 6-8 | up to 20 |
| Veiltail | 20 cm | 100 per couple | 14-30 | 6-8 | up to 20 |
| Zhemchuzhik | 15 cm | 100 per couple | 14-20 | 6.5-7.0 | 6-18 |
| Astrologer | 20 cm | 100 per couple | 15-30 | 6-8 | up to 20 |
| Calico (Shubunkin) | 20 cm | 100 per couple | 14-20 | 6.5-7.0 | 6-18 |
| Comet | 20 cm | 100 per couple | 15-30 | 6-8 | up to 20 |
| Oranda | 25 cm | 100 per couple | 14-20 | 6.5-7.0 | 6-18 |
| Sailfish (Mixotsoprin, Chukuchan Chinese) | 60 cm | 300 | 15-28 | ~ 7.0 | up to 20 |
| Ranchu | 20 cm | 100 per couple | 15-30 | 6-8 | up to 20 |
| Riukin | 20 cm | 100 per couple | 15-30 | 6-8 | up to 20 |
| Telescope | 20 cm | 100 per couple | 15-30 | 6-8 | up to 20 |
| Koi carp | 1m | 700 | 10-23 | 7-7,5 | up to 15 |
| Labyrinths, snakeheads, proboscis snouts | |||||
| White gourami | 12 cm | 50 per couple | 22-28 | 6-8 | 5-20 |
| Blue gourami | 15 cm | 30 per couple | 22-28 | 6-8 | 5-19 |
| Pearl gourami | 12 cm | 30 per couple | 22-28 | 6-8 | 5-19 |
| Snake skin gourami | 15 cm | 50 per couple | 23-30 | 6-8 | 4-25 |
| Golden gourami | 12 cm | 30 per couple | 22-28 | 6-8 | 5-20 |
| Moon gourami | 15 cm | 50 per couple | 25-30 | ~ 7.0 | up to 25 |
| Honey gourami | 5 cm | 20 per couple | 22-28 | ~ 7.0 | up to 15 |
| Marbled gourami | 12 cm | 30 per couple | 22-28 | 6-8 | 5-20 |
| Commercial gourami | 40 cm | 300 | 22-28 | 6-8 | until 22 |
| Spotted gourami | 15 cm | 13 | 20-26 | 6-8 | 5-20 |
| Gourami kissing | 15 cm | 100 per couple | 22-28 | 6-8 | 5-20 |
| Chocolate gourami | 5 cm | 5 | 25-28 | 7 | 4-16 |
| Snakehead red | 1m | 300 | 25-28 | doesn't matter | doesn't matter |
| Ctenopoma leopardum | 15 cm | 50 per couple | 23-28 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Labiosa green | 9 cm | 40 | 22-28 | 6-7 | to 10 |
| Labiosa orange | 9 cm | 40 | 22-28 | 6-7 | to 10 |
| Lyalius | 5 cm | 10 per couple | 22-24 | 6,5-7,5 | up to 20 |
| Lyalius coral | 6 cm | 10 per couple | 24-28 | 6-8 | 5-15 |
| Lyalius red coral | 6 cm | 10 per couple | 24-28 | 6-8 | 5-15 |
| Lyalius neon | 6 cm | 10 per couple | 24-28 | 6-8 | 5-15 |
| Macropod | 12 cm | 20 per couple | 15-28 | 6-8 | up to 20 |
| Macrognathus ocellata | 35 cm | 100 | 23-28 | ~ 7.0 | 25 |
| Mastocembel | 20 | from 100 | 21-27 | 6,5-8,0 | up to 25 |
| Cockerel | 7 cm | 3 for a couple | 23-28 | 6-8 | 5-15 |
| Mud jumper | 15 cm | 60 | 20-26 | 6-8 | up to 25 |
| Tetradon biocellatus | 17 cm | 60 | 23-28 | 7-8 | before 18 |
| Tetradon dwarf | 3 cm | 10 | 22-28 | 7-8 | up to 25 |
| Tetradon red-eyed | 7 cm | 40 | 24-28 | ~ 7.0 | 10-15 |
| Tetradon fahak, African rocktooth | 45 cm | 200 | 22-30 | 7-8 | before 18 |
| Tetradon fluviatilis | 17 cm | 60 | 23-28 | 7-8 | before 18 |
| Tetradon blackspot | 15 cm | 60 | 24-28 | 7-8 | 10-30 |
| The pike head is beautiful | 20 cm | 300 | 22-26 | 7-8 | up to 15 |
| Cichlids of Asia | |||||
| Parrot (hybrid) | 25 | from 150 per couple | 25-28 | about 7.0 | up to 20 |
| Etroplus striped | 46 | from 300 | 23-26 | 7,4-8,4 | up to 20 |
| Etroplus spotted | 12 | from 30 | 20-25 | 7,5-8,5 | up to 20 |
| Cichlids of America | |||||
| Akara turquoise | 25-30 cm | 160 | 25-28 | ~ 7.0 | up to 15 |
| Apistogramma of a cockatoo | 8 cm | from 40 per couple | 22-28 | 6.5-7.0 | 8-20 |
| Apistogramma Ramirez (chromis butterfly, microgeophagus Ramirez) | 5 cm | from 20 per couple | 24-28 | 6,5-7,0 | up to 14 |
| Astronotus | 30 cm | from 250 | 22-28 | 6.0-8.0 | 8-25 |
| Astronotus Oscar red form | 30 cm | from 250 per couple | 21-27 | 6.4-7.5 | 6-20 |
| Geophagus suriname | 30 cm | 300 | 22-28 | 6-8 | 8-20 |
| Common red discus | 18 cm | 200 per couple | 28-32 | 4.0-6.8 | 1-4 |
| Discus green | 19 cm | 200 per couple | 28-32 | 5.5-7.5 | 1-8 |
| Discus blue | 20 cm | 200 per couple | 28-32 | 5.8-7.5 | 1-8 |
| Discus brown | 18 cm | 200 per couple | 28-32 | 5.8-7.6 | 1-10 |
| Papiliochromis olive (Bolivian butterfly) | 8 cm | from 40 | 22-26 | 6,5-7,5 | 5-12 |
| Angel Angel | 15cm, h-up to 25 | from 200 per couple | 24-28 | 6,0-8,0 | 8-20 |
| Large angelfish (Pterophyllum altum Pellegrin) | 20 cm, h-up to 40 | from 200 per couple | 23-28 | 5.5-6.8 | 2-8 |
| Golden angelfish | 15cm, h-up to 25 | from 200 per couple | 24-28 | 6,0-8,0 | 8-20 |
| Marbled angelfish | 15cm, h-up to 25 | from 200 per couple | 24-28 | 6,0-8,0 | 8-20 |
| Angelfish (Pterophyllum scalare) | 15 cm, h-up to 24 | from 200 per couple | 22-28 | 6.0-7.0 | 2-12 |
| Thorichthys, Cichlazoma meeca | 15 cm | from 80 per couple | 22-28 | 6,8-8,0 | 8-30 |
| Uaru | 30 cm | from 300 | 27-29 | 5.5-7.5 | 3-12 |
| Diamond cichlasoma (pearl cichlasoma) | 30 cm | from 200 | 21-25 | 6.4-7.6 | 5-18 |
| Cichlazoma eight-striped (bee) | 20 cm | from 150 | 22-28 | ~ 7.0 | 2-20 |
| Cichlazoma Heller | 15 cm | from 60 | 19-27 | 7.5-9.0 | 18 — 30 |
| Cichlazoma Salvina | 15 cm | from 150 | 22-26 | about 7.0 | up to 20 |
| Cichlazoma severum (false discus) | 20 cm | from 200-400 | 22-26 | 6.0-7.2 | 4-15 |
| Cichlazoma Sedjika (rosy-finned) | 15 cm | from 60 | 22-26 | 6.6-7.6 | 6-16 |
| Cichlazoma black-striped | 15 cm | from 60 | 15-26 | about 7.0 | 30 |
| Elliot's cichlizoma | 14 cm | 100 per couple | 18-27 | 7.0-7.8 | Up to 15 |
| Cichlids of Africa Most African cichlids are kept in a harem, with at least three to four females per male. The number of shelters should exceed the number of fish. | |||||
| Aulonocara "Pink-blue" | 15 cm | 80 per couple | 24-28 | 7,0-9,0 | 8-25 |
| Blue dolphin (Cirtocara muri) | 25 cm | from 200 | 24-26 | 7,2-8,8 | 10-18 |
| Iodotropheus | 12 cm | 80 per couple | 24-28 | 7,0-9,0 | 8-25 |
| Red cichlid (Hemichromis Lifalili) | Up to 10 cm | from 50 per couple | 24-28 | 6.0-8.0 | up to 8 |
| Labidochromis cerulius yellow | 10 cm | 100 per couple | 24-27 | 7-9 | 8-25 |
| Melanochromis golden | 11 cm | 60 per couple | 24-27 | 7,0-9,0 | 8-25 |
| Pelvicachromis kribensis (Parrot, pulcher, common) | 10 cm | from 40 per couple | 23-26 | 6,5-7,5 | up to 20 |
| Princess of Burundi (Neolaprologus Brishara) | 10 cm | from 50 per couple | 22-26 | 7,0-8,5 | up to 20 |
| Pseudotropheus zebra | 12 cm | from 60 per couple | 24-27 | 7,0-9,0 | 8-25 |
| Pseudotropheus lombardo | 12 cm | 80 per couple | 24-27 | 7,0-9,0 | 8-25 |
| Telmatochromis dog | 10 cm | 60 per couple | 24-27 | 8,0-9,0 | 10-20 |
| Frontosa, Queen of Tanganyika | 35 cm | 400 per family | 24-27 | 7,0-9,0 | 8-25 |
| Burton's Haplochromis | 12 cm | 70 per couple | 24-25 | 7,0-9,0 | 8-25 |
| Handsome chromis (Hemichromis bimaculatus) | 15 cm | from 80 per couple | 24-28 | 7,0-8,0 | up to 20 |
| Julidochromis regan | 15 cm | 70 per couple | 22-26 | 7,0-9,0 | up to 20 |
| Characins, piranhas, wedge-bellied | |||||
| Astyanax mexicanis (Blind fish) | 12 cm | from 50 per couple | 20-25 | 6,8-9,0 | 8-30 |
| Distichodus six-lane, Distichodus zebra | 30 cm | 40 | 24-28 | 6.5-7.0 | 8-30 |
| Kerry inpaicht (false king tetra, purple neon) | 4 cm | from 20 | 22-27 | 6-7 | up to 5 |
| Metinnis spotted | 15 | from 80 per couple | 24-28 | about 7.0 | up to 15 |
| Neon blue | 3.5 cm | from 5 per couple | 23-27 | 5.0-6.5 | 3-8 |
| Neon green (Costelo) | 4.5 cm | 1,5 | 22-26 | 6.5-7.0 | up to 15 |
| Neon red | 5 cm | from 10 per couple | 24-28 | 5.0-6.5 | 3-8 |
| Neon ordinary | 4 cm | from 10 | 22-25 | 5.0-7.5 | Up to 15 |
| Neon black | 4 cm | from 10 per couple | 23-27 | 5.5-7.2 | Up to 12 |
| Ornathus redspotted | 5 cm | from 10 per couple | 22-28 | 6.0-7.5 | 2-15 |
| Ornatus red (phantom yellow-red) | 3.5 cm | from 10 per couple | 22-26 | 6.0-7.5 | up to 15 |
| Common piranha | 30 cm | from 150 per flock | 20-26 | about 7.0 | up to 20 |
| Rhodostomus | 4.5 cm | 1,5 | 20-26 | 6,0-8,0 | 2-15 |
| Ternetia vulgaris azure | 6 cm | from 15 per couple | 24-27 | about 7.0 | 4-16 |
| Tetra bloody (Minor) | 4 cm | from 10 per couple | 22-28 | 6.0-7.2 | 2-15 |
| Copper tetra | 5 cm | from 10 per couple | 22-28 | about 7.0 | 4-12 |
| Tetra von Rio (Fire Tetra) | 4 cm | from 10 per couple | 20-26 | 6.0-7.5 | 2-20 |
| Flashlight, Chemigrammus ocelifera | 4.5 cm | from 15 per couple | 22-28 | 6.0-7.5 | 2-18 |
| Hilodus | 10 cm | from 60 per couple | 22-28 | 6,0-7,0 | up to 15 |
| Catfish, catfish and loaches | |||||
| Agamix | 16 cm | 150 | 25-30 | 6.0-7.5 | Up to 25 |
| Acanticus Adonis | 50 cm | 300 | 22-28 | 6.5-7.0 | 4-15 |
| Acanthocobitis leopardis (Acanthocobitis - botia) | 15 cm | 60 per couple | 24-26 | 7,2 | 25 |
| Acantophthalmus (Spike-eye) Kühl | 8 cm | 50 | 22-28 | 6.0-7.5 | 4-10 |
| Acantophthalmus Myers | 8 cm | 50 | 24-28 | 6.0-7.5 | 4-10 |
| Acantophthalmus java | 8 cm | 50 | 24-28 | 6.0-7.5 | 4-10 |
| Ancistrina | 15 cm | 100 | 22-26 | 6.5-7.0 | Up to 20 |
| Ancistrus stellaris | 15 cm | from 100 | 20-26 | 5,5-7,5 | 20-26 |
| Ancistrus vulgaris | 15 cm | from 50 | 20-24 | 6,5-7,5 | up to 25 |
| Botia bengal | 7 cm | from 100 | 23-26 | 6.0-7.0 | 5-10 |
| Botsia Beforti (Byuforta) | 25 cm | 150 | 25-28 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Botsia Bradmore | 18 cm | from 100 | 23-26 | 6.0-7.5 | 4-12 |
| Botia bluish | 18 cm | from 150 | 22-28 | 6.0-7.0 | 5-8 |
| Botia zebra | 10 cm | 100 | 23-26 | 6.0-7.2 | 4-12 |
| Botia dwarf | 3 cm | 20 per couple | 24-28 | 6-7 | 18 |
| Clown botia (macracantha botia, clown loach) | 25 cm | 100 | 24-28 | 6.0-7.2 | 4-12 |
| Bocia Leconte | 12 cm | from 100 | 24-29 | 6.0-7.5 | 5-8 |
| Botia tape | 9 cm | from 100 | 24-28 | 6.0-7.2 | 4-10 |
| Botia modesta | 25 cm | 75 | 22-28 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Marbled botia (botia lohahata) | 10 cm | 100 per couple | 22-26 | 6.0-7.2 | 4-12 |
| Botia-mouse | 10 cm | 100 per flock | 26-30 | 6-7 | 4-12 |
| Botia striped | 10 cm | 100 | 22-28 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Mesh botia | 7 cm | from 30 | 24-28 | 6.0-7.2 | 4-12 |
| Tiger botia | 30 cm | 150 | 24-28 | 6-8 | up to 15 |
| Botia helodes (tape) | 22 cm | 200 | 25-30 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Botia histronica | 12 cm | from 200 | 20-26 | about 7.0 | up to 15 |
| Botia chess (Kubotae) | 10 cm | 80 per couple | 24-28 | ~ 7.0 | up to 15 |
| Common loach | 30 cm | 250 | 4-25 | doesn't matter | doesn't matter |
| Gastromizon punctulatus | 6 cm | 15 per couple | 22-25 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Gyrinocheilus | 20 cm | 20 | 22-28 | 7-8 | up to 20 |
| Girinocheilus siamese golden | 20 cm | 20 | 22-28 | 7-8 | up to 20 |
| Bronze dianema | 9 cm | from 50 | 22-26 | 6.0-7.5 | 2-15 |
| Band-tailed dianema | 12 cm | from 60 | 22-28 | 6.5-7.5 | 4-15 |
| Crossocheilus siamese (SAE) | 12 | from 60 | 18-25 | 6,0 — 8,0 | up to 20 |
| Wavy corridor | 5.5 | from 25 | 25-26 | no higher than 6 | 4-6 |
| Corridoras blue | 6.5 | from 25 | 20-26 | 6,0-7,2 | 4-6 |
| Corydoras golden | 6 cm | from 25 | 18-24 | 6.0-7.8 | 4-25 |
| Corydoras Meta (catfish Meta) | 6 | from 20 per couple | 24-27 | 6,5-7,5 | 5-15 |
| Mosaic corridor | 7 cm | from 25 | 22-28 | 6.0-7.0 | 4-12 |
| Natterera Corridor | 5 cm | from 25 | 18-26 | 6.5-7.2 | 4-12 |
| Pygmy corridor | 2.5 cm | from 10 | 22-28 | 6.5-7.2 | 2-10 |
| Corydoras five-tailed | 4 cm | from 25 | 22-28 | 6.0-7.5 | 4-12 |
| Three-line corridor | 5 cm | from 10 | 22-28 | 6.0-7.2 | 1-12 |
| Black-backed corridor | 12 cm | from 75 | 18-26 | 6.8-7.5 | 4-20 |
| Corydoras black-hatched | 6 cm | from 10 | 22-26 | 6.5-7.6 | 4-15 |
| Corridoras Sterby | 8 cm | from 50 | 22-26 | 6.5-7.2 | 3-12 |
| Mistus striped | 20 cm | from 100 | 22-28 | 6.0-7.0 | up to 15 |
| Leporacanthus galaxias | 25 cm | from 200 | 23-28 | 6.2-7.2 | 2-12 |
| Otocinclus vulgaris | 6 cm | 20 | 22-26 | about 7.0 | up to 20 |
| Pangasias vulgaris, pangasius, shark catfish | 50 | from 300 | 22-28 | 6,5-8,0 | 5-20 |
| Parancistrus magnum | 12 cm | from 150 | 22-26 | 6.2-7.0 | 3-12 |
| Platydoras striped | 22 | from 100 | 24-30 | 6,0-7,5 | up to 15 |
| Pterygoplicht brocade | 40 cm | from 200 | 22-26 | 6.5-7.5 | 2-15 |
| Synodontis (shift catfish) | 25 | 100 | 22-28 | 7,0-9,0 | 8-20 |
| Sacbranch catfish | 70 | from 300 | 15-28 | 7,0-9,0 | 8-20 |
| Indian glass catfish | 12 | from 80 | 22-32 | 6,8-7,5 | up to 15 |
| Torakatum (Hoplosternum Magdalena) | 20 | from 60 | 20-28 | 6,5-8,0 | up to 30 |
| Fractocephalus (redtail catfish, flathead catfish) | 120 | from 300 | 22-28 | 6,0- 7,0 | 2-15 |
| Horabagrus (Peacock's eye) | 40 | from 300 | 22-28 | about 7.0 | up to 15 |
| Atherine, spray, argus | |||||
| Argus spotted | 30 cm | 150 per couple | 20-28 | 7.0-8.0 | up to 20 |
| Badis chameleon | 8 cm | 60 | 20-26 | 6,5-7,5 | up to 20 |
| Badis Burmansky | 8 cm | 60 | 20-26 | 6,5-7,5 | up to 20 |
| Badis red | 8 cm | 60 | 20-26 | 6,5-7,5 | up to 20 |
| Red-tailed Bedocia | 10 cm | 60 | 20-24 | ~ 7.0 | up to 20 |
| Striped squirrel | 25 cm | 100 | 25-30 | ~ 7.0 | up to 20 |
| Glossolepis, Atherina Red, Iris crested | 15 cm | 80 | 22-25 | 7-8 | 10-25 |
| Glossolepis multisquamatus | 15 cm | 80 | 22-25 | 7-8 | 10-25 |
| Iriaterina Werner | 5 cm | 20 per flock | 25-29 | ~ 7.0 | to 10 |
| Mastacembelus redstripe | 1m | 300 | 24-28 | ~ 7.0 | up to 15 |
| Melanothenia australis (Nigrans) | 8 cm | 60 per couple | 22-26 | 7-8 | 8-20 |
| Melanothenia Australiana | 12 cm | 50 per couple | 23-25 | 7-8 | 8-25 |
| Melanothenia Axelrod | 9 cm | 60 per couple | 20-26 | 7-8 | 8-20 |
| Melanothenia Boesman | 10 cm | 80 | 25-29 | 7-8 | 10-18 |
| Melanothenia Blue | 12 cm | 50 per couple | 23-25 | 7-8 | 8-25 |
| Melanothenia gracilis | 8 cm | 60 | 24-28 | ~ 7.0 | up to 15 |
| Melanothenia McCulloch (Rainbow fish) | 7 cm | 80 | 20-26 | 7-8 | 10-20 |
| Melanothenia neon | 5 cm | 20 | 25-29 | ~ 7.0 | to 10 |
| Melanothenia lacustrine | 12 cm | 70 per couple | 22-25 | 7-8 | up to 15 |
| Melanothenia Papua | 7 cm | 60 per couple | 22-30 | 7-8 | up to 20 |
| Melanothenia Parkinson's | 12 cm | 80 | 25-30 | 7,5-7,8 | 8-20 |
| Melanothenia three-stripe | 12 cm | 80 | 25-29 | ~ 7.0 | up to 15 |
| Monodactyl silver (Silver swallow) | 25 cm | 150 | 24-28 | 7-9 | up to 25 |
| Monodactyl dark | 20 cm | 300 | 24-28 | 7-9 | 10-25 |
| Pseudomogile of Gertrude | 4 cm | 60 | 22-28 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Selenocurrent multibanded | 40 cm | 300 per couple | 20-28 | 7-9 | up to 30 |
| Selenocurrent multifasciata | 40 cm | 300 per couple | 20-28 | 7-9 | up to 30 |
| Telmotherina Ladiguesa (Sunbeam) | 7.5 cm | 60 | 22-28 | 7-8 | 10-30 |
| Siamese perch | 30 cm | 250 | 22-26 | 7-8 | up to 20 |
| Sunny perch | 20 cm | 400 | 10-22 | 7-8 | 10-30 |
| Glass perch | 8 cm | 40 | 20-30 | 7-8 | up to 15 |
| Popondetta Furcata | 5.5 cm | from 15 per couple | 22-26 | 6-7,5 | 5-12 |
| Rice eel | 90 cm | 400 | 25-28 | doesn't matter | doesn't matter |
| Sturgeon | |||||
| Sterlet | 1m | 700 | 10-18 | 7-7.5 | up to 20 |
| Mollusks and crustaceans | |||||
| Ampullaria yellow | 5-6 cm | from 10 | 22-24 | > 6,0 | 10-25 |
| Shrimp filter feeder | 6 | from 5 | 24-26 | doesn't matter | doesn't matter |
| Cherry shrimp, Cherry, Cherry | 2.5 | from 5 | 24-30 | doesn't matter | doesn't matter |
| Tiger shrimp | 1.5 | from 5 | 24-30 | doesn't matter | doesn't matter |
| Blue tiger shrimp | 3 | from 5 | 24-30 | doesn't matter | doesn't matter |
| Stingrays, lungfishes, armored | |||||
| Aravana South American | 120 cm | 300 | 24-28 | 6-8 | up to 15 |
| Kalamoicht | 90 cm | 200 | 22-28 | 7-7 | up to 15 |
| Freshwater moray | 60 cm | 200 | 23-28 | more than 7 | doesn't matter |
| Ocellated knife | 100 cm | 300 | 24-28 | 6-8 | Up to 15 |
| Knife black | 50 cm | 200 | 23-28 | ~ 7.0 | Up to 15 |
| Buchholz's Pantodon (Butterflyfish) | 10 cm | 40 | 22-30 | ~ 7.0 | up to 20 |
| Giant armored pike | 125 cm | 500 | 12-20 | ~ 7.0 | up to 20 |
| Spotted armored pike | 125 cm | 500 | 12-20 | ~ 7.0 | up to 20 |
| Polypterus delhesi | 40 cm | 300 | 24-28 | ~ 7.0 | up to 12 |
| Polypterus ornatypinnis | 40 cm | 200 | 22-28 | 6-7 | up to 15 |
| Polypterus senegalese | 30 cm | 300 | 25-28 | ~ 7.0 | up to 12 |
| Scleropagus Giardini (Northern Barramundi) | 120 cm | 300 | 24-28 | 6-8 | up to 15 |
| Scleropagus Malaysian (Arowana formosus) | 90 cm | 300 | 24-30 | ~ 7.0 | up to 15 |
| Nile elephant, Gnathonemus Peters | 20 cm | 100 | 22-28 | ~ 7.0 | up to 20 |
| Nile Elephant Snout, Long-finned Mormyr | 50 cm | 500 | 22-28 | 6-8 | up to 20 |
| Leopold's stingray | 50 cm, d-up to 25 | 300 | 20-25 | 6-7 | up to 12 |
| Stingray Motoro | 40 cm, d-up to 25 | 300 | 24-30 | ~ 7.0 | up to 15 |
| Common river stingray | 70 cm, d-up to 40 | 400 | 24-26 | 6-7 | up to 12 |
| River net stingray | 75 cm, d-up to 40 | 300 | 24-30 | ~ 7.0 | up to 15 |
| Henley stingray | 35 cm | 300 | 23-28 | 6-7 | up to 12 |
* Flock - 5 pieces.
Calculation of the number of fish per aquarium volume
When populating an aquarium with fish, you can also focus on the surface area of the water. Calculating the area is quite simple:
- for square and rectangular aquariums, multiply the length by the width;
- for round ones – 3.14*R2, where R is the radius of the aquarium.
Then follow the rule: small fish 2-5 cm with a narrow body require 90 cm2 of area, larger specimens or those with a round body shape - 150 cm2.
The disadvantage of this approach is that, like the first option, it does not take into account the characteristics of different types of fish, such as the amount of waste produced by the specimen, as well as the possibilities for improving gas exchange with forced aeration.
Which rule should I use?
In normal situations, the rule of three liters per 2 cm works quite adequately and is very easy to calculate. If you use this rule, always consider the net volume of water and take into account the size of the adult fish, as well as its shape. If the aquarium is non-standard (round or tall cube), the surface rule works better than the standard three-liter rule. In any case, always make preliminary calculations, and it is better to err on the smaller side than on the larger side.
Also, never populate an aquarium with the entire population at once. It is recommended to fill the container with 25% of the possible permissible amount of fish at a time. Fish waste is toxic, it is processed by colonies of beneficial bacteria, and the bacterial colony needs time to grow and adapt to changes in bio-load. By introducing the fish in stages, the bacteria will have enough time to grow and process the toxins released by the fish.
Calculation of the number of fish taking into account the characteristics of the species
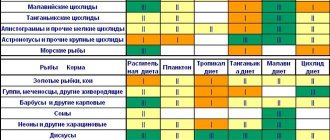
Before buying fish and populating the aquarium, you first need to decide on the species composition of the fish house. Ideally, having compiled a list, show it to an experienced aquarist, who will be able to determine how correctly the pets have been selected, taking into account:
- maintenance conditions (similar temperatures and pH of water, hardness);
- the nature of the selected species - the absence of aggressive breeds, differences in temperament (for example, it is difficult for quiet and calm guppies to get along in the same aquarium with active and frisky Sumatran barbs; it is generally recommended to keep males apart from all fish);
- dividing the inhabitants of the aquarium into layers - 25% should be in the upper and bottom layers, 50% in the middle;
- schooling or individualism of fish - species such as zebrafish, guppies, neons feel good in schools of 6 or more specimens.
It is necessary to very responsibly select fish of different breeds.
If there is no one to get qualified advice from, then you should study the information on each species in as much detail as possible, and only then determine the number of fish and their species composition.
Cleaning the soil
Regular cleaning of the soil is one of the main parts of maintaining comfortable living conditions for the inhabitants of the aquarium. If done in a timely manner, it will not only significantly increase the optimal state of the microclimate in the vessel, but will also help to avoid causing irreparable harm to it. To carry out this procedure, you can use a hose with a siphon, and place its free part in an empty container. Next, using a blower, we remove the water from the aquarium and begin to siphon through those areas where dirt has accumulated. After completing the procedure, we replenish the missing water.
How many fish can you keep in a small aquarium of less than 5 liters?
It’s worth noting right away that keeping fish in such microaquariums is a very troublesome task. It is very difficult to achieve equilibrium in the system; it requires a lot of effort and patience to clean the aquarium and change the water (at least 4 times a week). You can plant a couple of guppies or one cockerel in such a small volume. The cockerel will feel great, but the guppies will quickly breed and the container will become crowded.
3 liter aquarium
Aquariums smaller than 2 liters are not populated by animals, with the exception of some types of snails.
Interesting!
The smallest aquarium was created in Omsk by miniaturists A. Konenko and S. Konenko - in a volume of 10 ml of water they managed to place a nano-compressor, small cladophora bushes and a zebrafish fry.
If you already have an aquarium
If you have an aquarium and there are fish swimming and plants growing there, you can do self-monitoring. Enter your parameters, enter your fish. And find out how your aquarium is balanced in our opinion. How many more fish can theoretically be added? Or in general, you have an overpopulation, and therefore your fish are constantly dying. Anything you buy in addition will not survive.
It's the same with plants. If you have entered the parameters of your aquarium, but the plant that is dying is not there, then most likely you have the wrong conditions. At the very least you will see that the aquarium is not balanced. There are not enough conditions for the plants you plant.
How many fish can you keep in a 5 liter aquarium?
It is very difficult to stock very small 5 liter aquariums with fish. The main difficulties lie in maintaining biological balance and the required temperatures, which is more difficult to do in a small volume than in a large volume.
Therefore, for a 5-liter aquarium it is better to choose unpretentious, peaceful small fish - a couple of guppies or a couple of swordtails. Black mollies will look impressive in a small aquarium, but they are more demanding in terms of keeping conditions than the listed fish.
5 liter aquarium
If you want to keep larger fish in a 5-liter aquarium, you can populate it with a beautiful specimen of goldfish, or gourami.
Important!
Please note that large fish do not always look good in small containers. Therefore, the rule is more often used - small aquariums for small fish, large aquariums for large ones.
Small subtleties
Group effect
It has been noticed that peaceful fish living in schools are much calmer, which means they consume less oxygen than solitary fish. It is recommended to keep such species not even in pairs, but in small “companies”; in this case, their population density can be safely increased.
Dispersal by layers
The aquarium must be populated on all “floors”. If you don’t know what breed the fish belongs to (bottom-dweller, inhabitant of the middle or upper layers), look at its “face”. Turning the fish's mouth downwards will indicate its predilection for “digging” in the ground; it prefers to live in the depths. The fish's mouth is directed straight - its place is in the middle layers, upward - on the surface of the aquarium.
How many fish can be placed in a 10 - 15 liter aquarium?
You can diversify the species composition of a 10-liter aquarium compared to a 5-liter aquarium with bottom fish. Speckled catfish get along well with most species, so a couple of these bottom cleaners will come in handy.
One gourami or a family of bettas (a male and a pair of females) are well suited for living in the middle layer of a 10-liter aquarium. It would be quite nice in such a volume and a flock of neon fish, swordtails, guppies, and mollies. You can take a couple of each of these fish, but they feel more comfortable in schools of 5-7 pieces, so for such a large aquarium it is better to stick to just one species.
10 liter aquarium
Important!
To populate aquariums with a small volume of 10-30 liters, it is better to select small-sized fish - no more than 4-5 cm in length.
When calculating the number of fish for small aquariums, it is important to take into account other inhabitants - for example, large ampullaria snails. They also produce waste that pollutes the system, so snail populations need to be kept under control.
Number of fish for a 10 liter aquarium (table)
| Types of fish | Approximate number of fish, pcs. |
| Guppy | 4 |
| Mollies | 1 |
| Pecilia | 1 |
| Barbs | 1 |
| Danio | 2 |
| Cardinals | 2 |
| Lyalius | 2 |
| Betta fish (bettas) | 2 |
| Tetradons dwarf | 1 |
| Apistograms of Ramiresi | 1 |
| Neons | 4 |
| Ornathus | 4 |
| Ternetia | 1 |
| Tetras | 2 |
| Flashlights | 2 |
| Speckled Corydoratus catfish | 1 |
How many fish can you put in a 20 liter aquarium?
For 20-liter aquariums, you can safely populate both the top layer of water and the middle and bottom layers. If we take the species and quantitative composition of a 10-15 liter aquarium as a basis, then in a 20 liter aquarium you can add 2-3 zebrafish, but they may be too active for such a small aquarium.
Aquarium 20 liters
A pair of medium-sized labyrinth gouramis are also well suited for keeping in a 20-liter aquarium.
You can keep 1 goldfish, or its varieties - veiltail, telescope, but you need to understand that in such small containers, these species will never grow to the normal size of an adult.
Important!
Most often, small aquariums are bought for children, thinking that it will be easier to care for, but this is not so! All small aquariums require very frequent cleaning, good aeration, which does not create a current, and cleaning, otherwise the fish can die very quickly. Therefore, when choosing an aquarium for a child, it is better to opt for easier-to-care containers of 50-60 liters.
Number of fish for a 20 liter aquarium (table)
| Types of fish | Approximate number of fish, pcs. |
| Guppy | 8 |
| Mollies | 1 |
| Pecilia | 2 |
| Barbs | 1 |
| Danio | 4 |
| Cardinals | 4 |
| Gourami | 2 |
| Lyalius | 4 |
| Macropods | 1 |
| Betta fish (bettas) | 4 |
| Tetradons dwarf | 2 |
| Apistograms of Ramiresi | 2 |
| Neons | 8 |
| Ornathus | 8 |
| Rhodostomus | 6 |
| Ternetia | 2 |
| Tetras | 4 |
| Flashlights | 4 |
| Speckled Corydoratus catfish | 1 |
| Swordtails | 2 |
Conditions of detention
Aquarium fish, like all living things on earth, need oxygen. Since we are talking about a limited space, the lack of water, and, consequently, the oxygen contained in it, can have a detrimental effect on the health of the fish.
Another factor to consider is living space. In overcrowded reservoirs, even non-aggressive fish can experience conflict situations. Fish with bitten tails and fins will not decorate your aquarium.
The size of adult individuals and their feeding activity are also important. Larger fish produce more waste, resulting in higher levels of toxic nitrogen-containing products in the aquarium - nitrates, nitrites, ammonia.
Signs that may indicate overpopulation:
- fish swim to the surface and gasp for air or stay in the thickets of plants;
- the inhabitants of the aquarium have a paler color;
- poor growth gains, fish raised in cramped aquariums rarely reach the size characteristic of this species;
- lack of offspring.
The situation with overpopulation can be partially solved by additional means - blowing water and powerful filters, frequent changes of water and a slight decrease in its temperature - within normal limits for these types of fish, of course. Planting living plants will help saturate the water with oxygen; it is important not to overdo it - in dense plantings it will be difficult for fish to move, and it will be difficult to see them.
By observing all these conditions, it is possible to solve problems with overpopulation or increase population density. But it should be remembered that an aquarium filled to capacity is unlikely to serve as an aesthetic spectacle.
How many fish can you put in a 30 liter aquarium?
In such an aquarium you can already expand - make larger schools of fish, since most small fish look good among their relatives - about 10 neon fish and about 6 thorns, a couple of catfish. You can diversify the species composition with shrimp; most calm, medium-sized fish get along well with them.
You can populate the aquarium with a flock of 3-5 barbs, not forgetting that these bullies like to leave quiet guppies without fins.
Aquarium 30 liters
Most often, aquariums up to 30 liters are considered by professional aquarists only as spawning grounds, or for raising young animals, which will then be transferred to a larger house. Therefore, such aquariums do not shine with a variety of species - to keep them it is necessary to select the most unpretentious fish.
Number of fish for a 30 liter aquarium (table)
| Types of fish | Approximate number of fish, pcs. |
| Guppy | 12 |
| Mollies | 2 |
| Pecilia | 3 |
| Barbs | 2 |
| Danio | 6 |
| Cardinals | 6 |
| Gourami | 2 |
| Lyalius | 6 |
| Macropods | 2 |
| Betta fish (bettas) | 7 |
| Tetradons dwarf | 2 |
| Apistograms of Ramiresi | 3 |
| Neons | 12 |
| Ornathus | 12 |
| Princesses of Burundi | 1 |
| Rhodostomus | 8 |
| Ternetia | 3 |
| Tetras | 6 |
| Flashlights | 6 |
| Speckled Corydoratus catfish | 2 |
| Swordtails | 3 |
How many fish can you keep in a 40 liter aquarium?
For aquariums of 40 liters, it is already possible to select a wider range of species, including larger specimens: various types of gourami, except large pearl ones, dwarf tetrodons, lalius, macropods. A couple of large fish, a couple of bottom-dwelling catfish and a flock of 5-7 small fish - guppies, neon fish - are quite a sufficient number of inhabitants of a 40-liter aquarium.
Aquarium 40 liters
Important!
Since small aquariums can easily be overpopulated with fish, it is recommended to buy and add them to the aquarium in parts - for example, you bought a flock of guppies - stocked them, waited 2-3 days - bought gourami - stocked them, waited again. During this time, you can take a closer look at how the pets feel, how harmonious the aquarium looks with the fish already added, and, if necessary, stop and not buy the next batch.
This method is difficult to apply only in cases of purchasing young fish, when the fish have not yet reached adult size.
Number of fish for a 40 liter aquarium (table)
| Types of fish | Approximate number of fish, pcs. |
| Guppy | 16 |
| Mollies | 3 |
| Pecilia | 4 |
| Barbs | 2 |
| Danio | 8 |
| Cardinals | 8 |
| Gourami | 3 |
| Lyalius | 8 |
| Macropods | 3 |
| Betta fish (bettas) | 10 |
| Tetradons dwarf | 3 |
| Apistograms of Ramiresi | 4 |
| Neons | 16 |
| Ornathus | 16 |
| Princesses of Burundi | 1 |
| Rhodostomus | 10 |
| Ternetia | 4 |
| Tetras | 8 |
| Flashlights | 8 |
| Speckled Corydoratus catfish | 4 |
| Swordtails | 3 |
How many fish can you keep in a 50 liter aquarium?
In aquariums of this size it is already permissible to contain one labeo, a couple of schools of small fish of 7-9 copies, 3-4 catfish. It is imperative to take into account that if viviparous animals, such as guppies, swordtails, and Malinesias, are kept together with large fish, then the large specimens will happily eat the fry, considering them food, so special aquariums for the fry will be needed.
Aquarium 50 liters
A good water purification system and aeration, more powerful than in smaller aquariums, allow you to populate a 50-liter aquarium with more fish than expected.
Number of fish for a 50 liter aquarium (table)
| Types of fish | Approximate number of fish, pcs. |
| Guppy | 20 |
| Mollies | 4 |
| Pecilia | 6 |
| Barbs | 4 |
| Danio | 10 |
| Cardinals | 10 |
| Goldfish | 1 |
| Gourami | 4 |
| Ctenopomas | 1 |
| Lyalius | 10 |
| Labiosis green | 1 |
| Macropods | 4 |
| Betta fish (bettas) | 12 |
| Tetradons dwarf | 5 |
| Apistograms of Ramiresi | 5 |
| Neons | 20 |
| Ornathus | 20 |
| Common piranha | 1 |
| Princesses of Burundi | 2 |
| Rhodostomus | 12 |
| Ternetia | 5 |
| Tetras | 10 |
| Flashlights | 10 |
| Acantophthalmus | 1 |
| Ancistrus | 2 |
| Speckled Corydoratus catfish | 5 |
| Badisy | 2 |
| Swordtails | 4 |
How many fish can you keep in an aquarium 60 - 100 liters
Aquariums with a volume of 60 to 100 liters are already large enough to contain larger fish with a body length of 15-20 cm. When calculating the number of inhabitants, it is better to adhere to this principle - first select large breeds from 2 to 4 pieces depending on the volume (this can be gourami, cichlids, goldfish, labeo), and then they select several species of bottom fish and several top-level fish, buying them in schools, and always taking into account compatibility with the selected large fish.
In this volume range of 60-100 liters, it is very easy to get carried away and overpopulate the aquarium, especially when you initially buy young animals and until they grow up, the aquarium looks empty. It is important to clearly define the species you want to keep and stick to your choice, otherwise the aquarium will turn into a “fish hostel” with an endless flurry of all sorts of shapes and colors. In such conditions, the fish will suffer from constant stress, which will affect their appearance and well-being.
70 liter aquarium
It is imperative to take into account that large fish tend to choose a corner to their liking and protect it from the invasion of strangers, so a corner, for example, occupied by a pair of angelfish must already be deleted from the total volume of the inhabited territory. Barbs, on the contrary, tend to spread throughout the aquarium, giving no rest to slower fish, starting fights and bullying everyone and everything.
Number of fish for an aquarium per 100 liters (table)
| Types of fish | Approximate number of fish, pcs. |
| Guppy | 45 |
| Mollies | 12 |
| Pecilia | 12 |
| Barbs | 10 |
| Danio | 20 |
| Cardinals | 20 |
| Goldfish | 2 |
| Gourami | 7 |
| Ctenopomas | 2 |
| Labeo | 2 |
| Lyalius | 20 |
| Labiosis green | 2 |
| Macropods | 10 |
| Betta fish (bettas) | 25 |
| Tetradons | 2 |
| Tetradons dwarf | 10 |
| Cockatoo Apistograms | 4 |
| Apistograms of Ramiresi | 10 |
| Neons | 35 |
| Ornathus | 35 |
| Common piranha | 1 |
| Parrot | 1 |
| Princesses of Burundi | 4 |
| Pseudotropheus | 2 |
| Rhodostomus | 24 |
| Ternetia | 10 |
| Tetras | 20 |
| Flashlights | 20 |
| Acantophthalmus | 2 |
| Ancistrus | 2 |
| Yulidochromis Regan | 1 |
| Speckled Corydoratus catfish | 10 |
| Sacbranch catfish | 1 |
| Catfish Tarakatuma | 1 |
| Badisy | 4 |
| Swordtails | 6 |
What is the threat of overpopulation?
If there is overcrowding in the bank, the fish will begin to suffer from a lack of oxygen, which will negatively affect their health. In addition, a struggle for living space will begin, which can lead to damaged fins.
Large fish release a lot of waste into the water, which leads to an increase in ammonia, nitrates and nitrites. Because of this, pets can die.
Of course, you can install a powerful external filter in an overpopulated aquarium, change water more frequently, and plant a lot of plants. In this case, the fish will not be poisoned and die. But will they be comfortable? Of course not. And you are unlikely to like an aquarium densely populated with fish.
How many fish can you keep in an aquarium larger than 150 liters?
In large aquariums from 150 liters it is better to keep large specimens of fish - cichlids (acara, cichlosoma), goldfish, labeo, and from the bottom - ancistrus. Small breeds will simply get lost in a large aquarium.
In a 150 liter aquarium you can keep:
- up to 10 pieces of small cichlids or 8 pieces of large ones;
- labeo 4-5 pieces;
- large specimens of goldfish - 3 pieces (their smaller number compared to other species is due to the fact that they produce a lot of waste products, which upsets the balance in the system);
- large specimens of pearl gourami 8 pieces;
- a couple of large catfish, such as the sacbranch catfish.
Aquarium 200 liters
It should be borne in mind that the actual volume of a large aquarium will always be less than the declared volume by even more than 15%, since in large aquariums it is customary to place more decorations, driftwood, stones, which also takes up a certain volume.
In 200 liter aquariums you can already accommodate a couple of discus fish. It is not recommended to add anyone other than bottom-dwelling catfish to them, since discus fish require high temperatures, which is not always good for other fish species.
In a 300 liter aquarium, discus can be diluted with a flock of iris - 3-5 pieces.
How many fish can be kept in an aquarium from 300 to 1000 liters
Great attention must be paid to selecting fish for such large aquariums. Most specimens, having reached their adult size, will eat everything that can get into their mouth, so there is no point in “dilute” the inhabitants of the aquarium with small fish - they will all turn into food. Therefore, it is worth stopping at one species and populating the aquarium with the number of individuals that the volume allows.
Aquarium 500 liters
Suitable for aquariums from 300 liters:
- pterygoplix brocade;
- astronotus;
- African cichlids;
- silver arowana;
- Indian knives;
- discus,
- large sucker catfish.
All these fish grow to very large sizes, so they require from 100 to 300 liters per specimen.
Often, when the tank volume is over 300 liters, the aquarium is made into a marine one and is stocked with fish typical of coral reefs - clownfish, surgeonfish, yellow zebrafish, and chrysiptera sapphire. The number of fish in a marine aquarium is calculated as follows: 35 liters of water per 10 cm of small fish and 5 cm of large fish.
Number of fish depending on the volume of the aquarium:
| Aquarium volume | Recommended number of fish |
| 5 l | 2-3 small fish or a couple of medium ones (in particular swordtails, other species may be less able to tolerate small volumes) |
| 10-15 l | A pair of medium-sized fish or 5-7 small ones |
| 20 l | 2 medium-sized fish, 1 medium bottom fish, 2-3 small fish |
| 30 l | 10-16 small and a couple of bottom ones or 3-5 medium ones and a couple of bottom ones |
| 40 l | 2 large, 2 bottom and 5-7 small |
| 50 l | 1 large and 10-15 small and 3-4 bottom |
| 60-100 l | 2-4 large and 3-4 bottom and 10-15 small |
| More than 150 l | 8 large |
| 200 l | 2 very large |
| 300 l | 2 very large and 3-5 medium |
| 300 – 1000 l | Depending on the type of fish. |
Equipment
As can be seen from the types of aquariums presented, many of them are sold in a set with the necessary equipment. However, the kit does not always have everything you need, and it is often more profitable to take only a water container and buy the missing equipment yourself. And, by the way, you can buy higher quality equipment separately. Let's consider what we generally need to equip the aquarium.
Filter
Perhaps the filter is the most important addition to the aquarium. An aquarium filter helps keep the water clean and healthy, which is especially important in small tanks such as 30-40 liters where nitrates accumulate faster and the water volume is smaller.
There are several different types of filters. If you are going to keep a small number of fish, then it is enough to purchase an internal filter. If you plan to use all the biological space, that is, populate the aquarium with fish and other animals to the maximum, then choose a filter with good biological filtration - canopy or external.
However, the choice of filter also depends on everything that will be in the aquarium: living plants, types of fish, type of soil.
If a large number of plants and small tropical fish or shrimp are expected, then it is enough to choose any internal or other filter; biological filtration is not so important.
If you want to keep goldfish or other types of “dirty” fish, you need to choose a more powerful filter that passes at least 5 volumes of aquarium water per hour.
If there are no plants, then you should give preference to filters with predominantly biological filtration.
Various manufacturers offer filters of different power, you need to choose according to the size of the aquarium and the population. The filter should pass 3-5 volumes of aquarium water per hour.
The cost of filters varies, on average from 20-30 dollars and more. But if you want to choose more expensive equipment, then know that investing in a filter is always justified.
Lighting
What kind of lighting is needed in an aquarium also largely depends on its contents. Therefore, you need to decide before purchasing which plants, fish and other animals will live there.
Some plants require strong light, otherwise they will stop growing, wither, get sick and eventually die. Even if the lamp is included, you may have to buy additional lamps, or replace the standard ones with brighter ones. You can find out more about the requirements for maintaining aquarium plants in the catalog.
Some fish also require brighter lighting, while others prefer darker conditions, and this must be taken into account both when choosing lighting and when choosing plants.
If you are a beginner and are buying a complete aquarium, then first choose aquarium plants for beginners - they grow in medium and even low light.
Heater
Heaters are very rarely included in an aquarium starter kit, as they are needed primarily for keeping tropical aquarium fish and shrimp, as well as for marine installations. If your chosen tropical fish require heating, you will have to buy a heater yourself.
There are not as many heaters on sale as filters, and they work the same way - just install the equipment in the aquarium and set the desired temperature. Choose a heater only with a thermostat. The heaters always indicate the displacement of the appropriate volume of water.
The heater is always installed closer to the water flow from the filter.
A thermometer is not included in the kit, but you must purchase one yourself in order to control the water temperature. A thermometer is placed on the opposite side of the heater to ensure that the entire tank is maintained at the desired temperature.
Priming
The next important point that beginners pay little attention to is aquarium soil. However, it is an important aquarium equipment for several reasons.
Calculate the amount of soil for the aquarium
The choice of soil is determined by what and who will live in the aquarium.
If there are living plants, you need to choose the soil that is suitable for the plants first of all. There is now a good selection of soils on sale for growing healthy, beautiful aquarium plants.
For some tropical fish species, it is recommended to choose a substrate of darker colors - it not only imitates their natural habitat, but also helps to emphasize the beauty and brilliance of underwater inhabitants.
Aquarium plants are incompatible with goldfish - these pets love to dig up gravel and move decorations from place to place. But there should still be gravel at the bottom; it helps create a natural atmosphere. It is better to choose fine soil or sand.
Large cichlids are not suitable for keeping in aquariums up to 40 liters, but some small African cichlids are quite suitable. But for some of them there are special requirements for water parameters, namely alkaline PH. This can be achieved using special gravel for cichlids.
In any case, there must be soil in an aquarium with any aquarium fish (unless it is a spawning tank or a container for raising fry). Thanks to the substrate, the aquarium looks more natural, which reduces stress levels in fish and shrimp. The soil itself is a good aquarium filter.
Optional equipment
- Substrate. An aquarium with water, soil and other equipment is quite heavy, so it is better to take care of the surface on which it will be installed in advance.
- Compressor. Some fish require increased oxygen levels in the water, such as goldfish and some species of corydoras. Using a compressor, you can provide more oxygen to the water.
- CO2 generator . This equipment is only necessary if there are living plants, and even then not all species need it.
- Scenery. And again, everything depends on the future inhabitants of the aquarium. Most Amazon tropical fish will thrive among driftwood and living plants, as will most catfish, which prefer natural cover. Some species of cichlids, such as the aggressive mbuna, prefer the likes of rocky slopes, that is, caves made of stones. Both living plants and decorations are contraindicated for digging fish. And shrimp definitely need living plants, preferably mosses and any other shelters. If the future inhabitants of your aquarium do not have any special preferences, you can decorate it as you wish.
- A clean bucket, siphon, and net are necessary equipment for caring for an aquarium.
- Air conditioning, water tests for ammonia, nitrites, nitrates.