Habitat in nature
Endemic to Kerala state in India. It lives in the backwaters of Kerala, Lake Vembanad, the Periyar and Chalakudy rivers. Prefers places with weak currents, densely overgrown with aquatic vegetation. As a rule, these are low-lying areas of rivers and creeks with a muddy or sandy bottom.
Horabagrus brachysoma preys on insects, shellfish and fish. Adults can consume terrestrial insects and even frogs. This flexible diet is beneficial in variable habitats where food availability depends on the monsoon.
Voracity is known to increase during the breeding season in the months following the monsoon season.
PEACOCK EYE CATFISH (Horabagrus brachysoma)
FSB
0
5 478
Share
The peacock eye catfish or Horabagrus peacock eye catfish naturally lives in water bodies located in the southwestern part of India. Fish can be found in quiet creeks, lakes and swamps. The name Horabagrus is two-part - Hora in honor of the Indian ichthyologist Hora, and bagrus - the name of the genus of catfish, often used to form generic names.
Horabagrus brachysoma is a fairly large catfish, its length in nature reaches 45 cm, although in aquarium conditions their size usually does not exceed 30 cm. The peacock eye catfish is very reminiscent of a small shark, but unlike that it has a peaceful disposition. A kind of calling card of the catfish is a pair of black spots in a light areola, located on both sides of the head, thanks to which the fish got its name - peacock eye. The main color is dark gray, the belly is light, and the mouth has four small antennae. Sex differences are not pronounced.
Chorabagrus peacock eye is a calm, peaceful fish that can be kept in a common aquarium with other calm fish of comparable size (all fish that can fit into the mouth of Chorabagrus will certainly be eaten). It should be noted that, given the relatively large size of the fish, the aquarium should be quite large, its minimum volume should be 300 liters. You can keep fish either individually or in a small group.
The aquarium should have enough space for the fish to swim freely. At the bottom you need to place a large number of different shelters in the form of snags, stones and thickets of plants. Catfish show their main activity at dusk, and during the daytime they hide in shelters. If silence is maintained, catfish sometimes swim out into the open where they can be seen, but as soon as you make a careless movement, they instantly hide in shelters.
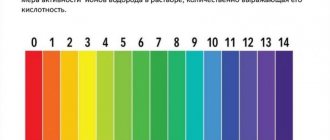
Water parameters: temperature 23-25° C, hardness dH 5-25°, acidity pH 6.0-7.5. Fish produce large amounts of waste, so a high-efficiency water filter is necessary. A weekly change of at least 1/3 of the aquarium water with fresh water is also required.
Low lighting is required, with an intensity of about 0.2 W/l. This must be taken into account if the aquarium is intended to contain aquarium plants and select species that can grow in such conditions.
Peacock's eye catfish is a picky fish. Almost all the food you give him will be eaten with appetite. Catfish are fed with small fish, mussel and shrimp meat, earthworms, as well as dry granular and flake food that sinks to the bottom. The fish are fed once a day at dusk.
Reproduction
In aquarium conditions, the Peacock's eye catfish does not reproduce.
Tags peacock eye catfish, horabagrus brachysoma
Found an error or a dead link?
Select the problematic fragment with the mouse and press CTRL+ENTER. In the window that appears, describe the problem and send it to the resource Administration.
Breeding
There is no reliable data on successful breeding in captivity.
This catfish is easily recognized by two rather large spots located on each side, slightly behind the head. The peacock catfish gets its name because of the similarity of these spots to the spots on the peacock's tail. Like the peacock, each spot is dark and surrounded by a light halo, so it appears like an eye.
The peacock eye catfish lives in reservoirs in southern India. Its body length is 40 - 45 cm.
Aquarists from Southeast Asia, in order to diversify the appearance and body shape of the peacock catfish, using genetic engineering, created a “scoliosis” form of this fish:
- Due to the curvature of the spine, the body of such a fish has lost its natural slenderness. This form of catfish is sometimes called a "balloon".
- All other features of the complex coloring of body parts are the same as those of catfish of this species living in natural reservoirs.
Description
The catfish has a large head and large eyes, four pairs of whiskers (on the upper lip, lower lip and at the corners of the mouth). The body is yellow with a large black spot in the pectoral fin area.
It is often stated on the Internet that the peacock eye grows small, about 13 cm. And most people think that it is a small fish, but this is not so. In fact, it can grow up to 45 cm in nature, but in an aquarium it rarely exceeds 30 cm.
Conditions of detention
Astronotus is a peaceful, calm and rather shy fish. Subject to stress from attacks from bullying neighbors. However, despite their peaceful nature, some small fish (for example, catfish and gyrinocheilus) can be eaten by a large astronotus, usually this happens on “fasting” days. Therefore, it is recommended to keep a flock of astronotuses of 5-7 individuals in a separate species aquarium, or also choose large aquarium fish as neighbors (for example, synodontis catfish, ancistrus, large cichlases). Astronotuses get used to their owners and easily recognize them, even allowing themselves to be petted. To keep Astronotus, it is recommended to use an aquarium with a volume of at least 100 liters per individual. You need to decorate the aquarium with driftwood without sharp edges (so that the fish do not get hurt), large smooth stones and several pots with plants. The aquarium should be tightly closed with a lid, the equipment should be securely fastened, and the thermostat should be covered with a protective cover. These precautions are necessary, since in panic attacks the astronotus often hits the walls and tries to jump out of the aquarium. For optimal maintenance of astronotuses, the water parameters should be: hardness up to 25°, pH 6-8, temperature 23-24° C in winter and up to 30° C in summer. Good filtration is needed (it is best to use a mechanical-biological type of filter), abundant aeration and weekly water changes up to 30% of the aquarium volume. Astronotuses can easily catch ichthyophthirius (breeding forms are most susceptible to this disease). Treat with a combination of malachite green and formaldehyde. Astronotus ocellata feeds on chopped sea fish, chopped ox heart, earthworms, small insects and their larvae. He also does not refuse dry food (preferably in granules for large cichlids) with a protein content of 40%. Prone to gluttony, it is advisable to arrange a “fasting” day.
Description of the mosque
This fish reaches a size of 20 centimeters. Its natural habitat is the waters of Venezuela. With its body shape and habits, the fish resembles a pike. The swordmouth is colored in silvery-greenish tones, and has a black round spot on its tail that resembles an eye.
An amazing feature of this fish is the color of its fins that changes depending on its mood, which varies from gray-blue to black. A characteristic distinguishing feature of a male and a female is the shape and appearance of the anal fin.
In females it is triangular, while males have an elongated and slightly rounded fin. You can easily distinguish the sex of the fish closer to the third or fourth month.
Most of the time, the swordfish stays in the upper layer of water; the main diet of this fish consists of bloodworms and coretras. For successful further breeding and to avoid unfertilized eggs, swordfish must be fed with live fish.
Also, we note that the adult fish of the guppy eats fish corresponding to the size of an adult female guppy, but does not touch larger and larger fish. Prefers hunting from ambush.
Moslems are undemanding to the temperature and chemical environment of water. The most suitable water for them will be water with a temperature of 21-23 degrees Celsius, an acidity of pH 6.5 - 7.5 and a hardness dH of no more than fifteen degrees
Water for keeping : dH up to 15°; pH 6.5-7.5; t 21-23° C.
In preparation for spawning, spawners are placed in spacious aquariums and fed generously with live fish. After 7-10 days they are placed in a long and low spawning tank with a volume of at least 7 liters. It is tightly covered with a cover glass on which the fish spawn. The distance from the water level to the glass is 5-10 cm. Plants and a spawning grid are not needed.
Stimuli for spawning are softening the water and increasing the temperature by 3-4° C. For group spawning, the volume of the aquarium should be significantly larger. Breeding by pituitary injections is possible. Breeding swordfish is complicated by raising fry. Due to active cannibalism, out of 1000 fry received, only 2-3 can be raised. The aquarium for raising fry should be spacious, without plants (since the swordfish prefers to hunt from ambush) with mandatory mixing of the water by aeration to ensure even distribution of food throughout the entire aquarium.
Water for dilution : dH up to 7.0°; pH 6.5-7.0; t 27-29° C.
The pair is planted in the evening, and spawning usually begins in the morning. Producers throw eggs upward with their fins, they stick to the cover glass, the walls of the aquarium and partially fall to the bottom. There is a lot of caviar. At the end of spawning, the spawners are planted. After a day, the larva hatches and is washed off the glass and walls into the water. When the fry begin to swim, they are fed.
Starter food : Artemia.
Frequent sorting of fry by size and timely increase in the size and amount of food are necessary, since fry grow very quickly.
Reproduction
Sexual maturity in swordsmouth pikes occurs at the age of two.
It should be noted that for successful spawning it is necessary to periodically feed the swordfish with live fish. If this is not done, then during the spawning process most of the eggs will be unfertilized.
Before spawning, the spawners are placed in different aquariums and fed generously with a variety of food.
An aquarium of 10 liters or more is suitable as a spawning aquarium.
The spawning aquarium is covered with a cover glass, and the distance from the water to the glass should be no more than 5 cm (during the spawning process, fish will spawn on it). The stimulus for the start of spawning is an increase in temperature and softening of the water.
The spawners are planted in the spawning aquarium in the evening, and spawning begins the next day in the morning. Spawning is quite interesting; the fish use their fins to throw the eggs upward, as a result of which they stick to the cover glass. Spawning lasts about 2.5 hours, during which one female spawns about 2000 eggs. At the end of spawning, the spawners should be removed.
After the larvae appear after 24 hours, they are washed off the cover slip into water. After another 100 hours, the fry begin to swim in search of food. During this period they are fed artemia.
The lifespan of a swordmouth in aquarium conditions is about 10 years.
Breeding Swordfish fry
At the end of the procedure, the producers must be planted. After a day, the larvae hatch and must be washed off all walls and surfaces of the glass into water. Afterwards, when the young begin to swim, they should be fed. Artemia is suitable as a starter feed.
As for the aquarium for breeding swordfish fry, it should also be spacious and have sufficient free space; should be without plants, but with the obligatory mixing of water using aeration, the latter is necessary to achieve uniform distribution of food throughout the entire volume of the aquarium.
The water environment in the aquarium used for breeding fry must be maintained at the following levels:
— hardness up to 7.0 degrees;
— acidity from 6.5 to 7.0;
- temperature from 27 to 29 degrees Celsius.
Ensure that fry are sorted frequently by size. Increase the size and amount of feeding in a timely manner. Remember, the fry grow at a fairly fast pace.