General information and appearance
Guppies are viviparous fish. Unlike many other species of aquarium fish that lay eggs in the external environment, in guppies the development of eggs occurs in the female’s body itself, i.e. an already formed fry emerges from it. This method of reproduction has its advantages, because the fry has a much greater chance of survival.
Females turn out to be much larger than males, exceeding them in size by about 2 times (the size of a female is about 6 cm, a male is 3 cm). In most cases, the color of the female is not as bright as that of the male.
Male guppies have a gonopodium, which is a modified anal fin. With its help, fertilization of the female occurs by moving reproductive products into her abdominal cavity.
The color of fish in their natural habitat is not particularly diverse: gray body color and a few spots on the caudal fin. This is due to the fact that in the wild the main task is survival, i.e. The bright color will certainly attract predators. But the situation is completely different with those fish that breeders breed. Their colors are varied: with a metallic sheen, single-color, with spots, etc.
Possible fish diseases: what do guppy owners need to know?
Guppies have strong immunity and high resistance to disease. Diseases typical of tropical fish are almost never found in these individuals. Possible pathologies include:
Photo of a male gupeshka suffering from tuberculosis.
- Fish tuberculosis. The fish looks emaciated and the back is arched. If a disease is suspected, affected individuals must be destroyed and all instruments must be disinfected.
- Parasitic influence. Weakened guppies are susceptible. The disease can be treated without killing the fish.
- Curvature of the dorsal fin, scoliosis. Guppies are susceptible after close contacts, injuries and damage, lack of air, or feeding with low-quality dry food.
- Parasitic disease - plistophorosis. Usually transmitted from the mother. Signs: angular and abrupt movements, dullness of color, lack of appetite, exhaustion. The disease has no success in treatment. Sick guppies must be destroyed and the equipment must be processed.
- “Split” of the fin due to changes in living conditions or water composition. If the splitting affects no more than a third of the tail, the fish can be cured.
- Hermaphroditism is observed in females. Self-fertilization occurs (97% of the offspring are also hermaphrodite females - there is an ovary and a testis).
To the question: “Why do diseases occur?”, the answer is due to the lack of proper care and love for aquatic inhabitants. To prevent the development of pathologies and infection by parasites, keep the aquarium clean, do not overpopulate, and quarantine new individuals . To prevent the loss of valuable varieties due to infectious diseases, it is advisable to have a “double”. This will preserve the entire gene pool. Individuals should be kept in a separate container and given high-quality artificial feed for food. The optimal number is 4-5 guppies. The fish will not be beautiful, but with their help it will be possible to restore the species.
Guppy fish: maintenance and care
Guppies are viviparous fish, i.e. already developed offspring are born, which can absorb small food. This can be called the main distinguishing feature of these aquarium inhabitants, whose maintenance differs from many other fish. In this regard, it is very important to know how to care for guppies in an aquarium so that the individuals live as long as possible.
Price
Aquarium fish can be purchased at pet stores or online to order. The average price of a guppy fish is 80 rubles, but sellers determine the lower and upper limits depending on the type, size and external appearance of the fish. Individuals that meet international selection standards take part in competitive exhibitions.
A small, peaceful and cute guppy fish is a wonderful pet for your home. It does not require large expenses and does not cause any problems. While caring for a guppy fish, we gain experience and simply enjoy the peaceful spectacle.
If you liked the article, leave comments and share a link to it on social networks.
Which aquarium is better to choose?
After purchasing guppies, they need to be given time to adapt so that they get used to their new conditions - temperature and water quality. If this is not done, then there is a high probability that they will simply die.
In most cases, two or three liters of water are enough for one fish (accordingly, for 6 individuals, the volume of the aquarium should exceed 20 liters). The aquarium should be well lit for 10-12 hours a day. Lack of light can cause the fish to become sick, which can also lead to death.
It is better to choose vegetation with soft leaves (hornwort is well suited for these purposes). You can plant Riccia on the surface of the water, in the thickets of which it will be convenient for the fry to hide. Indian fern can be used as a natural biofilter.
Guppy habitats
The historical habitat of guppies is the Caribbean islands, Central America and northern South America. Such fish can be found in the reservoirs of Guiana, Tobago, Brazil, Venezuela, and on the island of Trinidad.
The unique endurance of such fish and the ability to quickly adapt to a variety of conditions contributed to their settlement in any body of water - rivers, canals, lakes and swamps. Populations of guppies are sometimes found in warm sewage waters of megacities. Some are even found in springs that flow into the oceans with negligible salt content.
They prefer warm rivers with gentle currents. The fish live in small schools (up to 10 pieces) in dense thickets of plants, where they hide in case of danger. They usually swim near the surface of the water.
Currently, thanks to artificial acclimatization to combat the larvae of the malaria mosquito, the fish can be found on all continents. The widespread use of fish as an aquarium pet also played an important role.
Habitat of guppy
Water quality requirements
The tropics are the natural habitat for these fish, so appropriate conditions must be maintained in the aquarium. The optimal temperature is 24-26 degrees, but guppies are fish that can adapt to new conditions, so they normally tolerate fluctuations within 19-30 degrees.
Indicators of water hardness and acidity are not decisive, because guppies can adapt to these conditions. Therefore, if the changes were not very drastic, then there will be no problems. But there is something that you should not forget to do - change the water in the aquarium every week (about 1/3 of the total volume).
The water itself must be clean and oxygenated. Accordingly, you need to take care in advance about purchasing a reliable filtration system. But keep in mind that the flow of the filter should not be very intense: it will be simply difficult for small individuals to withstand strong water pressure.
Water temperature for guppy
There is still no consensus among guppy fans about the temperature in a guppy aquarium. One part of aquarists believes that the higher it is (up to 27ºС), the better. Others claim that low temperatures have a more beneficial effect on their pets' bodies. Everyone has quite compelling arguments that make them believe in the correctness of both one and the other opinion.
However, the following recommendations are common and work well: guppies do not feel discomfort at temperatures from 18 to 30ºC. Is that reproduction is more active when the thermometer shows a figure slightly higher than 24ºС. At temperatures below 17ºС, diseases, including infectious ones, begin to appear. In general, the lower temperature limit for guppy: 4ºС. Daily fluctuations of 3-5ºС will not harm them.
What to feed guppies: basic diet
Many novice breeders are interested in what they feed guppies. This is understandable, because proper nutrition is the basis for keeping any type of aquarium fish. The advantage of guppies is that they are quite omnivorous, so they can be given small food - animal and plant. It is better to remove leftover food to keep the aquarium clean.
You can start feeding them 30 minutes after turning on the lights. At the same time, about twice a week you need to arrange fasting days, which the fish tolerate quite well.
Their diet includes:
- Daphnia;
- bloodworm larvae;
- tubifex and various worms;
- spirulina, etc.
Specialized stores sell dry food that can be used to supplement your diet. In this case, it is better to consult a sales consultant.
Here are the basic rules to follow when feeding:
- It is important to have a balanced diet so that the food contains all the necessary nutrients.
- No need to feed the same thing. Alternate animal and plant food, add specialized dry food from the store.
- It is better to approach feeding rationally, i.e. giving the fish a small amount of food. If there is too much food, it will subsequently begin to rot, polluting the aquarium.
By following these simple rules, you will get healthy and active individuals that will delight you with their appearance for a long time.
What fish can live without oxygen supply?
Fish breathe using gills. They are represented by gill arches on which gill filaments are located. During respiration, water passes through the gill slits located in the pharynx, washes the gill filaments, and oxygen dissolved in it enters the blood. For the normal implementation of all internal processes, fish need to live in oxygen-rich water. In water with low oxygen content, fish suffocate and quickly die.
However, in nature, the water in many reservoirs is poor in oxygen. Fish species that live in shallow reservoirs, swamps, ditches, and puddles have, in the process of evolution, adapted to such living conditions. These fish have developed organs that allow them to use atmospheric oxygen for breathing.
Fish that are able to breathe atmospheric air and can live in oxygen-poor water include:
- Labyrinthine. These fish capture air with their mouths and direct it into a special labyrinthine organ that communicates with the gill cavity. The labyrinthine organ is formed by several thin bony plates covered with a mucous membrane, which is abundantly supplied with blood. Oxygen from the air enters the blood.
- Species with intestinal respiration. These include loaches and some catfish. These fish have intestinal protrusions in the form of bags on the sides of the body. Fish capture atmospheric air with their mouths, which enters these bags. Oxygen from the air penetrates into the blood through the thin wall of the intestine.
- Species that use a swim bladder for respiration. These include representatives of the multifeather family. The swim bladder of these fish consists of 2 sections and communicates with the intestines. The atmospheric air captured by the mouth enters the swim bladder, where gas exchange occurs.
Gourami
Gourami are labyrinth fish. The body length of most species does not exceed 10 cm. The body is graceful, flattened laterally; The pelvic fins are thread-like, transformed into organs of touch. Color depends on the species and usually includes silver, gold and brown shades.
In nature, gouramis live in shallow ponds and rice fields in Southeast Asia. They are adapted to life in turbid and oxygen-poor water, so these fish do not need oxygen in the aquarium. However, the aquarium should be covered with a cover glass to keep the layer of air above the water warm. Cold air damages the labyrinth organ of fish.
Cockerels
Cockerels are also classified as labyrinthine. In nature, they inhabit stagnant ponds and rice fields in Southeast Asia. During the time the species was kept in captivity, breeders bred more than 70 breeds, differing in color and shape of fins.
The betta is suitable for those who want to have an aquarium fish in a round aquarium without a filter. Due to pronounced territorial behavior and intraspecific aggression, male cockerels are kept strictly alone. Bettas do not require much space to swim, so they can be kept in a small aquarium; To keep the water clean, change it 2-3 times a week.
Lyalius
Lalius are labyrinthine fish that naturally live in slow-moving streams, vegetated lakes and rice fields. The body size of the lalius reaches 6-7.5 cm. On the sides there is a pattern in the form of vertical red and blue stripes.
Lalius are kept in groups in which females predominate. Lalius can live without air in the aquarium, but filtration is advisable. Lalius are quite shy, so it is recommended to plant the aquarium with plants to imitate their natural habitat. The species is sensitive to the content of nitrogenous compounds in water and does not like temperatures below 24°C.
Labioses
Lyabiasis are labyrinth fish 7-10 cm in size. The body has a pattern of brownish-red and greenish-blue vertical stripes. In nature, labiases are found in Southeast Asia in slow-flowing rivers and lakes with dense vegetation.
Labiasis are considered the most peaceful of the labyrinth fish. They lack intraspecific aggression, so they can be kept in pairs or large groups. This species tolerates temperatures from 22 to 28°C well, so it can live in aquariums without heating. The pond is planted with plants (including floating species) and creates soft filtration without strong currents.
Macropods
Macropods are labyrinthine fish 8-10 cm in size. In nature, they inhabit stagnant reservoirs of Southeast Asia. The fish have large elongated fins; on the sides there is a pattern of blue and red vertical stripes.
Macropods are one of the most aggressive labyrinth fish. They are kept in groups of 1 male and several females. Macropods are unpretentious and hardy; they can be kept in an aquarium without a filter or heater. These fish can live without oxygen and can tolerate temperatures from 15 to 26°C without harm to health. When kept without a filter, it is necessary to regularly change the water.
Common spined loach
The common spined loach is a fish of the loach family that lives in the waters of Europe. It has an elongated body 7-15 cm long. The body color is light brown with several longitudinal rows of rounded dark brown small and large spots.
The spined loach is kept at a temperature of 3-30°C, pH 6-8 and dH 4-20°. These are peaceful fish that get along with any neighbors. Spiked loaches lead a bottom-dwelling lifestyle and like to burrow into the ground. Thanks to intestinal respiration, these fish can be kept in an aquarium without a compressor. The reservoir must be covered with a lid, since when the atmospheric pressure changes, the pikelets begin to worry and can jump out of the water.
Acantophthalmus
Acantophthalmus are representatives of the loach family. They have an elongated snake-like body up to 12 cm long. The color is yellow-orange with wide vertical brown stripes. There are spines under the eyes. In nature, acanthophthalmus is found in slow-moving rivers and streams in Southeast Asia.
Acantophthalmus is kept at a temperature of 24-28°C, pH 6-7.5 and dH 5-10°. Thanks to intestinal respiration, these aquarium fish can live without oxygen, but they need clean water, so the aquarium must have a filter. Acantophthalmus likes to burrow into the substrate and hide under snags and other shelters.
Features of reproduction
There should not be any particular difficulties with the reproduction of guppies, because they themselves can mate quite well in a common aquarium. But if you want to get rich offspring, then the fish will certainly need to be removed from the general group. Fortunately, this will not be a problem because the male and female are very different in appearance, i.e. you won't confuse them.
Guppies do not lay eggs in water, and all the formation of the fry occurs inside the female. At the same time, there were cases when offspring appeared a long time after mating, when there were no longer males in the aquarium. This is explained by the fact that the female is capable of storing the male’s reproductive materials in the abdominal cavity. For this reason, when breeding these fish, breeders use virgin females, which are bred separately from the males.
The number of fry may vary (temperature and other living conditions play a big role). There are quite fertile females that can reproduce more than 100 fry.
After they are born, it is necessary to move them into a separate container for a kind of “quarantine”, which should last 10 days. When the fry reach 1.5 cm in length, they can be placed in a common aquarium. About 1 month after the appearance of the fry, it is already possible to determine where the male is and where the female is. If you want to get beautiful offspring, then you need to immediately place the males in a separate tank to avoid uncontrolled reproduction.
Main types of guppy fish
Guppy is the common name for many different varieties of this species. They all differ from each other in color, patterns, fin size, etc. There is no strict classification, especially since only hybrid varieties can be found on sale (pure breeds can only be found in breeders’ aquariums).
Carpet guppies
They are distinguished by the presence of a red-brown tail. Body color can be different: yellow-orange, brown, etc. There is another variety - veil emerald, which has a characteristic emerald tint.
Snake skin
The main feature of these guppies is the presence of spots of different sizes throughout the body. Actually, this is why this breed got its name, because its appearance resembles snake skin. The color of these guppies can vary.
Single color
The guppy's body is painted in one color (sometimes there may be a metallic sheen). One of the varieties is Moscow - males have a bright turquoise color with an azure or blue tint (females are predominantly gray tones).
Black
The front part of their body is silver and the rest is black. A striking representative of this subgroup is the Black Prince - males have a graphite color, and females are slightly paler.
White
This category includes:
- Albino. These fish have all the features that are associated with albinism. The whole body is rich white, the eyes are red.
- Blond. The eyes are dark, the scales are almost completely white.
- Pearlescent white. Characterized by a pearlescent tint. In some individuals the head may be dark.
In addition to differences in color, guppies are classified according to the shape of their fin and tail: tiptail, spiny-tailed, lyre-tailed, fan-tailed, spear-tailed, flag-tailed, etc.
Natural types of guppies:
- Ordinary. Most often found in natural habitats. The appearance is very simple, they do not differ in bright colors. Average size – 3-6 cm.
- Endler's guppy. The length of these individuals does not exceed 2.5 cm (females are slightly larger - 3.5 cm). Males have brighter colors: black, purple, yellow, etc.
- Micropecilium. This species is quite rare in its natural habitat. The mouth is more sharply shaped, the color of males is brighter than that of females.
Recommendations for proper feeding
Stores sell special, balanced food for these fish.
Guppy is an omnivorous fish: individuals equally need products of plant and animal origin. There are many options available for feeding:
- main food is plankton (small microorganisms);
- crustaceans – larvae, cyclops;
- bloodworms (or coretra) - excessive amounts pollute the aquarium;
- plant particles – chlorella, spirulina;
- varieties of algae;
- bread crumbs and dry food;
- vitamin granules.
The level of daily intake depends on the gender and size of the fish. For an adult male, 1 small bloodworm per day is enough, for a female – at least 3.
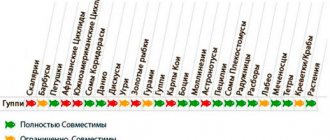
Compatibility
The guppy fish itself is quite peaceful, so it can get along with other aquarium inhabitants. The problem here is different - a number of other fish can behave quite aggressively towards them.
Fish that are fully compatible with guppies include:
- Danio.
- Pecilia.
- Sword bearers.
- Rasbory.
- Tetras.
- Mollies, etc.
Accordingly, they can be kept together with aquarium fish that are approximately identical in size to them. For this reason, guppies are not kept with large cichlids, for which they can become natural food.
Tendency to disease
Guppies are fairly hardy fish, but like all living creatures they can sometimes get sick.
The most common disease among such fish is semolina. The main signs are the presence of numerous white dots throughout the body, causing itching and causing the fish to rub against various objects.
Another common problem is tailings rotting.
Special medications will help cope with the above diseases.
Following a number of rules will help reduce the likelihood of developing various infections. Among them:
- maintaining optimal temperature conditions;
- equipping the aquarium with high-quality filters;
- regular water renewal;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- varied diet;
- avoiding overfeeding.
How long do guppies live in an aquarium?
In most cases, if all conditions of their maintenance are met, individuals live for about 3 years. This is a short period of time, but considering that females can reproduce up to 100 or more fry, this is a small problem for the breeder.
Guppies are a fairly unpretentious species of aquarium fish that perfectly adapts to various conditions. But this does not mean that it is enough to simply buy guppies and place them in an aquarium without monitoring the purity of the water, without buying a filtration system and without periodically changing the water. There must be care and it depends on it whether the guppies will reproduce, what color the fry will acquire and how long they will live.
Our specialists have extensive experience in creating and maintaining aquariums in Moscow and the region. We carry out cleaning, change the water in the required quantity, treat and replace fish if necessary. Possibility of visiting your home or office.
Lack of oxygen
No matter how unpretentious fish may be that live without additional enrichment of water with oxygen, they can also suffer from a lack of it. The critical air content in water is different for each type of underwater inhabitants.
Symptoms of deficiency:
- rapid breathing, “protruding” gills;
- fish swim from above and swallow air;
- even bottom-dwelling fish often swallow air above;
- decreased activity of pets;
- Over time, the brightness of color, resistance to diseases decreases, and growth slows down.
Oxygen consumption by fish in an aquarium increases after feeding, when the water temperature rises, and at night, especially in the presence of dense vegetation. All aquatic plants absorb oxygen in the dark.
The most effective way to save fish suffering without oxygen is to install a compressor with an air stone. The air flow dissipates, then rises to the surface, mixing the water and saturating it with oxygen. In a small aquarium, the compressor may not be stationary, but temporary, in order to preserve the decor. It is enough to connect it for 40 minutes a day (or as needed) and put it away until next time. However, you cannot take water from the tap! It must be settled.
If temporary measures do not help, stationary equipment is required to supply oxygen to the aquarium - a compressor and a filter. A filter is needed to purify water from organic matter, the decomposition of which absorbs a significant part of the oxygen. The power and type of filter depends on the volume of the tank - a 500-liter one will require an external filter, and a 50-liter one will need an internal one.